
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes NCERT Question Answers with Detailed Explanations
In Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes, understanding key processes like nutrition, respiration, transport, and excretion is essential. NCERT questions and answers for this chapter focus on these processes and help students prepare for exams effectively. Each Class 10 Science Chapter 5 question answer is carefully explained according to the NCERT guidelines, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentWhether it’s understanding how plants make their food, how oxygen is transported in our body, or how waste is excreted, these Class 10 Science Life Processes question answers provide simple yet comprehensive explanations. Each answer is aligned with the NCERT Class 10 Science Syllabus, making it easier for students to revise and confidently write in their exams.
This resource will not only help you practice the chapter but also ensure that you can answer every NCERT question correctly, building a strong foundation for your Class 10 Science exam preparation.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes (2025-26)
Life Processes Class 10 Questions and Answers for CBSE Exam Preparation
1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Ans: Diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans because the process of diffusion is very slow and will take a lot of time to reach each and every cell of the body since our body is very huge and complex and each and every cell of the body requires oxygen.
2. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans: The main criteria that we use to decide whether something is alive or dead are the events of Life processes. These fundamental life processes include nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, control and coordination, growth, and reproduction. If these processes occur normally then the organism is considered living because in the case of non-living organisms these processes do not take place
3. What are outside raw materials used by an organism?
Ans: Food, water, and oxygen are the outside raw materials that are used by an organism. These raw materials vary in amounts, source, and type depending upon various organisms and are used mainly for some important functions in the body of the organisms. They also provide energy to the body to perform various functions.
4. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Ans: The processes that are essential for maintaining life are nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, and control, and coordination. These are the processes that make the organism living.
5. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans: The differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are:
Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
The organisms make their own food with the help of various raw materials that include carbon dioxide and water and the process occurs in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. | The organisms do not make their own food, instead obtain their nutrition from other living organisms like plants (autotrophs). |
Autotrophs require energy that is obtained from light to synthesize their food. | Heterotrophs obtain energy from food that they consume by digesting them and other organic substances as well. |
Eg: All green plants, algae, some bacteria, seaweeds, etc. | Eg: All animals, Humans, fungi such as mushrooms, yeast, etc. |
6. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Ans: These raw materials required by plants for photosynthesis are as follows: sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll.
Carbon dioxide in plants can be obtained from the atmosphere and is absorbed through the stomata.
Water is absorbed by the roots of plants from the soil as soil mainly holds the water.
Sunlight is obtained from nature.
Chlorophyll acts as the main component and is found in the plant organelle called a chloroplast. (Chlorophyll is found in all of the green parts of the plants).
7. What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Ans: The role of the acid in our stomach is to mainly dissolve the large chunks of food and create an acidic medium to activate various digestive enzymes. In the acidic medium, the enzyme pepsinogen is activated and then converted to pepsin, which is a protein-digesting enzyme and helps in the digestion of proteins and can also kill the bacteria present in the stomach that enters along with food. The enzyme pepsin requires HCl to get activated in the presence of HCl. The acid will break down the food more easily and helps in absorbing nutrients and easy digestion of food.
8. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Ans: The digestive enzymes perform certain important functions that include the breaking down of complex food molecules into simpler food molecules that can be easily absorbed by the cells of the body. These enzymes also function as a biocatalyst that increases the rate of reaction and thus accelerates the rate of breaking down of complex food. There are various digestive enzymes present in the body, such as pepsin, trypsin, amylase, lipase, etc.
9. Write the role of villi in the human digestive system.
Ans: Villi are the finger-like projections that are present throughout the lining of the internal surface of the small intestine. They are primarily responsible for increasing the surface area of the small intestine which in turn increases surface area for absorption of the digested food. Villi are majorly supplied with blood vessels that help to absorb digested food into the bloodstream.
10. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: The advantage terrestrial organisms have over aquatic organisms is the amount of oxygen present in the surroundings. Terrestrial organisms have air in the atmosphere that surrounds them making it easy for them to breathe while in the case of aquatic organisms they breathe the air which is dissolved in the water. Thus the amount of oxygen present in the air is much more than the amount of oxygen present in the water.
