




Step-by-Step Guide: Drawing and Interpreting Bar Graphs
Bar Graph Definition
A bar graph is a great tool for representing data that are unrelated to one another and do not need to be displayed in any particular sequence. The bars provide a visual representation for comparing amounts in several categories. The x and y axes, commonly known as the horizontal and vertical axes, the title, labels, and a bar graph are all included.
Bar Graph shows all the data, the heights of the rectangular bars are proportional to the values they represent. The graph's bars can be displayed either vertically or horizontally. Bar graphs, commonly referred to as bar charts, are a visual depiction of groups of data. It is one method of processing data.
What is a Bar Diagram and How to Draw a Bar Graph?
With the help of an example, let's learn how to draw a bar graph. Lana visited the market to purchase a variety of fruits, including 5 apples, 3 mangoes, 2 watermelons, 3 strawberries, and 6 oranges. She wants to create a bar graph to present the data so she can see what kinds of fruits she purchases the most frequently.
Let's use the next few stages to create a bar graph of the fruit that is most frequently purchased.
Step 1: Take a piece of graph paper, and label the bars with a caption like "Most Bought Fruit."
Step 2: On a plane, draw the horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis) axes.
Step 3: Give the horizontal axis, which is an independent category, the name "Types of Fruits," and the vertical axis, which is a dependent category, the name "Number of Fruits."
Step 4: Write the names of the fruits on the horizontal axis, such as apples, mangoes, watermelon, strawberries, and oranges, and leave an equal gap or spacing between each fruit.
Step 5: Describe the graph's scale, which demonstrates how numbers are used in the data. It is a system of markers spaced at specific intervals that aids in object measurement.
Step 6: Start constructing rectangular bars for each fruit, leaving equal spaces between them, and assigning heights to the corresponding numbers.
Step 7: Now that the bar graph is complete, determine which fruit is the most popular by measuring the height of the rectangle bars for each fruit.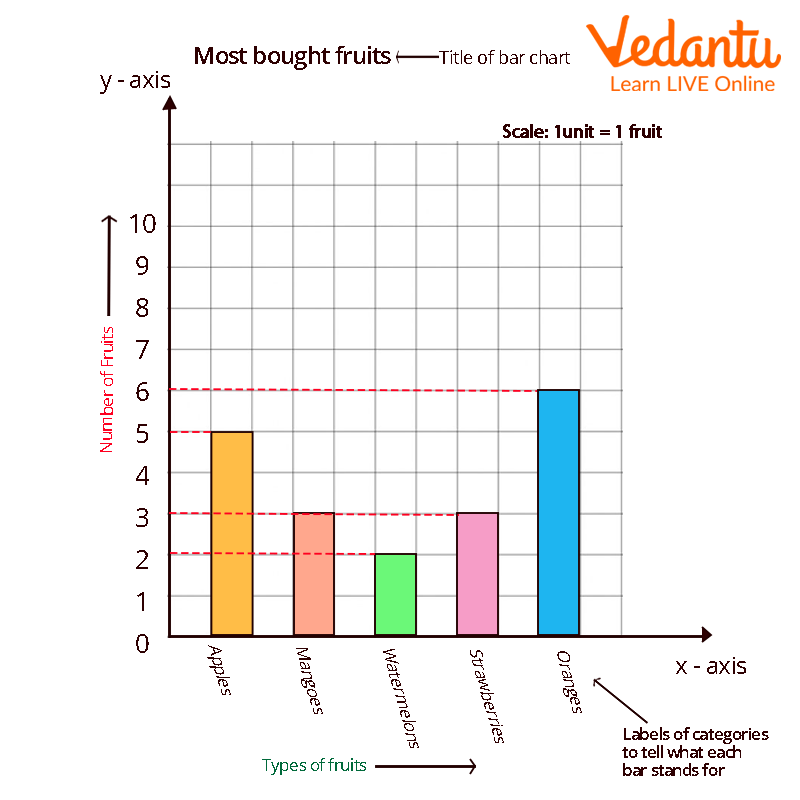
Bar Diagram Example
It is crucial to note four elements while creating a bar graph: the title, scale, and names of the axes.
