




How to Choose the Perfect Maths Project for Your Grade
Maths might seem like a tough subject at times, but when you turn it into a fun project, it becomes a whole new adventure! Whether you're in Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12, there are so many exciting ways to explore math beyond textbooks. In this article, we'll share some cool project ideas, creative designs, and helpful tips that will make your next maths project stand out. So, let’s look into the world of numbers and shapes, and get ready to impress your teachers with your brilliant work!
Simple Maths Project Works for Students
Project 1
Probability:
Probability is such a native part of your life that you rarely think about it. However, every time you use a word like “might,” “may,” “undoubtedly,” “without fail,” or “maybe,” you can see and even a probability that an event will occur.
Scientists and great mathematicians like to express probability more accurately. For example, if you toss a coin in the air, the probability (P) that it will land heads or tails.
Materials Required:
A book and a pencil.
Four coins.
Procedure:
Using a paper and pencil, draw circles with an “H” or a “T” in the centre of the paper to illustrate the different results when you toss these three coins.
Using the circles that you drew as mentioned above, express the following:
The probability of getting three heads while tossing the coins.
The probability of getting three tails while tossing the coins.
The probability of getting one head and three tails while tossing the coins.
The probability of getting one tail and three heads while tossing the coins.
Hint: There are eight distinctly different possibilities so make sure you haven’t left any of them out.
Try tossing three coins 16 times and writing down the outcomes. Are the probabilities roughly equal as you calculated in step 2? Try tossing three coins 24 times. Are the probabilities any closer?
Project 2
Pythagoras Theorem:
This theorem states that the square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal in area to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
Materials Required:
Colour papers
Ruler and sketches
Procedure:
Make a right angle Triangle, of 3cm, 4cm and 5cm as shown 3cm 5cm.
Make 3 square sheets of 3 * 3 cm, 4 * 4 cm, 5 * 5 cm.
Fix these square sheets to the sides of the triangle.
Make the square sheets into 3 * 3 cm such that 9 squares of equal length
Similarly, repeat the same thing with the remaining square sets. 4cm
By this work, we can prove the above-said theorem.
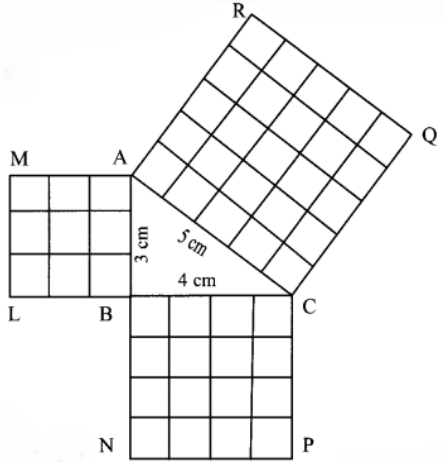
In the above work, we have considered a = 3cm, b = 4cm and c = 5cm.
Henceforth, 3 square + 4 square = 5 square.
3 * 3 + 4 * 4 = 5 * 5
9 + 16 = 25
25 = 25
Hence the theorem is proved.
Maths Project Ideas
Maths Project enables students to put their ideas into practice and get real-world experience. It will assist students in developing interpersonal skills and cognitive ability, as well as increasing their degree of confidence in the topic. Let's look at several maths models here;
Real-world Mathematical Number System
Area and perimeter of various sorts of forms and shapes
Angle Types
Probability and statistics
Algebraic Equations and Quadratic
Pythagoras' Theorem
Conic Sections
These are the few general themes for which students can develop a model.
Class 12 Maths Project Topics
1. Applications of Calculus: Explore how calculus is used in real-world scenarios like population growth, motion, or optimisation problems.
2. Probability in Real Life: Study probability applications in games, weather predictions, and risk assessment through practical experiments.
3. Linear Programming: Solve optimisation problems related to maximising profits or minimising costs in industries or daily life scenarios.
4. Mathematics in Cryptography:Understand the role of math in securing digital communication through encryption techniques like RSA.
5. Statistics and Data Analysis: Analyse real-world data from surveys or experiments and present findings using statistical tools like mean, median, and standard deviation.