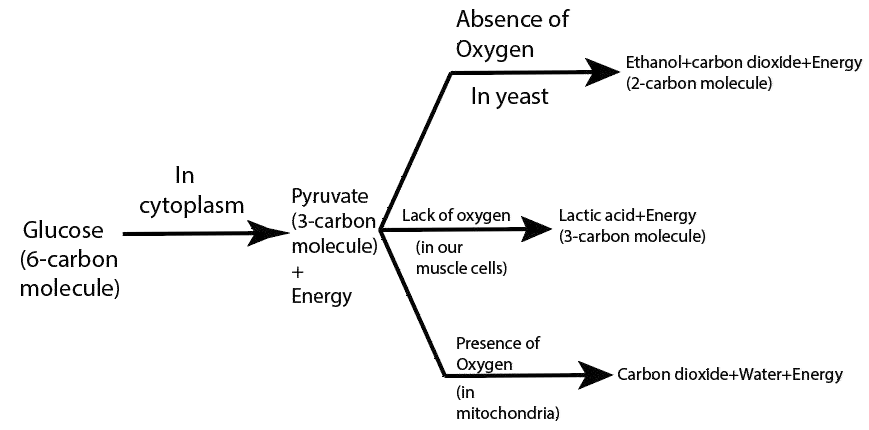
11. What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Ans: The different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms are:
12. In mammals and birds, why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Ans: In Mammals and birds it is important to separate the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood because they are homoeothermic and warm-blooded animals. Due to this character, they can maintain their temperature constant throughout and the changes in their environment do not affect their body temperature regulation. This process also results in a good supply of oxygen in the case of birds and mammals so that optimum oxidation of glucose can take place. So to supply the required amount of oxygen it is important to have separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
13. List three characteristics of the lungs that make them an efficient respiratory surface.
Ans: The characteristics that make lungs an efficient respiratory surface are:
1. Thin: The walls of the alveoli or air sac are very thin resulting in the quick diffusion of gases. They help in the absorption of oxygen inside the blood by inhalation process and also remove the carbon dioxide from the lungs by exhaling it to the outside.
2. Moist: The air sacs are composed of mucus that makes them moist which helps the gases to dissolve easily before diffusing.
3. Large surface area: In the lungs of human beings, its surface area is almost similar to the surface area of the tennis court that helps in the diffusion of gases. The alveoli or air sacs results in increasing the surface area of the lungs for the absorption of oxygen.
4. Good blood supply: The air sacs or alveoli are composed of a large capillary network that helps in the exchange of large volumes of gases. Thus greater the flow of blood in the lungs the greater would be the exchange of gases.
14. What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Ans: The main components of the transport system in human beings are the heart, blood, and blood vessels and their function are as follows:
The heart helps in pumping the oxygenated blood throughout the body. From the various parts of the body the deoxygenated blood is accumulated in the heart and from there it goes to the lungs for oxygenation.
Blood is the main body fluid that helps in the transport of nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogenous wastes, and hormones. Blood also consists of white blood cells (WBCs) thus making it the main component of our immune system. Blood also consists of platelets that cause the clotting of blood that helps in repairing the damaged blood vessels. Also, the temperature of the body is also maintained by transportation.
Blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) are responsible for blood transportation either from the heart to various other body organs or from various body organs to the heart. All arteries carry oxygenated except pulmonary arteries and they transport blood from the heart to various parts of the body while all veins carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary veins. The material that exchanges between the blood and tissues takes place inside the capillaries.
15. What are the components of the transport system in highly organized plants?
Ans: In highly organized plants, the transport system consists of vascular tissues. These are also called conducting tissues that two are of different types which include − xylem and phloem. The water and mineral which is obtained from the soil through roots are conducted through the xylem tissues to various parts of the plant while the food materials are conducted through the phloem tissues from the leaves to different parts of the plant body.
16. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans: The transportation of water and minerals in the plants occurs through the xylem tissues which is a part of the vascular system and occurs mainly in the upward direction that is from roots to the leaves while the other part of the vascular system includes phloem vessels which help in the transportation of the photosynthetic products within the plants, from leaves to all parts like the stem, roots, fruits, etc. and the transportation takes place in all directions.
