




Materials Needed and Key Principles Explained
Have you ever wondered how to make an electromagnet? So, before going on to it, let’s first know what a simple electromagnet is. It is a type of magnet that generates a magnetic field by using an electric current. It has the ability to attract and magnetise ferromagnetic elements such as iron, nickel, and cobalt. A basic electromagnet can be easily constructed at home using common household components.
In this article, you will learn how to make a simple electromagnet, as well as how to make one at home. You'll also find out what things are necessary for the process, and get a description of how it actually works. Below are images of electromagnet.

An Electromagnet
How to make an Electromagnet at home?
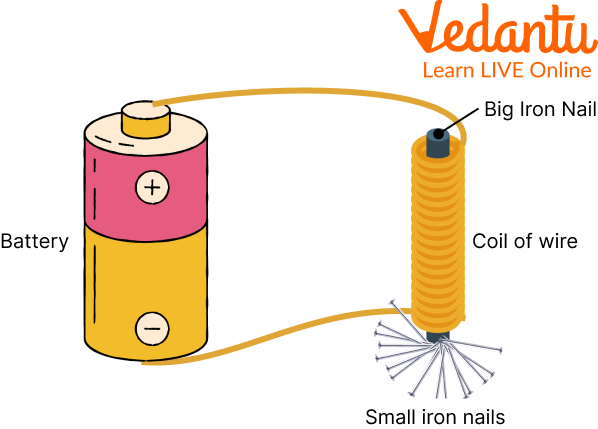
You might be wondering how to make an electromagnet. Is it that simple? Can it be made at home? A simple electromagnet can be made at home only. The following are the things required to make an electromagnet:
A plastic insulated thin wire
A battery of 5 volts
Some small nails that are made up of iron
A big Iron nails