Bar Graphs Parts
There are two basic categories for bar graphs:
Vertical Bar Graph
Horizontal Bar Graph
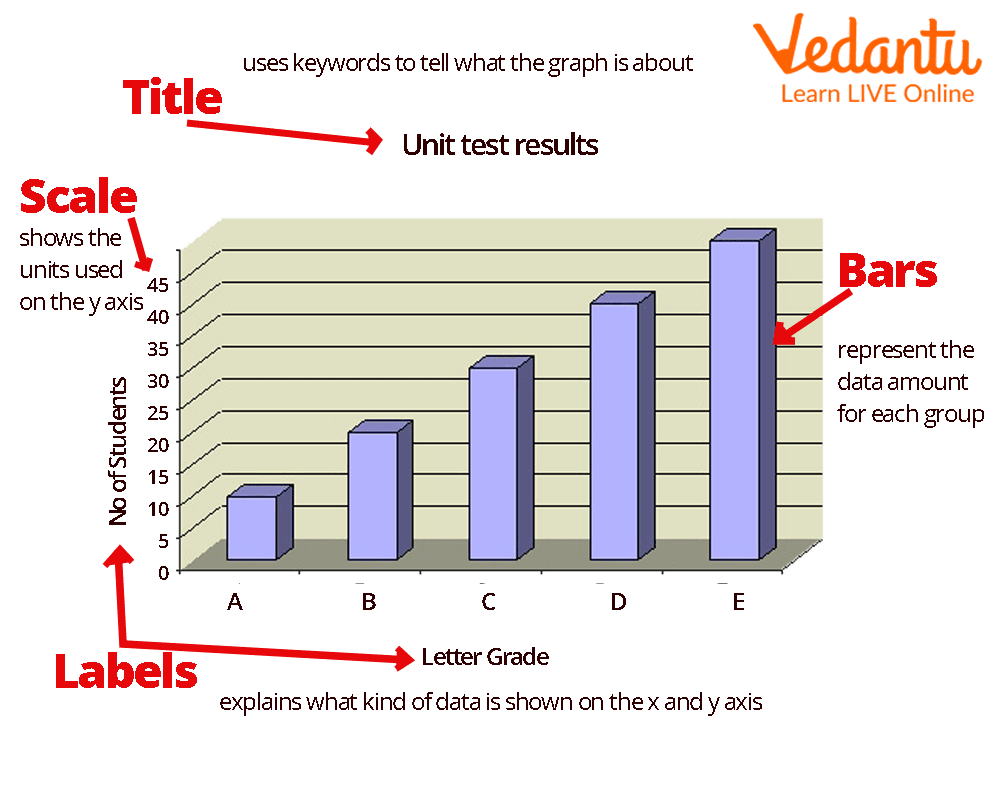
Bar Graph Parts
Properties of Bar Graph
The following list includes some characteristics that set a bar graph apart from other types of graphs:
The width and spacing between each rectangular bar should be the same.
Either horizontally or vertically can be used to draw the rectangular bars.
The rectangular bars' height is equal to the height of the data they depict.
There must be a common base for the rectangular bars.
Conclusion
A bar graph is a great method for showing data that does not need to be displayed in any specific order and is unconnected to one another. The bars offer a visual way to compare quantities across many categories. The title, labels, x and y axes, also known as the horizontal and vertical axes, as well as a bar graph are all present.
Solved Examples
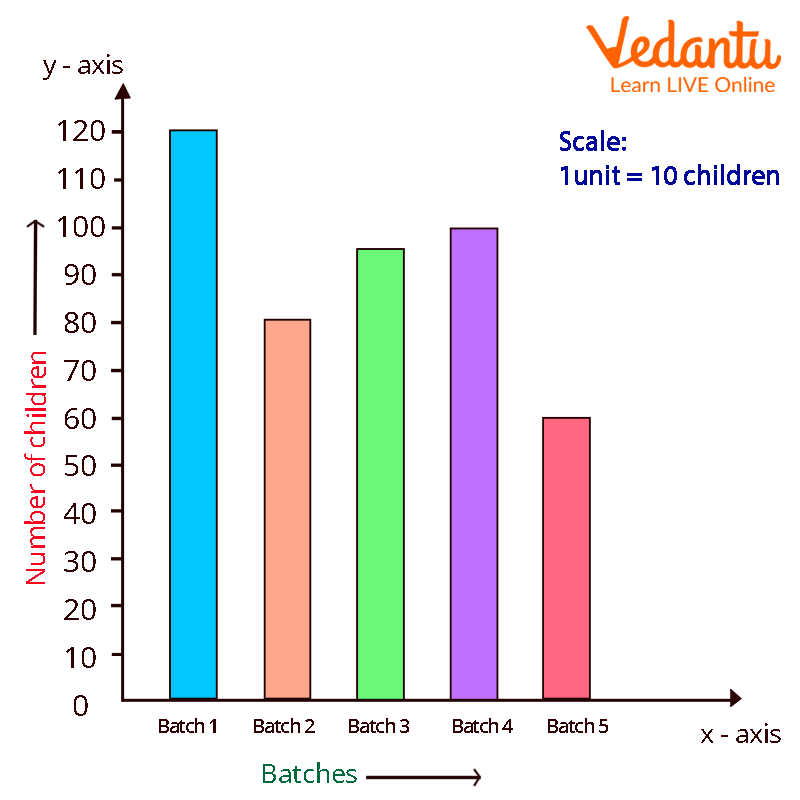
Example 1: The following information about a school's five separate batches of students. Create a bar graph to represent the following data.
Answer: The data can be represented as:
Example 2: What kinds of bar graphs are there?
Answer: Vertical bar graphs, horizontal bar graphs, stacked bar graphs, and grouped bar graphs are the four different types of bar graphs. A vertical bar graph shows the grouped data in a vertical direction. A horizontal bar graph shows the grouped data in a horizontal direction.