17. How is food transported in plants?
Ans: The food is produced in the leaves of the plants through the process of photosynthesis and from leaves it is then transported to various parts of the body through phloem tissues. The phloem requires energy in the form of ATP for the transportation of food materials. This results in the development of osmotic pressure inside the tissue that increases the movement of water into the tissues. The osmotic pressure results in the movement of the material in the phloem to those tissues which have less pressure. This helps the tissue in moving the food materials according to the needs of the plant. Sucrose is a food material that requires energy in the form of ATP when it is transported into the phloem tissue.
18. Describe the structure and function of the nephron in the human body.
Ans: The structural and functional units of the kidney are Nephrons (filtration units). Each kidney consists of a large number of nephrons. Nephrons are composed mainly of two parts - renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
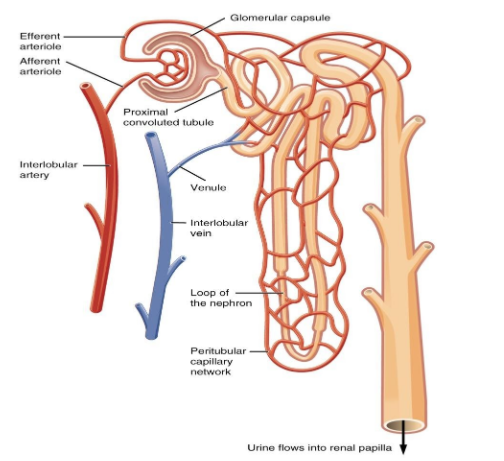
The renal corpuscle is composed of a cup-shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule which is surrounded by a cluster of capillaries that helps in the collection of filtered urine. The composition of urine changes as it passes through the tubular part of the nephron due to the reabsorption of amino acids, glucose, salts, and water. The reabsorption of the amount of water and other substances depends on their presence in the body. The urine then enters the collecting duct of the kidney from where it is then transported to the long tube called the ureter. Lastly, the urine is then collected in the urinary bladder.
19. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Ans: The excretory products of the plants may either be excreted out or may be stored as per the need of the plant. The excess amount of water in the plants can be removed by transpiration while the waste materials may be stored in the cell vacuoles or especially in old xylem vessels such as gum and resin. If it is also stored in the leaves then they fall off later. By the process of diffusion through stomata, the waste products that are obtained at the end of photosynthesis (oxygen) and respiration (carbon dioxide) are released.
20. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Ans: The amount of urine that is regulated depends upon the amount of water and other substances that are present. The urine is composed mainly of water so water is the main component in its regulation. If the amount of water is more in the body then the water reabsorbed will be less and more water will be released from the body and vice versa. There are various other factors that are responsible for the regulation of urine hormone such as Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and also the habitat of an organism that regulates the amount of urine produced.
21. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) Nutrition.
(b) Respiration.
(c) Excretion.
(d) Transportation.
Ans: (c) The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for excretion. They are the organs that help in the excretion and removal of waste materials from the body through the regulation of urine.
22. The xylem in plants is responsible for
(a) The transport of water.
(b) Transport of food.
(c) Transport of amino acids.
(d) Transport of oxygen.
Ans: (a) The xylem in plants is responsible for the transport of water. The xylem tissues are the vascular or conducting tissues that help in the transport of water and minerals from the roots to various parts of the plant. These minerals and water are absorbed from the soil through the roots.
23. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(a) Carbon dioxide and water.
(b) Chlorophyll.
(c) Sunlight.
(d) All of the above.
Ans: (d) The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll, and sunlight. Autotrophic nutrition is the process of making food by the organism itself. The food here is prepared by the process of photosynthesis which requires all the raw materials that are mentioned above.
24. The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water, and energy takes place in
(a) Cytoplasm.
(b) Mitochondria.
(c) Chloroplast.
(d) Nucleus.
Ans: (b) The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water, and energy takes place in mitochondria. This process is known as aerobic respiration where oxygen is required.