Class 11 Maths Project Topics
1. Golden Ratio and Its Applications: Explore the concept of the golden ratio and its occurrence in nature, art, architecture, and design. Use examples like the Parthenon, Fibonacci sequence, and modern design elements to demonstrate its relevance.
2. Mathematical Modelling in Real Life: Create models to solve real-world problems, such as calculating population growth, analysing traffic flow, or optimising resource distribution. Use statistical tools and graphs for better visualisation.
3. Trigonometry in Navigation: Study how trigonometry is applied in navigation and positioning systems like GPS. Include practical examples of angle measurements and distances, supported by diagrams or simulations.
4. Applications of Calculus: Showcase real-world applications of differentiation and integration in fields like physics, biology, economics, and engineering. Topics could include rates of change, area under curves, or motion analysis.
5. Probability in Everyday Life: Analyse the role of probability in decision-making, games, weather forecasting, and financial markets. Use relatable examples like dice rolls, lottery systems, or sports predictions.
Ideas for Maths Project Class 10
For pupils in class 10, we've included some project ideas for maths that are related to their curriculum and can be simply reproduced.
Surface area and volume of a Cube and a Cuboid: Students in Grade 10 must be able to compute the surface areas and volumes of specified 3D objects such as a cube, a cuboid, and so on. Try to recognise the 3D forms around you and investigate how we can calculate their surface area and volume.
Areas of two comparable triangles are compared:The notion of similar triangles is simple to memorise; however, understanding the link between the areas of two similar triangles using their sides is essential.
Finding the angles using trigonometric ratios: As we all know, trigonometry can be used to locate the missing sides or angles of a right triangle. More similar situations will be practised with the assistance of a maths project model on trigonometry. The use of trigonometric ratios will aid in determining the needed parameters.
Following are the mean values of the provided data: In general, we deal with many numbers in our daily lives, and it is often necessary to know the average of these figures, such as the average time to complete a given activity. In this scenario, the idea of mean values is the most efficient way to get the desired outcome.
Probability of random experiments: This probability maths project aids in understanding different types of random experiments and determining the probabilities of occurrences related to them. For example, in the experiment of tossing a coin three times, receiving exactly two heads.
Class 9 Maths Project Topics
Students in Class 9 can utilise these project ideas to construct maths models that are aligned with their curriculum. Try out these 9th grade Math project ideas and have fun while learning.
Numbers are represented in a number line.
In Coordinate Geometry, the Cartesian Plane is used.
Geometry Shapes Types of Triangles Euclid's Geometry Model.
Maths Project for Class 8
Secondary students in Class 8 can create some of the greatest functional models based on the following topics:
Creating various types of quadrilaterals
Number line representation of rational numbers
Data grouping, organisation, and display using charts and graphs.
Profit and loss for commodities, as well as the discovery of simple interest
Having fun with numbers
Linear graphs (use matchsticks to represent)
3D Object Visualisation
Maths Project for Class 7
With the aid of practical models, students in Class 7 may easily grasp Mathematics and related principles. They can acquire several project ideas from here to make such models. These models will assist students in visualising topics and developing their confidence in any given area.
Here are the subjects on which students will base their projects.
Integer data types (positive and negative)
Fractional Forms (Proper and Improper fractions)
In two-dimensional space, what are lines and angles?
Triangle Shapes (Scalene, Isosceles and Equilateral)
Quantity Comparison
Symmetry
Imagining Solid Shapes
Maths Project for Class 6
When pupils advance from class 5th to class 6th, their educational level rises. They will be introduced to numerous new topics that they did not study in elementary school.
As a result, doing maths projects based on various topics and properly understanding them will be quite fascinating for children.
Knowing and comparing various figures
Whole-number patterns
Defining a Point, a Line, and an Angle (Basic geometry)
Line models of parallel and perpendicular lines
What exactly are decimals and fractions?
Matchstick Patterns in Algebra
Formal symmetry
Maths Project Ideas for Exhibition
Several mathematical projects may be made in school displays, such as:
Calculator: The calculator is constructed of cardboard and has four holes, with the first, third, and fourth holes containing moveable numbers and the second hole containing all the symbols depending on the operations performed: addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication. In this manner, we might construct a man-made calculator and assess the abilities of the exhibition's attendees.
