
Class 12 Maths Miscellaneous Exercise Chapter 8 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
In NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Miscellaneous Exercise, you’ll learn how to use integrals to find areas under curves and between lines—skills that can seem tricky at first, but become easy with a bit of practice. These concepts are important for Class 12 maths and help you solve real-world problems using calculus. If you ever wonder how to calculate the area between two curves, you’ll find clear answers here.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentVedantu’s step-by-step NCERT Solutions are perfect if you're feeling confused by integration or want to revise faster for exams. You can also download the full solutions PDF for offline practice. Wondering what else you need for boards? The Class 12 Maths syllabus will keep you on track with the latest topics.
This chapter carries 6 marks in your CBSE exam, so understanding these exercises can really help you score better!
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Application of Integrals
Miscellaneous Exercise
1. Find the area under the given curves and given lines:
(i) \[\text{y=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,x=1,x=2}\] and \[\text{x-axis}\]
Ans:
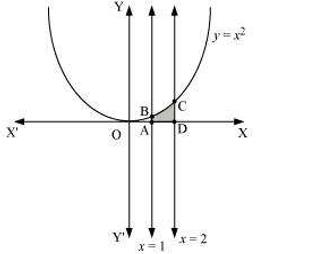
\[\text{AreaADCBA=}\int_{\text{1}}^{\text{2}}{\text{y}}\text{dx}\]
substitute $y={{x}^{2}}$
\[\text{=}\int_{\text{1}}^{\text{2}}{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}}\text{dx}\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{=}\frac{\text{8}}{\text{3}}\text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]
\[\text{=}\frac{\text{7}}{\text{3}}\text{units}\]
(ii) \[\text{y=}{{\text{x}}^{4}}\text{,x=1,x=5}\] and \[\text{x-axis}\]
Ans:
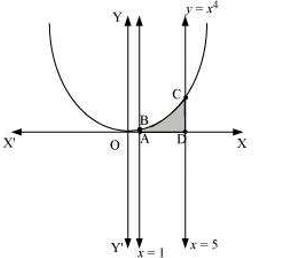
\[\text{AreaofADCBA=}\int_{\text{1}}^{\text{5}}{{{\text{x}}^{\text{4}}}}\text{dx}\]
Integrating using the power rule,
\[\text{=}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{5}}}}{\text{5}} \right]_{\text{1}}^{\text{5}}\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{=}\frac{{{\text{(5)}}^{\text{5}}}}{\text{5}}\text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\]
Simplifying,
\[\text{=(5}{{\text{)}}^{\text{4}}}\text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\]
\[\text{=625-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\]
\[\text{=624}\text{.8 units}\]
2. Sketch the graph of \[\text{y=}\left| \text{x+3} \right|\] and evaluate \[\int_{-6}^{0}{\left| \text{x+3} \right|}\text{dx}\].
Ans:
\[\text{x}\] | \[\text{-6}\] | \[\text{-5}\] | \[\text{-4}\] | \[\text{-3}\] | \[\text{-2}\] | \[\text{-1}\] | \[\text{0}\] |
\[\text{y}\] | \[\text{3}\] | \[\text{2}\] | \[\text{1}\] | \[\text{0}\] | \[\text{1}\] | \[\text{2}\] | \[\text{3}\] |
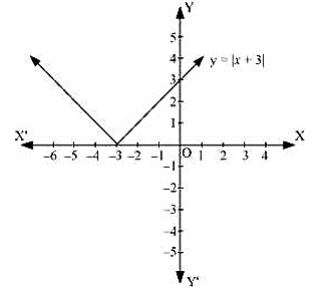
\[\left( \text{x+3} \right)\le 0\] for \[\text{-6}\le \text{x}\le \text{-3}\]
\[\left( \text{x+3} \right)\ge \text{0}\] for \[\text{-3}\le \text{x}\le 0\]
Therefore,
\[\int_{\text{-6}}^{\text{0}}{\text{ }\!\!|\!\!\text{ }}\text{(x+3) }\!\!|\!\!\text{ dx=-}\int_{\text{-6}}^{\text{-3}}{\text{(x+3)}}\text{dx+}\int_{\text{-3}}^{\text{0}}{\text{(x+3)}}\text{dx}\]
Integrating using the power rule
\[\text{= -}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}}{\text{2}}\text{+3x} \right]_{\text{-6}}^{\text{-3}}\text{+}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}}{\text{2}}\text{+3x} \right]_{\text{-3}}^{\text{0}}\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{=-}\left[ \left( \frac{{{\text{(-3)}}^{\text{2}}}}{\text{2}}\text{+3(-3)} \right)\text{-}\left( \frac{{{\text{(-6)}}^{\text{2}}}}{\text{2}}\text{+3(-6)} \right) \right]\text{+}\left[ \text{0-}\left( \frac{{{\text{(-3)}}^{\text{2}}}}{\text{2}}\text{+3(-3)} \right) \right]\]
Simplifying,
\[\text{= -}\left[ \text{-}\frac{\text{9}}{\text{2}} \right]\text{-}\left[ \text{-}\frac{\text{9}}{\text{2}} \right]\]
\[\text{=9}\]
3. Find the area bounded by the curve \[\text{y=sinx}\] between \[\text{x=0}\] and \[\text{x=2 }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }\].