25. How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Ans: Fats are present in the small intestine of our body in the form of large globules. The various juices from the liver (bile juice) and liver (pancreatic juice) are secreted in the small intestine. The bile salts that are released from the bile juice of the liver will help in breaking down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes (lipases) can easily act on them. The process of breaking down large fat globules into smaller fat droplets is termed emulsification.
26. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Ans: Saliva is a watery fluid that is secreted by the salivary glands present in the mouth. The functions of saliva start from the moistening of food that results in the formation of a food bolus, this food bolus can be easily swallowed and thus saliva helps in the process of digestion of food starting from the mouth. Saliva breaks down starch into maltose and dextrin with the help of an enzyme amylase present in it.
27. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Ans: Autotrophic nutrition is the process where the organisms make their own food by themselves; this takes place through the process of photosynthesis. The necessary conditions that are required for autotrophic nutrition are the presence of sunlight along with raw materials that include carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll. The by-products of autotrophic nutrition are the carbohydrates in the form of glucose (food) and oxygen which are inhaled by animals.
$6{ CO }_{ 2 }+6{ H }_{ 2 }O\xrightarrow { Sunlight\quad Energy } { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }+6{ O }_{ 2 }$
28. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Ans: The differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are:
Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
1) Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen. | 1) Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. |
2) In this process, glucose breakdown completely results in oxidation. | 2) In this process, the glucose molecule breaks down incompletely. |
3) carbon dioxide, water, and energy are released in the form of end products. | 3) The ethyl alcohol or lactic acid, carbon dioxide, and energy are formed as the end products. |
