




How to Identify Proper, Improper, Mixed, Like & Unlike Fractions
In mathematics, fractions are categorised into three main types: proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed fractions. A fraction is a term that consists of a numerator and a denominator, and its type is determined based on these two parts.
Fractions represent parts of a whole object. For example, if a pizza is cut into four equal slices, each slice is represented as 1/4 of the pizza. Here, the number 1 is the numerator, and 4 is the denominator.
In addition to the three main types of fractions, there are three more categories: like fractions, unlike fractions, and equivalent fractions. Therefore, there are a total of six types of fractions: proper fractions, improper fractions, mixed fractions, like fractions, unlike fractions, and equivalent fractions.
What is a Fraction?
A fraction is a portion of a whole object. The fraction indicates how many parts you have of anything when it is divided into several pieces. It is expressed as the number of equal parts counted (the numerator) divided by the total number of parts (the denominator).
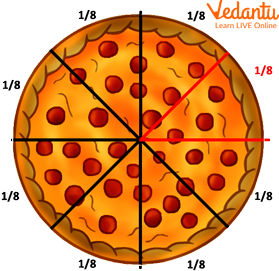
Fraction
Types of Fractions with Examples
In Maths, there are three Different Types of Fractions They are
Proper Fractions,
Improper Fractions
Mixed Fractions.
1. Proper Fraction
A proper fraction is one in which the numerator (number of equal parts counted) is less than the denominator (total number of parts). These fractions are all less than on the number line.
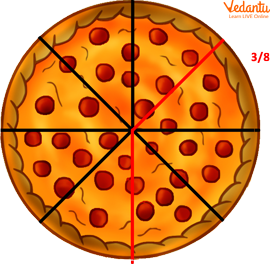
Proper Fraction
The above pizza example, with each person receiving ⅜ th of the pizza, demonstrates a proper fraction.
2. Improper Fraction
An improper fraction occurs when the numerator (number of equal parts counted) is greater than the denominator (total number of parts). These fractions are greater than one and lie on the number line beyond one. When more than one thing is divided into equal halves, they come into play. The number of equal parts is represented by the denominator. The numerator represents the number of available parts.
For example, there are a total of 8 slices in each. One has 8 slices left, and the other has only 6 slices. So, the fraction representing;
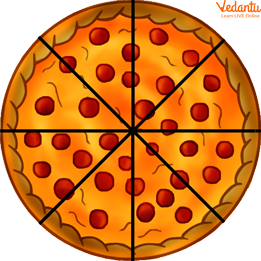
Improper Fraction
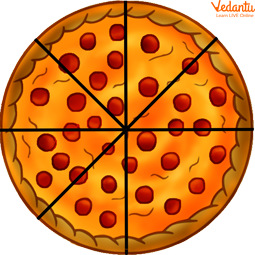
Improper Fraction with 6 Parts
Addition of both pizza’s parts and whole = $1+\dfrac{6}{8}=\dfrac{14}{8}$
3. Mixed Fraction
As the name suggests, it combines a whole and a 'part.' By dividing the numerator by the denominator and obtaining the quotient and remainder, an improper fraction can be stated as a mixed fraction.
For example: $2 \dfrac{4}{6}$
4. Unlike Fractions
Fractions with different denominators are called unlike fractions. Here the denominators of fractions have different values.
So, it can also be defined as fractions having the same numerator and different denominators are known as unlike fractions.
For example: $\dfrac{4}{7}, \dfrac{4}{5}, \dfrac{4}{11}, \dfrac{4}{13}, \dfrac{4}{15}$
5. Like Fractions
Fractions with same denominator and different numerators are known as like fractions.
For example: $\dfrac{7}{8}, \dfrac{12}{8}, \dfrac{15}{8}, \dfrac{9}{8}, \dfrac{23}{8}$
6. Unit Fractions or Unique Fractions
Fractions that have 1 as a numerator are known as unit fractions or unique fractions.
For Examples: $\dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{3}, \dfrac{1}{4}$
7. Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are fractions that have the same value when simplified.
For example: $\dfrac{1}{2} \text { and } \dfrac{50}{100}$ are equivalent to 0.5. As a result, these are comparable fractions.