Here are some more nice ideas for developing workable models based on mathematical concepts:
Construct a school project in which each building is represented by a distinct form. For example, the school's roof will be shaped like a triangle.
Create a model using LED lights that are based on trigonometric ratios (Sine, Cosine, and Tangent).
Make a "height and distance" model out of cardboard, paper, pulleys, threads, and other materials.
Using LED lights, match the following model for square and cube numbers.
A model that represents the centroid of several sorts of triangles (Acute, Obtuse and right triangle)
Make a model that depicts the many sections of a circle (radius, diameter, the centre of the circle, chord, sector, arc, etc.)
Geometrical forms in three dimensions
General Maths Project Work Ideas:
Geometry Map Project: Angles, Lines, and Triangles: Your assignment is to design a map that includes several distinct kinds of lines, angles, and triangles. Your map can be of a town, your neighbourhood or a made-up place of your own. It must, however, incorporate the following: 2 sets of streets that are parallel Two sets of streets that are perpendicular One street that intersects another street to form an obtuse angle.
Restaurant Menu Project: Create a menu for a themed restaurant. The student will write word problems using their menu. It can be a very fundamental element, just adding prices of different items, to more complex problems, like finding the cost of a meal for you and a friend plus tax or figuring the cost of the meal for grandma with her senior discount of 10%. The criteria for each of the following items in the menu are as follows: 4 different types of appetisers, 4 different types of beverages and 4 main dishes.
Compare Two Fractions: Two proper fractions are given to you with different denominators (show how to write these fractions as decimal numbers and as a percentages. Compare both the fractions using an appropriate mathematical symbol.) Be sure to explain what you are thinking!
Supplementary and Complementary Angles: Label and highlight the given angles from 6 different pictures. Select six of the following angles: acute angle, obtuse angle, straight, right angle, supplementary angle, and complementary angle. Then measure the acute angle, obtuse angle, supplementary angle, and complementary angles, and write their measures inside the interior of each angle.
Design Your Dream House: Draw a 2D version of how you want the front of your house to look like. Must include four windows, and two doors. All lines must be drawn with the help of a ruler and must be in centimetres. Students must then determine the perimeter and area of each window and the door. You must also do the same for the front of the house such as the perimeter and the area. Then you must convert these measurements to millimetres. Each dimension must be written in a typical drafting fashion. Houses must be uniformly coloured, and students may add additional features.
Mathematics Article: Draft an article about mathematics, which may include a mathematician. Write 2 important things you learned from the article. At least one page minimum. Note, write the summary in your own words!
Advantages of Maths Projects in Schools
Traditional learning methods are less effective for solving math problems; teachers and boards should promote rational, project-based learning.
Rote learning lacks long-term effectiveness, while math projects enhance problem-solving and lifelong understanding.
Projects improve planning, critical thinking, and reasoning skills by fostering "habit of thinking and mind skills."
Real-world examples and practical applications deepen understanding and retention of concepts.
Engaging in projects ensures concepts are learned meaningfully and retained for life.
Conclusion
CBSE now includes math projects in both formative and summative classes, with 10-15% of marks assigned to them. These projects involve high-level thinking questions, case studies, or open-book assessments. This approach helps students apply math to real-life situations and learn more holistically, benefiting their careers and future. Interactive sessions and videos are also used to make learning dynamic and engaging, ensuring students understand concepts in a practical and meaningful way.
FAQs on Maths Project Ideas for Classes 6 to 12
1. What exactly is a Maths project?
A Maths project is a practical assignment where students explore a mathematical concept in depth. It goes beyond textbook problems, often involving research, data collection, model building, or applying mathematical principles to real-life scenarios. The main importance of a Maths project is to develop critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deeper, more intuitive understanding of the subject.
2. What are the main benefits of working on a Maths project?
Working on a Maths project offers several academic benefits that contribute to a student's growth. These include:
- Deeper Understanding: It helps you visualise and internalise abstract concepts, theorems, and principles.
- Skill Development: It enhances crucial skills like critical thinking, research, planning, and data analysis.
- Real-World Connection: It bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and its practical application in everyday life.
- Increased Engagement: It makes learning Maths more interactive, fun, and memorable compared to rote learning.