Ans:
Therefore, \[\text{area = Area OABO+ Area BCDB}\]
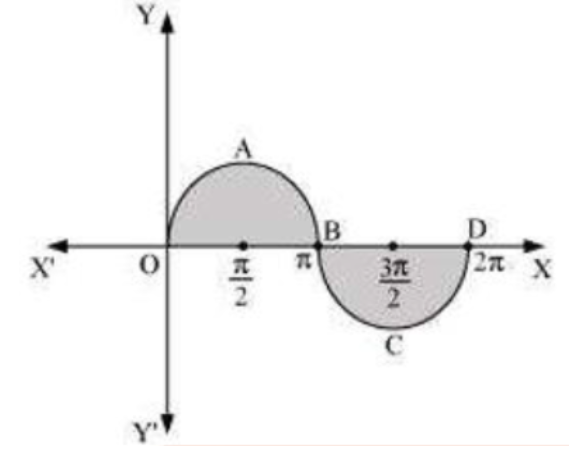
Area Bounded by Curve y=sinx
\[\text{=}\int_{\text{0}}^{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}{\text{sin}}\text{xdx+}\left| \int_{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{2 }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}{\text{sin}}\text{xdx} \right|\]
\[\text{= }\!\![\!\!\text{ -cosx }\!\!]\!\!\text{ }_{\text{0}}^{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}\text{+}\left| \text{ }\!\![\!\!\text{ -cosx }\!\!]\!\!\text{ }_{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{2 }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }} \right|\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{= }\!\![\!\!\text{ -cos }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ +cos0 }\!\!]\!\!\text{ + }\!\!|\!\!\text{ -cos2 }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ +cos }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }\!\!|\!\!\text{ }\]
Simplifying,
\[\text{=1+1+ }\!\!|\!\!\text{ (-1-1) }\!\!|\!\!\text{ }\]
\[\text{=2+ }\!\!|\!\!\text{ -2 }\!\!|\!\!\text{ }\]
\[\text{=2+2}\]
\[\text{=4 units}\]
4. Area bounded by the curve \[\text{y=}{{\text{x}}^{3}}\], the \[\text{x-axis}\] and the ordinates \[\text{x = -2}\] and \[\text{x = 1}\] is
A. \[\text{-9}\]
B. \[\text{-}\frac{\text{15}}{\text{4}}\]
C. \[\frac{\text{15}}{\text{4}}\]
D. \[\frac{\text{17}}{\text{4}}\]
Ans:
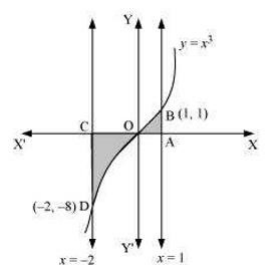
As shown in the diagram, the required area is:
\[\text{Required area =}\int_{\text{-2}}^{\text{1}}{\text{y}}\text{dx}\]
\[\text{=}\int_{\text{-2}}^{\text{1}}{{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}}\text{dx}\]
Integrating using the power rule
\[\text{=}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{4}}}}{\text{4}} \right]_{\text{-2}}^{\text{1}}\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{=}\left[ \frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{-}\frac{{{\text{(-2)}}^{\text{4}}}}{\text{4}} \right]\]
Simplifying,
\[\text{=}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{-4} \right)\]
\[\text{= -}\frac{\text{15}}{\text{4}}\text{ units}\]
So, the correct answer is \[\text{ -}\frac{\text{15}}{\text{4}}\text{ units}\] option B.