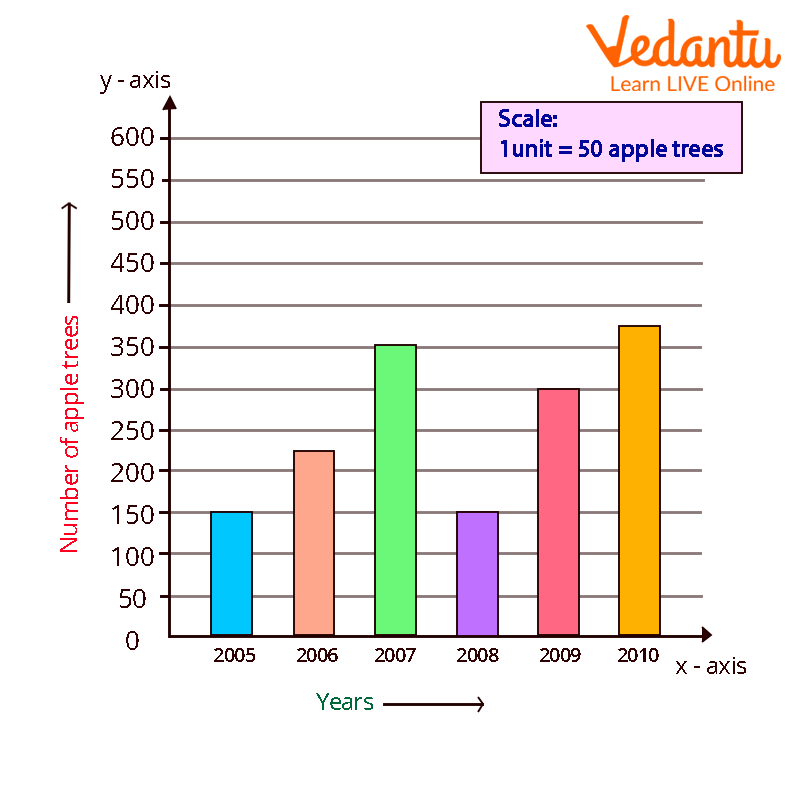
Example 3: The number of apple trees a school's gardener planted over the course of many years is displayed in the following table. Create a bar graph to represent the below given data.
Answer: Above data can be represented as:
FAQs on How to Draw a Bar Graph
1. What is a bar graph and how does it help to represent data for kids?
A bar graph is a visual tool that uses rectangular bars to represent data, making it easier for kids to compare quantities in different categories. Each bar's height or length shows the value for that category, helping young learners see which groups have more or less instantly.
2. How do you draw a simple bar graph step-by-step for a maths class activity?
To draw a simple bar graph, follow these steps:
- Draw two perpendicular lines to make the x-axis (horizontal) and y-axis (vertical).
- Label the x-axis with the categories (like types of fruits) and the y-axis with the values (like number of items).
- Decide and mark an appropriate scale on the y-axis.
- Draw equal-width bars for each category, making the height or length match its value.
- Give your graph a title that explains what it shows.
3. Why is it important to keep the width and spacing of bars equal in a bar graph?
Keeping the width and spacing of bars equal prevents confusion and ensures that the visual comparison is accurate and fair. Uneven bars or spaces can mislead viewers about the values or importance of data categories.
4. What are the key parts that every bar graph must have according to the CBSE maths syllabus?
Every bar graph must include:
- A clear title
- Labeled x-axis and y-axis
- A proper scale on the y-axis
- Rectangular bars with equal width and spacing
- Category names marked on the x-axis
5. How does a bar graph differ from a pie chart in representing data?
A bar graph shows discrete categories using separate bars to compare values, while a pie chart represents data as parts of a whole circle, displaying the proportion each category contributes to the total. Use bar graphs for clear comparisons; use pie charts for showing fractions of a whole.
6. What types of bar graphs are commonly used in primary maths, and when should you use each?
Common types include vertical bar graphs (bars stand upright) and horizontal bar graphs (bars lay flat). Use vertical bar graphs for fewer categories or when values are not too large; use horizontal ones for longer category names or many groups for clarity.
7. Can bar graphs mislead viewers? How can students avoid such mistakes?
Bar graphs can mislead if scales on the axes are uneven or if bars do not start from zero. Students should:
- Start axes from zero
- Use equal intervals on scales
- Keep bar widths and spaces uniform
- Label axes and give the graph a clear title
8. How can using real-life examples, like shopping for fruits, help kids understand bar graphs?
Real-life examples make bar graphs relatable and easier to understand. By using familiar situations, such as counting fruits bought, children can visualize data collection and understand how bar graphs help in comparing quantities in everyday life.
9. What are the common misconceptions students face while interpreting bar graphs?
Common misconceptions include:
- Assuming the width of the bar shows value instead of the height/length
- Misreading the scale on the y-axis
- Thinking that the order of bars changes their meaning (order doesn't alter values in bar graphs)
- Ignoring the need for equal spacing between bars
10. Why is understanding bar graphs important for higher classes and real-world applications?
Understanding bar graphs builds the foundation for analyzing data in higher classes and real-life careers. Skills learned help with interpreting statistics, making informed decisions, and presenting information clearly in projects, research, and various professions.

















