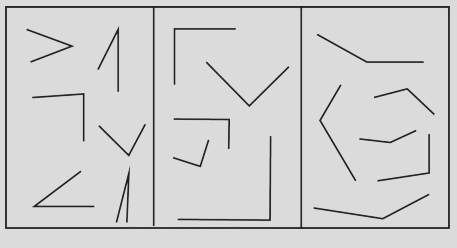
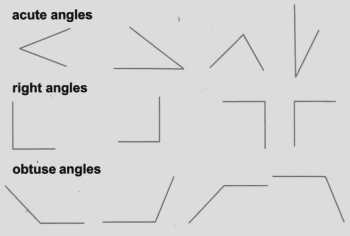
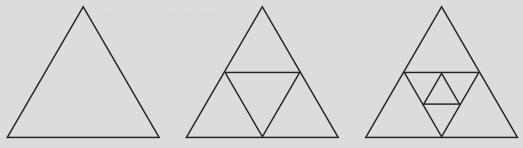
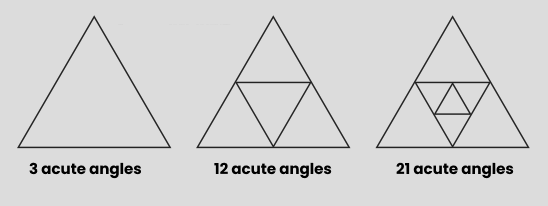
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Lines And Angles Exercise 2.8 - 2025-26
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Lines And Angles Exercise 2.8 (2025-26)
1. What are the main topics explained in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, Whole Numbers?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, Whole Numbers, provide step-by-step guidance on the following core concepts:
- Introduction to whole numbers and their distinction from natural numbers.
- Finding the predecessor (the number before) and successor (the number after).
- Performing operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication on a number line.
- Understanding and applying the properties of whole numbers, including Commutative, Associative, and Distributive properties.
- The roles of 0 as the additive identity and 1 as the multiplicative identity.
2. How do you correctly solve problems using the distributive property as per NCERT Chapter 2?
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 show how to use the distributive property to simplify complex multiplication. For example, to calculate 15 × 104, you follow these steps:
- Step 1: Express 104 as a sum, like (100 + 4).
- Step 2: Apply the property: 15 × (100 + 4).
- Step 3: Distribute the multiplication: (15 × 100) + (15 × 4).
- Step 4: Solve the simpler parts: 1500 + 60.
- Step 5: Add the results to get the final answer: 1560.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 help in representing whole numbers on a number line?
The NCERT Solutions provide a clear, visual method for using the number line. They explain that a number line for whole numbers starts at 0 and extends indefinitely to the right. The solutions demonstrate step-by-step how to perform:
- Addition by making jumps to the right.
- Subtraction by making jumps to the left.
- Multiplication by making repeated jumps of equal size starting from 0.
4. Why is the number 0 called the additive identity for whole numbers?
The number 0 is called the additive identity because when it is added to any whole number, the identity (or value) of that number does not change. As per the NCERT textbook, for any whole number 'n', the property is n + 0 = n. For instance, 42 + 0 = 42. The solutions reinforce this principle to show that adding zero has no effect on the original number.
5. How does understanding the associative property of addition help in solving problems faster in Chapter 2?
The associative property, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c), is a powerful tool for mental maths that the NCERT solutions highlight. It allows you to regroup numbers in a long sum to create easier pairs. For example, to solve 55 + 79 + 45, instead of adding in sequence, you can regroup it as (55 + 45) + 79. This simplifies the problem to 100 + 79 = 179, which is much quicker to solve.
6. What is a common mistake students make with the predecessor of the smallest whole number?
A common mistake is assuming that 0, the smallest whole number, has a predecessor within the set of whole numbers. The NCERT solutions clarify this by explaining that the predecessor is found by subtracting 1. The predecessor of 0 would be 0 - 1 = -1. Since -1 is an integer and not a whole number, the solutions correctly state that 0 has no predecessor in the system of whole numbers.
7. Why is division of a whole number by zero considered 'undefined'?
The NCERT Solutions help build the logical foundation for this rule. Division is the inverse of multiplication. If we say 12 ÷ 0 = x, this would mean that x × 0 = 12. However, any number multiplied by zero is always zero, never 12. Because no number 'x' can satisfy this equation, the operation is impossible. Therefore, division by zero is classified as undefined in mathematics.
8. Where can I get reliable and free step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 for the 2025-26 session?
You can find complete and accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, Whole Numbers, on the Vedantu website. These solutions are created by subject matter experts, are fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, and provide detailed, easy-to-understand methods for every problem in the NCERT textbook exercises.