3. What are some good topic ideas for a Maths project?
The best topic depends on your class level and interests. Some popular examples of Maths project topics include:
- Applied Maths: Creating a personal budget, designing a restaurant menu to explain percentages, or analysing sports statistics to understand probability.
- Geometry: Exploring tessellations in art, building 3D models of polyhedra, or verifying the Pythagoras theorem with a working model.
- Algebra: Using graphs to model real-world data like population growth or exploring the use of matrices in creating simple codes.
- Number Theory: Investigating the patterns in Pascal's triangle or researching the role of prime numbers in digital security.
4. What are the essential sections to include in a Maths project report?
A well-structured Maths project report, as per general academic standards, typically includes the following sections:
- Cover Page: Project title, your name, class, school, and date.
- Acknowledgement: Thanking your teacher, parents, or anyone who helped.
- Introduction: Briefly explaining the topic and its objective.
- Theory/Concepts: Detailing the core mathematical principles involved.
- Methodology: Explaining the step-by-step process you followed.
- Observation & Analysis: Presenting your findings, data, or calculations.
- Conclusion: Summarising the outcome of your project.
- Bibliography: Listing all the sources you referred to.
5. How can a Maths project connect theory to a real-world situation?
A Maths project builds a bridge between theory and reality by requiring you to apply abstract formulas to tangible problems. For example, a project on profit and loss moves beyond formulas by involving a task like creating a business plan for a small stall. Here, you would use concepts of cost price, selling price, and percentages to calculate a realistic profit. Similarly, a project on trigonometry could involve measuring the height of a tall building using angles of elevation, making the concept practical and visible.
6. How can the complexity of a Maths project be adjusted for different classes?
You can scale a project's complexity by adjusting the depth of the mathematical concepts and the scope of the investigation.
- For Junior Classes (e.g., 6-8): Focus on visual and hands-on projects. A project on fractions could be about dividing a pizza model, while a geometry project could involve identifying different types of angles and lines in the school playground.
- For Senior Classes (e.g., 9-12): The same topics can be explored with more rigour. A project on fractions could evolve into rational numbers and their properties. A geometry project could involve proving complex theorems or using coordinate geometry to design a detailed floor plan.
7. Are Maths projects only about making physical models?
No, this is a common misconception. While physical models are a great way to visualise concepts, a Maths project can take many forms. Other types of Maths projects include:
- Investigative Projects: Researching the history of a mathematical symbol like Pi (π) or exploring number patterns like the Fibonacci sequence.
- Survey-Based Projects: Collecting data from classmates (e.g., on favourite sports) and using statistics to create graphs and draw conclusions.
- Case Studies: Analysing how mathematics is used in a specific field, like architecture, finance, or computer graphics.
- Application-Based Projects: Designing a simple board game based on probability.
8. What is a good step-by-step process for completing a Maths project successfully?
A systematic approach is key to a successful Maths project. Follow these steps for a smooth process:
- 1. Select a Topic: Choose a concept that interests you and is appropriate for your grade level.
- 2. Research and Plan: Gather information and create a clear outline of your project structure and methodology.
- 3. Execute the Project: Carry out the necessary experiments, calculations, or model construction.
- 4. Document Your Work: Take notes, click pictures, and record your data and observations at every stage.
- 5. Draft the Report: Write the full report, following the standard structure (Introduction, Theory, Conclusion, etc.).
- 6. Review and Finalise: Proofread your report for any errors and assemble the final project for submission.
9. How do I design an effective cover page for my Maths project?
An effective cover page should be neat, informative, and visually appealing. Be sure to include the project title, your name, class, roll number, and school name. For the design, consider using elements related to your topic. You can create a border using geometric shapes, numbers, or mathematical symbols like π, Σ, or ∞. Using a clean layout with clear, readable fonts will make it look professional.
10. How should I write the acknowledgement section for a Maths project?
The acknowledgement section is where you express gratitude to those who supported you. Start by thanking your Maths teacher for their valuable guidance and supervision. You can then thank your parents or family members for their encouragement and any material support provided. It is also good practice to thank your school principal for providing the opportunity and facilities. Keep the tone sincere and professional.



