Summary
This article discusses that a fraction is a portion of a complete part of the object. The fraction shows how many parts you have of anything when divided into several pieces. It is expressed as the number of equal parts counted (numerator) divided by the total number of parts (denominator). There are 7 kinds of fractions; Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, Mixed Fractions, Like Fractions, Unit Fractions, Equivalent Fractions and Same Numerator Fractions. If you enjoyed reading this and want to learn more about fractions, visit our website.
FAQs on Types of Fractions in Maths: Explained with Examples
1. What are the 7 types of fractions?
The 7 types of fractions typically discussed in mathematics include:
- Proper fractions (numerator < denominator)
- Improper fractions (numerator ≥ denominator)
- Mixed fractions (whole number + fraction, e.g., $2\frac{1}{3}$)
- Like fractions (same denominator)
- Unlike fractions (different denominators)
- Unit fractions (numerator = 1)
- Equivalent fractions (represent the same value, e.g., $\frac{1}{2}$ and $\frac{2}{4}$)
2. What are the 13 types of fractions?
The identification of 13 types of fractions is a more detailed categorization, sometimes found in advanced curricula. These include:
- Proper fractions
- Improper fractions
- Mixed fractions
- Like fractions
- Unlike fractions
- Equivalent fractions
- Unit fractions
- Decimal fractions
- Vulgar fractions
- Complex fractions
- Recurring fractions
- Compound fractions
- Simplest form fractions
3. What is 0.333333333333333 as a fraction?
The decimal 0.333333333333333 is a recurring decimal that can be expressed as the fraction $\frac{1}{3}$. Since 3 repeats indefinitely, it is written as $0.\overline{3}$, and the equivalent fractional form is: $$0.\overline{3} = \frac{1}{3}$$ Vedantu’s teachers can help you learn to convert repeating decimals to fractions quickly and accurately.
4. What type of fraction is 9 9?
The notation 9 9 is ambiguous, but if you mean a mixed fraction, such as $9\frac{9}{1}$, this would equal 18 and is not commonly used. If you refer to $\frac{9}{9}$, it's called an improper fraction (numerator equal to denominator) and its simplest form is 1, a whole number. Vedantu provides lessons and practice problems on different kinds of fractions for conceptual clarity.
5. What is the difference between like and unlike fractions?
Like fractions have the same denominator (e.g., $\frac{2}{5}$ and $\frac{3}{5}$), while unlike fractions have different denominators (e.g., $\frac{2}{5}$ and $\frac{1}{4}$). This difference is important for operations like addition and subtraction. At Vedantu, students learn techniques to convert unlike fractions into like fractions for easier computation.
6. How do you convert a mixed fraction to an improper fraction?
To convert a mixed fraction to an improper fraction, use this method:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
- Add the numerator.
- Place the result over the original denominator.
$3 \times 5 + 2 = 17$, so the answer is $\frac{17}{5}$. Vedantu provides step-by-step guidance and practice exercises for mastering fractions.
7. What are some real-life examples of improper fractions?
Improper fractions commonly appear in scenarios like:
- Measuring more than one whole object (e.g., $\frac{9}{4}$ meters of ribbon)
- Cooking recipes with combined ingredient measurements (e.g., $\frac{7}{3}$ cups of flour)
- Distributing items among groups when total items exceed a single group (e.g., $\frac{8}{5}$ pizzas for students)
8. How can Vedantu help students understand types of fractions?
Vedantu offers live online classes, study notes, and practice quizzes on types of fractions. Our expert teachers explain each concept using visual aids, real-life problems, and engaging animations. Students can clarify doubts instantly and track their progress through regular assessments and feedback sessions.
9. What is the simplest form of a fraction and how do you find it?
The simplest form of a fraction is when the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. To simplify,
- Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of both numbers.
- Divide the numerator and denominator by the GCD.
10. What are decimal fractions and how are they different from simple fractions?
Decimal fractions are fractions where the denominator is a power of 10 (e.g., $\frac{7}{10}$, $\frac{13}{100}$), and are written as decimals (0.7, 0.13). Simple fractions can have any integer as denominator. Decimal fractions are useful for precise calculations and metric measurements. Vedantu helps students transition smoothly between simple fractions and decimals through interactive learning modules.



































