
A light beam is being reflected by using two mirrors, as in a periscope used in submarines. If one of the mirrors rotates by an angle θ, the reflected light will deviate from its original path by the angle-
A. $2\theta $
B. $3\theta $
C. $\theta $
D. $4\theta $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First think about the periscope. Also think about working principles and arrangement. Then draw a picture. Now remember what the law of reflection is for the smooth plane and apply it. Check the angle of deviation from its original path.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we have to think about how the mirror is arranged. They give two mirrors arranged like periscopes. For that we need to know what is periscope? A periscope is an instrument used for looking over, around or through an obstacle or object which is prevented by a direct line of sight. The two plane mirrors in a periscope are parallel to each other inside the periscope.
Because it reflects the light rays from the upper end of the periscope to the lower end of the periscope and the reflecting surfaces of it face each other. The two planes are at an angle of ${45^0}$ with each other and with respect to the sides of the tubes. Actually, the propagation of light rays through the inner gap of the periscope becomes easier for the inclination of the plane, hindering reflections on any wrong part. Now let’s draw a picture.
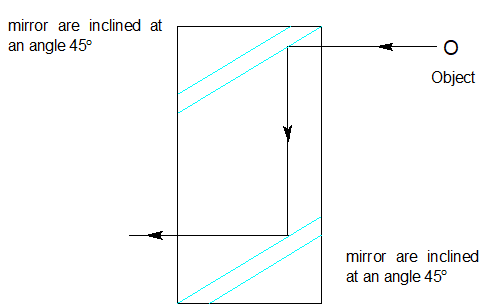
Here we draw structures like periscopes. I think it’s absolutely clear to us how the mirrors are arranged in periscope. Now move to the next part. We rotate a mirror by an angle $\theta $ .
Let's draw another picture to visualize this.
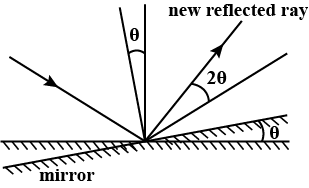
Here we compare the reflection of light by rotating a mirror by an angle $\theta $ . So, try to check out the angle between two reflected lights. The ideal angle of reflection is equal to $i$. As we know in case of reflection through a plane surface reflected angle = incident angle. So the reflected angle is also equal to $i$. Then when we rotate the mirror by an angle $\theta $.
The incident angle becomes $i + \theta $ and the reflected angle is now $i - \theta $. As they are the same so we can write that the angle between two reflected light is $2\theta $. Then imagine that it will be reflected by the second mirror. But no deviation occurs there. Hence the light is deviated by an angle $2\theta $ when the mirror is rotated by $\theta $ .
Therefore option A is the correct answer.
Notes: A periscope is an instrument used for looking over, around or through an obstacle or object which is prevented by a direct line of sight. The two plane mirrors in a periscope are parallel and inclined at an angle ${45^0}$ to each other inside the periscope. For reflection of light through a smooth plane angle of incidence is the same as angle of reflection.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we have to think about how the mirror is arranged. They give two mirrors arranged like periscopes. For that we need to know what is periscope? A periscope is an instrument used for looking over, around or through an obstacle or object which is prevented by a direct line of sight. The two plane mirrors in a periscope are parallel to each other inside the periscope.
Because it reflects the light rays from the upper end of the periscope to the lower end of the periscope and the reflecting surfaces of it face each other. The two planes are at an angle of ${45^0}$ with each other and with respect to the sides of the tubes. Actually, the propagation of light rays through the inner gap of the periscope becomes easier for the inclination of the plane, hindering reflections on any wrong part. Now let’s draw a picture.

Here we draw structures like periscopes. I think it’s absolutely clear to us how the mirrors are arranged in periscope. Now move to the next part. We rotate a mirror by an angle $\theta $ .
Let's draw another picture to visualize this.

Here we compare the reflection of light by rotating a mirror by an angle $\theta $ . So, try to check out the angle between two reflected lights. The ideal angle of reflection is equal to $i$. As we know in case of reflection through a plane surface reflected angle = incident angle. So the reflected angle is also equal to $i$. Then when we rotate the mirror by an angle $\theta $.
The incident angle becomes $i + \theta $ and the reflected angle is now $i - \theta $. As they are the same so we can write that the angle between two reflected light is $2\theta $. Then imagine that it will be reflected by the second mirror. But no deviation occurs there. Hence the light is deviated by an angle $2\theta $ when the mirror is rotated by $\theta $ .
Therefore option A is the correct answer.
Notes: A periscope is an instrument used for looking over, around or through an obstacle or object which is prevented by a direct line of sight. The two plane mirrors in a periscope are parallel and inclined at an angle ${45^0}$ to each other inside the periscope. For reflection of light through a smooth plane angle of incidence is the same as angle of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