5. The area bounded by the curve \[\text{y=x}\left| \text{x} \right|\text{,x-axis}\] and the ordinate \[\text{x = 1}\] and \[\text{x = -1}\] is given by (Hint \[\text{y = }{{\text{x}}^{2}}\] if \[x>0\] and \[\text{y = -}{{\text{x}}^{2}}\] if \[x<0\])
A. \[0\]
B. \[\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]
C. \[\frac{2}{\text{3}}\]
D. \[\frac{4}{\text{3}}\]
Ans:
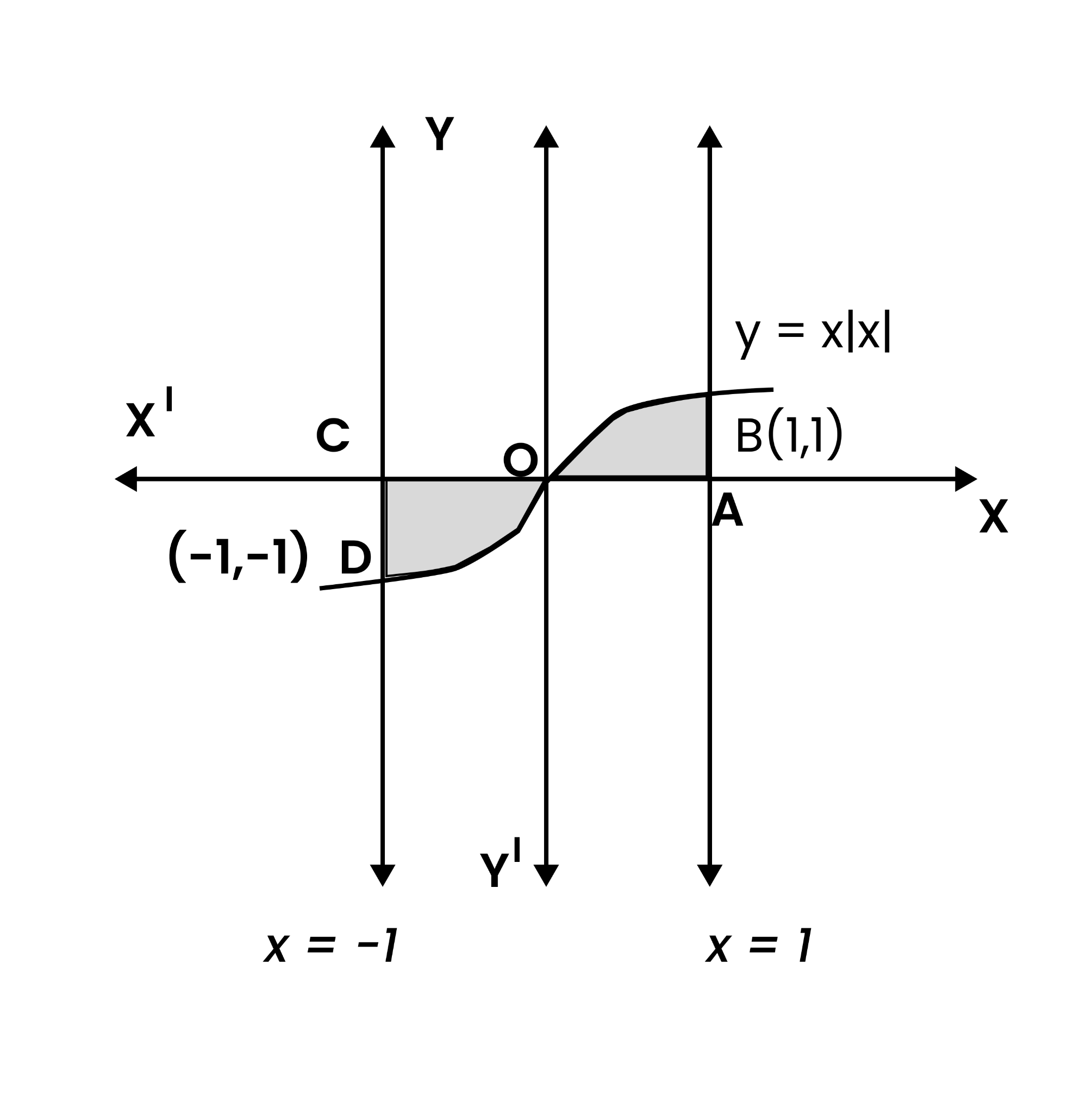
\[\text{Required area=}\int_{\text{-1}}^{\text{1}}{\text{y}}\text{dx}\]
\[\text{=}\int_{\text{-1}}^{\text{1}}{\text{x}}\text{ }\!\!|\!\!\text{ x }\!\!|\!\!\text{ dx}\]
\[\text{= -}\int_{\text{-1}}^{\text{0}}{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}}\text{dx+}\int_{\text{0}}^{\text{1}}{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}}\text{dx}\]
Integrating using the power rule
\[\text{= -}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}}{\text{3}} \right]_{\text{-1}}^{\text{0}}\text{+}\left[ \frac{{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}}{\text{3}} \right]_{\text{0}}^{\text{1}}\]
Substituting the limits,
\[\text{= -}\left( \text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}} \right)\text{+}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]
\[\text{=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{units}\]
So, the correct answer is \[\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{units}\] option C.
Conclusion
The Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Miscellaneous Exercise Solutions is important for understanding various concepts thoroughly. Application of Integrals Class 12 Miscellaneous includes a variety of issues that call for the use of several formulas and methods. It's crucial to concentrate on comprehending the fundamental ideas behind every question, as opposed to merely learning the answers by heart. To successfully complete this task, keep in mind that you must comprehend the theory underlying each idea, practise frequently, and consult solved examples.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 8: Exercises Breakdown
Exercise | Number of Questions |
4 Questions and Solutions |
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Other Study Materials
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 8 Application of Integrals |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter-wise List |

















