
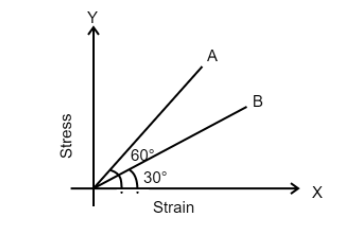
The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials (A)and (B) are as shown in the figure. If ${Y_A}$and ${Y_B}$ are Young's moduli of the materials, then:
(A) ${Y_B} = 2{Y_A}$
(B) ${Y_B} = {Y_A}$
(C) ${Y_B} = 3{Y_A}$
(D) $3{Y_B} = {Y_A}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
.Hint. We solve this question by finding the values of Young’s modulus for both the materials. We find Young’s modulus by finding the slope of the line in the graph for each material. We find the slope by using trigonometric properties. The angle made by the line in the stress vs strain graph is already given. By using these angles in trigonometry properties to find Young’s modulus we get a relation between ${Y_A}$and ${Y_B}$
Complete step by step answer. The slope of stress vs strain graph gives us Young’s modulus.
In the graph, we are given the angle made by the line in the stress vs strain graph in both cases.
We know that slope is equal to $\tan \theta $
In the case of material (A)
The slope is equal to $\tan 60^\circ $
Material (B)
The slope is equal to $\tan 30^\circ $
We know that slope is equal to Young’s modulus hence
${Y_A} = \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 $
${Y_B} = \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Diving Young’s modulus of (A) with Young’s modulus of (B) we get $\dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}} = 3$
Hence $3{Y_B} = {Y_A}$
Option (D) $3{Y_B} = {Y_A}$ is the correct answer.
Additional information Young’s modulus is defined as the measure of ability of a material to withstand changes in length when it is under a lengthwise tension of compression. It is also referred to as modulus of elasticity.
Note We find the slope in the graph by using tanθ because we are assuming the graph as a right-angled triangle. And $\tan \theta $is equal to the opposite by the adjacent side of the assumed triangle. In the case of stress vs strain graph opposite is equal to stress and adjacent is equal to the strain. Hence $\tan \theta $ is equal to Young’s modulus. Therefore, we use $\tan \theta $ to find the slope.
Complete step by step answer. The slope of stress vs strain graph gives us Young’s modulus.
In the graph, we are given the angle made by the line in the stress vs strain graph in both cases.
We know that slope is equal to $\tan \theta $
In the case of material (A)
The slope is equal to $\tan 60^\circ $
Material (B)
The slope is equal to $\tan 30^\circ $
We know that slope is equal to Young’s modulus hence
${Y_A} = \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 $
${Y_B} = \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Diving Young’s modulus of (A) with Young’s modulus of (B) we get $\dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}} = 3$
Hence $3{Y_B} = {Y_A}$
Option (D) $3{Y_B} = {Y_A}$ is the correct answer.
Additional information Young’s modulus is defined as the measure of ability of a material to withstand changes in length when it is under a lengthwise tension of compression. It is also referred to as modulus of elasticity.
Note We find the slope in the graph by using tanθ because we are assuming the graph as a right-angled triangle. And $\tan \theta $is equal to the opposite by the adjacent side of the assumed triangle. In the case of stress vs strain graph opposite is equal to stress and adjacent is equal to the strain. Hence $\tan \theta $ is equal to Young’s modulus. Therefore, we use $\tan \theta $ to find the slope.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