4) It takes place in both the plant and animal cells. | 4) It takes place in many anaerobic bacteria, yeast, and human muscle cells. |
29. How are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases?
Ans: Alveoli are the air sacs that are in the form of tiny pouches or sac-like structures present inside the lungs. They are in the form of balloon-like structures which increase the surface area for inhalation of air composed of blood capillaries. The alveoli present in the lungs are more than millions that increase the surface area of the lungs for the exchange of gases. Thus, a large amount of air is brought in contact with the air in the lungs; this maximizes the exchange of gases in the lungs.
30. What would be the consequences of a deficiency of hemoglobin in our bodies?
Ans: Haemoglobin is found in the red blood cell of the blood as the respiratory pigment that helps in the transportation of oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Therefore, if the hemoglobin is deficient in the blood then it will affect the oxygen supplying capacity of blood resulting in the deficiency of oxygen in the body cells. This can also lead to anemia, an iron deficiency condition where the amount of blood in the body is quite less than required.
31. Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Ans: Double circulation is a process of blood circulation in which blood flows twice through the heart.
It constitutes of two steps:
1. Pulmonary circulation.
2. Systemic circulation.
Pulmonary circulation starts from the right ventricle and ends in the left atrium after the process of oxygenation occurs from the lungs.
While the systemic circulation starts from the left ventricle and ends in the right atrium after the materials get exchanged throughout the body.
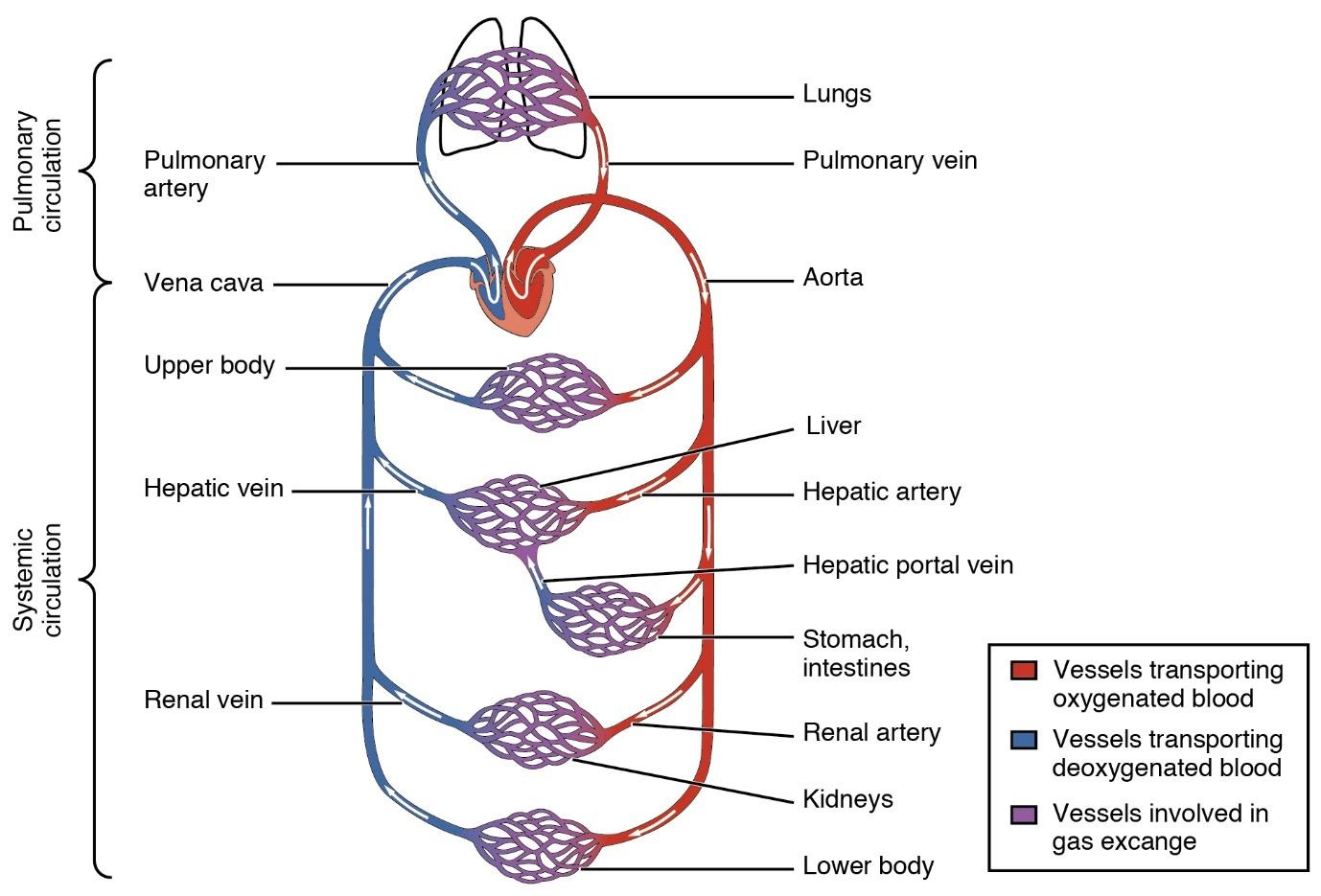
Importance Of Double Circulation:
The oxygen is supplied more efficiently to the body cells when there is a separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The efficient oxygen supply in human beings is very useful for the maintenance of high blood pressure for various processes and also provides pure blood to reach various parts of the body.
