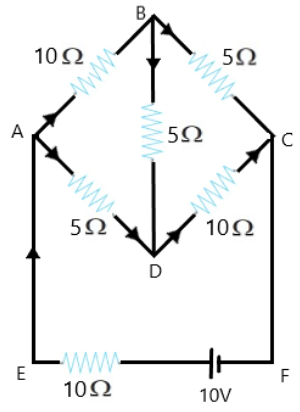
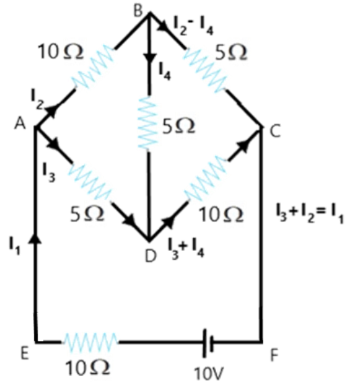
Current Electricity Questions and Answers for Class 12 Physics



FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current Electricity - 2025-26
1. What key topics are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current Electricity as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus?
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 Current Electricity comprehensively address:
- Definition and calculation of electric current and its direction
- Ohm’s Law and its applications in circuits
- Concepts of resistivity and conductivity
- Calculation of drift velocity
- Methods of combining resistors in series and parallel
- Understanding internal resistance of cells
- Working with Kirchhoff’s Rules for complex networks
- Wheatstone bridge and potentiometer principle and applications
Each topic is approached with stepwise, CBSE-approved methodology for the Class 12 Board exam.
2. How should students approach solving NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 questions for maximum marks?
To maximise marks:
- Read the question carefully, identifying all given values
- State the relevant formula before solving (e.g., Ohm’s Law: V = IR)
- Write every calculation step, showing substitution of values and units
- Justify steps with correct physical reasoning
- Add clear, neatly-labelled diagrams if required
- Highlight or box the final answer
This method, aligned with the CBSE marking scheme, increases accuracy and scoring potential.
3. Why is Ohm’s Law essential for solving NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 exercises?
Ohm’s Law (V = IR) is a fundamental principle that relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It enables students to:
- Determine unknown quantities in simple and complex circuits
- Understand how changes in one parameter affect the others
- Solve both theoretical and numerical problems in Chapter 3
Mastery of Ohm’s Law is required for scoring in both short and long answer questions as per the latest Physics NCERT Solutions.
4. What are common pitfalls to avoid when solving numericals from NCERT Solutions for Current Electricity?
Students should avoid these typical mistakes:
- Omitting units or using incorrect units (e.g., confusion between ohms and kilo-ohms)
- Failure to convert temperatures when necessary (e.g., Celsius to Kelvin)
- Ignoring the internal resistance of cells in calculations
- Applying Ohm’s Law to non-ohmic conductors where it does not hold
- Not drawing or mislabelling required circuit diagrams
Awareness of these pitfalls leads to more accurate and CBSE-compliant answers.
5. How do Kirchhoff’s Laws enable solving complex circuit problems in Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
Kirchhoff’s Laws—the Current Law (KCL) and Voltage Law (KVL)—allow students to set up equations for electrical quantities in multi-loop and bridge circuits where simple series/parallel rules do not apply. By applying these laws, students can:
- Formulate simultaneous equations
- Calculate unknown currents and voltages
- Analyze circuits featured in advanced NCERT and board exam questions
6. What is the role of drift velocity in the flow of current according to the NCERT Solutions?
Drift velocity (vd) is the average velocity attained by free electrons in a conductor due to an electric field. It determines the current using the formula: I = nAe vd, where n = carrier density, A = area, and e = charge of an electron. Calculating drift velocity is crucial for connecting theory with practical current flow in Class 12 Physics numericals.
7. Why does resistance of a metallic conductor increase with temperature as explained in Chapter 3?
As temperature rises, metal ions vibrate more intensely, causing free electrons to undergo more frequent and stronger collisions with the lattice. This increased scattering raises the resistance. The temperature coefficient of resistance quantifies this relationship—a commonly tested concept in NCERT Physics and CBSE exams.
8. How can the Wheatstone Bridge principle be applied to find unknown resistances as per NCERT Solutions?
The Wheatstone Bridge is balanced when the ratio of two known resistors equals the ratio of the unknown to the standard resistor (R1/R2 = R3/R4). At this balanced point, with zero galvanometer current, students can accurately calculate unknown resistance. This technique is often applied in board-style NCERT questions.
9. What are the limitations of Ohm’s Law discussed in Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions?
Ohm’s Law only applies to ohmic materials—those exhibiting a linear relationship between current and voltage and a constant resistance (such as most metals at constant temperature). It does not apply to semiconductors, diodes, or materials with variable resistance (affected by temperature, voltage, or light). Recognizing these limitations is necessary to avoid misconceptions on MCQs and HOTS questions.
10. If two resistors with different temperature coefficients are placed in series, how is the overall temperature coefficient determined?
For resistors R1 and R2 with temperature coefficients α1 and α2, the overall temperature coefficient α is calculated using:
α = (α1R1 + α2R2) / (R1 + R2). This formula ensures precise analysis in application-based circuit problems in the NCERT curriculum.
11. What is the difference between resistance and resistivity based on the NCERT Solutions for Current Electricity?
Resistance (R) depends on size and geometry: R = ρ(l/A), where ρ is resistivity, l is length, and A is the cross-sectional area. Resistivity (ρ) is a material property, independent of the conductor’s dimensions, characterizing how strongly a material opposes current flow. It remains constant for a material at a given temperature.
12. How should students revise Chapter 3 Current Electricity for the CBSE 2025–26 board exam?
Effective revision strategy includes:
- Reviewing all solved NCERT exercise questions using correct stepwise method
- Memorising important formulas and their application
- Drawing and interpreting circuit diagrams
- Practising previous years’ questions for pattern understanding
- Clarifying concepts such as drift velocity, resistance, and combination of resistors
This preparation method ensures coverage of both conceptual and numerical aspects for board exams.
13. Why is understanding internal resistance crucial in Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
Internal resistance determines the terminal voltage and actual current delivered by a cell or battery, not just the theoretical emf value. It is vital when calculating real-world circuit outputs. All CBSE-compliant NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 require incorporating internal resistance in stepwise calculations for accurate answers.
14. What is the SI unit of electric current according to NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 3?
The SI unit of electric current is ampere (A). One ampere is defined as one coulomb of charge passing through a section of conductor per second. This unit is essential for all calculations in Current Electricity as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
15. How do stepwise NCERT Solutions for Current Electricity help improve exam performance?
Using stepwise, syllabus-based solutions:
- Enhances conceptual clarity and problem-solving skills
- Encourages the correct use of formulas and units
- Reduces common errors seen in board exams
- Boosts confidence in tackling both numerical and theory questions
- Improves answer presentation, which leads to higher scores as per CBSE marking guidelines