
The slopes of isothermal and adiabatic curves are related as:
A) Isothermal curve slope = Adiabatic curve slope
B) Isothermal curve slope = $\gamma \times $adiabatic slope
C) Adiabatic curve slope = $\gamma \times $isothermal slope
D) Adiabatic curve slope = $\dfrac{1}{2} \times $isothermal curve slope
Answer
530.8k+ views
Hint: Before we understand about these processes, it is important to understand the significance of the term slope. The slope represents the steepness of the curve, which is represented by the ratio of how high the curve is moving to the width of the curve. Hence, if we draw a tangent at the curve, the slope is given by tan of the angle made by the tangent with the horizontal.
The slope of the tangent drawn to a curve is equal to the derivative of the curve at the point where it touches the curve. Thus,
$Slope = \tan \theta = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us understand the meaning of the isothermal and adiabatic process in a thermodynamic system.
Isothermal process is a process that takes place in the system under constant temperature. The equation that represents an isothermal process is –
$PV = C$
where P = pressure and V = volume and C = constant
Adiabatic process is a process which takes place with zero heat transfer from the system or surroundings. The equation that represents an adiabatic process is –
$P{V^\gamma } = C$
where C = constant and $\gamma $ is the ratio of specific heats calculated at constant pressure and constant volume.
$\gamma = \dfrac{{{C_p}}}{{{C_v}}}$
Plotting these two processes on a pressure v/s volume graph, we obtain as follows:
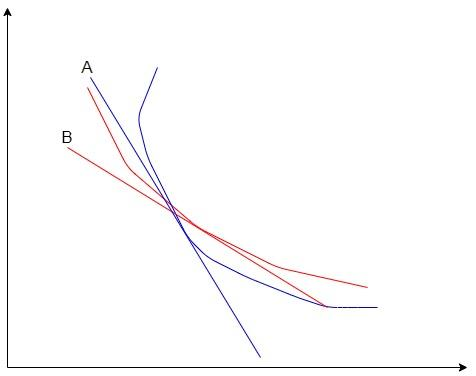
The red curve represents the isothermal process and the blue curve represents the adiabatic process. A and B are the slopes of the isothermal and adiabatic curves respectively. We can see from the graph, that the slope of adiabatic is higher than that of the isothermal process.Let us prove that.
If we differentiate the equation of the isothermal process, we obtain the slope of the line B in the above graph.
$PV = C$
Differentiating with respect to V,
$V\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} + P\dfrac{{dV}}{{dV}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow V\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\dfrac{{dV}}{{dV}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - \dfrac{P}{V}$
Hence, the slope of line A = $ - \dfrac{P}{V}$
Similarly, differentiating the equation for adiabatic process, we get the slope of line B.
$P{V^\gamma } = C$
Differentiating with respect to V,
$P\dfrac{{d\left( {{V^\gamma }} \right)}}{{dV}} + {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\dfrac{{d\left( {{V^\gamma }} \right)}}{{dV}}$
$ \Rightarrow {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1}}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = \dfrac{{ - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1}}}}{{{V^\gamma }}} = - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1 - \gamma }} = - P\gamma {V^{ - 1}}\]
\[\therefore \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - \gamma \dfrac{P}{V}\]
Comparing the slopes, we see that the slope of the adiabatic curve is $\gamma $ times the slope of the isothermal curve.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The value $\gamma $ is referred to as the adiabatic index. If nothing is given, the value of adiabatic index for normal conditions of air should be taken as 1.4 approximately, while solving problems in adiabatic processes.
The slope of the tangent drawn to a curve is equal to the derivative of the curve at the point where it touches the curve. Thus,
$Slope = \tan \theta = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us understand the meaning of the isothermal and adiabatic process in a thermodynamic system.
Isothermal process is a process that takes place in the system under constant temperature. The equation that represents an isothermal process is –
$PV = C$
where P = pressure and V = volume and C = constant
Adiabatic process is a process which takes place with zero heat transfer from the system or surroundings. The equation that represents an adiabatic process is –
$P{V^\gamma } = C$
where C = constant and $\gamma $ is the ratio of specific heats calculated at constant pressure and constant volume.
$\gamma = \dfrac{{{C_p}}}{{{C_v}}}$
Plotting these two processes on a pressure v/s volume graph, we obtain as follows:

The red curve represents the isothermal process and the blue curve represents the adiabatic process. A and B are the slopes of the isothermal and adiabatic curves respectively. We can see from the graph, that the slope of adiabatic is higher than that of the isothermal process.Let us prove that.
If we differentiate the equation of the isothermal process, we obtain the slope of the line B in the above graph.
$PV = C$
Differentiating with respect to V,
$V\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} + P\dfrac{{dV}}{{dV}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow V\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\dfrac{{dV}}{{dV}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - \dfrac{P}{V}$
Hence, the slope of line A = $ - \dfrac{P}{V}$
Similarly, differentiating the equation for adiabatic process, we get the slope of line B.
$P{V^\gamma } = C$
Differentiating with respect to V,
$P\dfrac{{d\left( {{V^\gamma }} \right)}}{{dV}} + {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\dfrac{{d\left( {{V^\gamma }} \right)}}{{dV}}$
$ \Rightarrow {V^\gamma }\dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1}}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = \dfrac{{ - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1}}}}{{{V^\gamma }}} = - P\gamma {V^{\gamma - 1 - \gamma }} = - P\gamma {V^{ - 1}}\]
\[\therefore \dfrac{{dP}}{{dV}} = - \gamma \dfrac{P}{V}\]
Comparing the slopes, we see that the slope of the adiabatic curve is $\gamma $ times the slope of the isothermal curve.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The value $\gamma $ is referred to as the adiabatic index. If nothing is given, the value of adiabatic index for normal conditions of air should be taken as 1.4 approximately, while solving problems in adiabatic processes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




