




Key Formulas and Step-by-Step Solutions for Railway Timing Clock Problems
It is important to comprehend time properly whether it is observed through an analogue or digital clock. In the first place, kids have trouble understanding time. The fact that the time is constant throughout the day and that the unit of time is composed of 60 units rather than other units, which are composed of 10 or 100, are the two main causes of difficulties in understanding time. Two different time formats—a 12-hour format and a 24-hour format—increase the difficulty of this task.

Clock
Railway Timing Clock
A 12-hour clock is what we use in daily life. However, several agencies, including the military, airlines, and Railway Time, employ a 24-hour clock. Additionally, 24-hour clock time is displayed on digital timepieces. The Railway Timing Clock operates on a 24-hour cycle. Similar to numerous other digital clocks.
The 24-hour clock utilizes the numbers 00:00 to 23:59 to indicate the time of day (midnight is 00:00) Time is defined as the 24-hour period in the 24-hour format. As a result, 9.20 AM would be written as 0920 hours, and 9.20 PM as 2120 hours.
Railway Time Calculation
Let’s understand How to convert Railway Time to Normal Time:
Changing the first 12 hours of 24-hour time to 12-hour time is the first step.
In 24-hour time, 00:00 corresponds to 12:00 AM. The remaining hours, from 0:00 to 12:00 correspond to the 12-hour period between 12:00 AM and 12:00 PM.
As in
\[\begin{array}{l}0:00 = 12:00AM\\01:00 = 1:00AM\\02:00 = 2:00AM\end{array}\]
Changing the second 12 hours of 24-hour time to 12-hour time is step two.
Subtract 12 from the hours to get the time in PM if the hourly display is 12:00 or higher.
For instance,
\[\begin{array}{l}13:00 = 1:00PM\\14:00 = 2:00PM\\15:00 = 3:00PM\end{array}\]
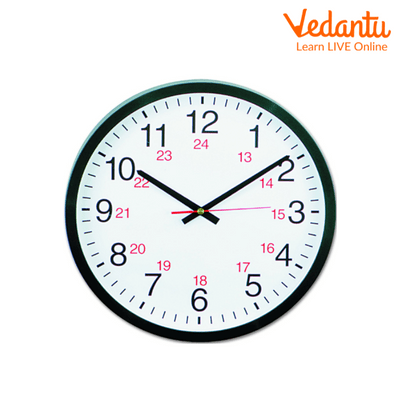

24/12 Hour Clock
24 Hour Clock Conversion Table
We take help from the below given table to convert Railway Time (24 – Hour system) into Normal time (12 – Hour system).
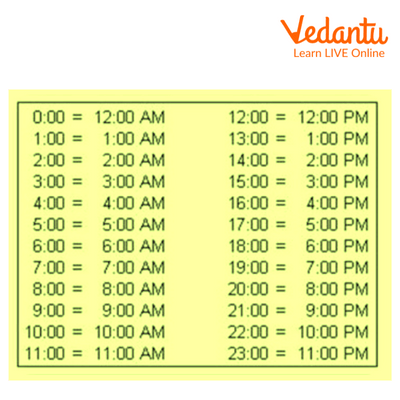
24 Hour Clock Conversion Table
Let’s understand it more clearly with the help of an illustration:
Think about 15:30. Given that the day has already been going for 15 hours, it is the afternoon rather than the morning. The time is 3:30 P.M. since subtracting the 12 hours from the morning produces 3 hours. We just add 12 to the 12-hour clock's hours and subtract PM to create the 24-hour clock. For instance, 10:00 PM on a 12-hour clock is 22:00 on a 24-hour clock (\[10 + 12 = 22\]). And we may easily convert 22:00 in the 24-hour clock to 10:00 in the 12-hour clock by deducting 12 from the hours and adding P.M.
Conclusion
The two ways that time is represented are in 12-hour and 24-hour forms. Railway timings follow 24-hour forms in general.
Solved Examples
Example 1: The time is 15:00, according to the clock at the train station. How late is it in 12-hour time?
A: 4:00 am
B: 3:00 am
C: 5:00 pm
D: 3:00 pm
Ans: In 12-hour time it should be 3:00 PM.
Option D is the correct answer.
Example 2: Convert 7:15 p.m. in 24 – Hour clock station or Railway time.
Ans: The answer is 1915 hours.
Example 3: The time is 20:30 then, What is the time in both railway time and the 12 – Hour clock system at night?
Ans: In the 12 – Hour clock system it is 8:30 pm.
In the 24 – Hour clock system it is 20:30.