32. What are the differences between the transport of materials in the xylem and phloem?
Ans: The differences between the transport of materials in the xylem and phloem are:
Transport Of Materials In Xylem | Transport Of Materials In Phloem |
(i) They help in the transportation of water. | (i) They help in the transportation of water and minerals. |
(ii) Xylem elements consist of vessels and tracheids. | (ii) Phloem elements consist of sieve tubes and companion cells. |
(iii) Transportation starts from the roots to various parts of the plant. | (iii) Transportation starts from the leaves and then moves towards the roots. |
(iv) Helps in providing water and minerals to all parts of the plant. | (iv) Helps in providing nutrients to all parts of the plant. |
33. Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Ans: The comparison of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys are:
Alveoli | Nephron |
Structure (i) Alveoli are air-sacs that are present in the lungs in the form of balloon-like structures. (ii) The cell walls of alveoli are thin, only one cell thick and composed of an extensive network of blood capillaries. | Structure (i) Nephrons are present inside the kidneys in the form of tubular structures. (ii) Nephrons consist of three main parts - glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tube. They are composed of a cluster of thin-walled capillaries. |
(Image will be uploaded soon) | (Image will be uploaded soon) |
Function (i) The gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in between the blood of the capillaries that are present around the alveoli and the gases that are present in the alveoli. In alveoli, there is no selective reabsorption. | Function (i) Nephron helps in the process of filtration of the blood and removal of wastes. The solutes and excess water is filtered out when the filtration starts in the nephron. The selective reabsorption of essential molecules like amino acids, sodium salts, glucose, and water occurs before the formation of the final filtrate (urine). |
(ii) The exchange of gases for the process of respiration takes place in alveoli. | (ii) The basic filtration unit for excretion is nephrons. |
Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
List of Topics Covered in Science Chapter 5 Class 10 | |
Topics | Subtopics |
What are Life Processes? | |
Nutrition | Autotrophic nutrition, Heterotrophic nutrition, Nutrition in human beings |
Transportation | Transportation in human beings, Transportation in plants |
Excretion | Excretion in human beings, Excretion in plants |
Benefits of NCERT Science Chapter 5 Life Processes Class 10
Experts at Vedantu have made class 10 science chapter 5 question answers in a simple and easy-to-understand format. Students can get the benefits given below:
Subject matter experts have designed the class 10 science ch 5 Solutions. That is why the NCERT ch 5 science class 10 solutions can be considered the students' most comprehensive, easy-to-understand, and to-the-point study materials.
Students have the unique ability to ask experts whenever they face any problem.
Life Processes Class 10 Solutions PDF has arranged all the concepts and equations in a proper sequence, thus saving students time while studying.
The students are encouraged to perform several Science experiments to understand the concepts.
Since class 10 science life processes question answers can be downloaded, students can read and revise the concepts at their convenience.
CBSE Science class 10 Science ch 5 becomes more helpful when students plan for a quick revision before the examination.
Science class 10 science chapter 5 question answers solutions promise a significant increase in marks for the students.
Important Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 5
S. No | Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 |
1. | |
2. | |
3. |
Conclusion
Chapter 5 Life Processes Class 10 solutions provide students with simple and detailed definitions and explanations of each concept covered in the chapter. Therefore, it is highly recommended that students download and refer to our comprehensive and expert-curated ch 5 Science Class 10 to get a gist of the chapter before the exam and to know how to answer the questions in the exam. Students can also refer to our plethora of other study resources related to this chapter, which are available for free on our website and mobile app.
FREE PDF Links for other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
You can also access chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science from the links below and kick-start your preparation for Class 10 Board exams.
S.No. | Links to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | |
9. | Chapter 10 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World Solutions |
10. | |
11. | |
12. |
Related Links for Class 10 Science
S.No. | Related Links for Class 10 Science |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes (2025-26)
1. What do the Class 10 Science Life Processes questions and answers cover?
The Class 10 Science Life Processes questions and answers available on Vedantu include all NCERT textbook questions explained clearly with step-by-step answers.
2. Are the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 question answers written in simple language?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 question answers on Vedantu are written in student-friendly language for easy understanding.
3. Do the Life Processes Class 10 Q&A follow the NCERT textbook order?
Yes, the Life Processes Class 10 Q&A on Vedantu follow the same sequence and question pattern as presented in the NCERT textbook.
4. Are the Class 10 Science Life Processes question answers useful for homework?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Life Processes question answers from Vedantu can be used to complete homework and written assignments.
5. Can private students use the Life Processes Class 10 question answer solutions?
Yes, private students following the NCERT curriculum can use the Life Processes Class 10 question answer solutions available on Vedantu.
6. Are the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 solutions helpful for exam preparation?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 solutions on Vedantu are written in an exam-ready format that helps students prepare for school and board exams.
7. Do the Life Processes Class 10 question answers include step-by-step explanations?
Yes, the Life Processes Class 10 question answers on Vedantu include clear, step-by-step explanations wherever required.
8. Are the Class 10 Science Life Processes answers aligned with the latest syllabus?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Life Processes answers available on Vedantu are aligned with the latest NCERT and CBSE syllabus.
9. Are all textbook questions included in the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 solutions?
Yes, all textbook questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes are covered in the NCERT Solutions on Vedantu.














 Watch Video
Watch Video
