Things Required to make an Electromagnet
Steps to Prepare
Wrap 20 turns of insulated wire on an iron nail firmly.
Trim about an inch of plastic covering from the two ends of the wire.
Attach one end of the wire with the positive terminal of the battery, and the other with the opposite terminal. Utilising the electric wire tape is vital.
Get some iron nails and bring your electromagnet close to them. You will see the iron nails will be drawn in towards your electromagnet.
Separate wires from the battery, if the wire or battery gets hot.
The image of an electromagnet is shown below:
Preparation of Electromagnet
How Does Electromagnet Work?
At the point when you connect the wires to the battery, an electric current flows into the wires. This electric flow creates the magnetic field around the wire. The iron nails act as a magnetic core. Magnetic cores are utilised to improve the magnetic field.
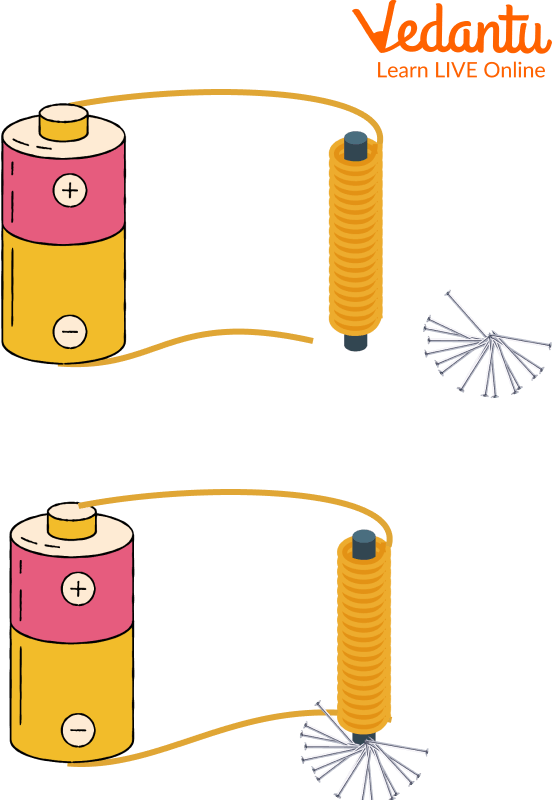
Working of Electromagnet
Give It a Try!
You can use this method to know practically about the electromagnet. Attempt to utilise two 1.5 volts AA batteries, and attach them in series. Then, connect the wires to this battery and notice the impacts. Find out, does it influences the strength of the electromagnet
Use a thicker wire rather than a thin wire, and fold over the iron nail. Then, at that point, notice the strength of an electromagnet.
Use thick iron nails or bolts. Then, at that point, they notice does it influence the strength of an electromagnet.
Attempt the above techniques, and note down your outcome. Eventually, you will find which strategy is influencing the strength of the electromagnet most.
Magnetic Field of an Electromagnet
The magnetic field of an electromagnet is produced by the flowing electric current. The wire which is turned around the magnetic core is made from a ferromagnetic material such as iron. The current flowing through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole.
Advantages of Electromagnet
The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be changed as per our requirement just by changing the amount of electric current flowing in the wire. Electromagnets are widely used in electrical devices, such as generators, motors, loudspeakers, MRI machines, and solenoids. These magnets are also for picking up and moving heavy objects in the industry. The poles of electromagnets can be changed by changing the direction of the electric current. They are also inexpensive and lightweight.
Summary
An electromagnet is the sort of magnet which utilises electric flow to make an attractive field. It can draw in and charge ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel and cobalt. Making a simple electromagnet at your home from household materials is easy. Electromagnetic devices comprise a centre of magnetic material encompassed by a coil through which an electric current is passed to magnetise the centre. An electromagnet is utilised in any place where controllable magnets are expected, as in contraptions in which the magnetic flux is to be changed, turned around or turned on and off.
FAQs on How to Make an Electromagnet: Step-by-Step Guide
1. What is an electromagnet and how does it work?
An electromagnet is a type of magnet where the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Unlike a permanent magnet, its magnetism is temporary and can be controlled. It works on the principle that an electric current flowing through a wire generates a magnetic field around it. By wrapping this wire into a coil, known as a solenoid, and often placing a ferromagnetic material (like an iron nail) inside, the magnetic field becomes strong and concentrated.
2. How can you make a simple electromagnet step-by-step for a school project?
To make a simple electromagnet, you will need an iron nail, insulated copper wire, and a battery (like a D-cell). Follow these steps:
- Step 1: Tightly wrap the insulated copper wire around the iron nail, leaving about 10 cm of wire free at both ends. The more turns you make, the stronger the magnet will be.
- Step 2: Carefully strip the insulation off the last 2 cm of each end of the wire.
- Step 3: Connect one stripped end of the wire to the positive terminal of the battery and the other end to the negative terminal. You can add a switch in the circuit for safety and control.
- Step 4: Once connected, the iron nail becomes an electromagnet and can pick up small metal objects like paperclips.
Remember to disconnect the battery when not in use as it can get hot and drain quickly.
3. What is the main difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet?
The main difference lies in the source and control of their magnetism. A permanent magnet, made from materials like ferrite or neodymium, has a constant magnetic field and does not require any external power. An electromagnet, on the other hand, only becomes magnetic when an electric current flows through its coil. Its strength can be changed by adjusting the current, and its magnetism disappears completely when the current is switched off.
4. How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased?
The strength of an electromagnet can be increased in three primary ways:
- Increasing the current: A higher electric current flowing through the coil produces a stronger magnetic field.
- Increasing the number of turns: The more times the wire is wrapped around the core, the more concentrated and powerful the magnetic field becomes.
- Using a soft iron core: Inserting a core made of a ferromagnetic material like soft iron inside the coil significantly enhances the magnetic field strength.
5. What are some real-world applications of electromagnets?
Electromagnets are essential components in many everyday devices and industrial machines. Some common applications include:
- Electric Bells and Buzzers: An electromagnet pulls a striker to hit the bell, which breaks the circuit, and the process repeats rapidly.
- Scrapyard Cranes: Large, powerful electromagnets are used to lift and move heavy iron and steel objects.
- Motors and Generators: They use the interaction between magnets and electric currents to create motion or generate electricity.
- MRI Machines: Superconducting electromagnets create strong magnetic fields used for medical imaging.
- Speakers and Headphones: An electromagnet causes a diaphragm to vibrate, creating sound waves.
6. Why is a soft iron core used in an electromagnet instead of steel?
A soft iron core is preferred because it has high magnetic permeability and low retentivity. This means it can be easily and strongly magnetised when the current is on, but it loses its magnetism almost instantly when the current is turned off. Steel, in contrast, has high retentivity and would remain magnetised, turning it into a permanent magnet. This would defeat the purpose of an electromagnet, whose key advantage is the ability to be switched on and off.
7. What happens to the magnetic field of an electromagnet if the direction of the current is reversed?
If the direction of the electric current flowing through the coil of an electromagnet is reversed, the polarity of the magnetic field also reverses. This means the end that was the North pole will become the South pole, and the end that was the South pole will become the North pole. This principle of reversing polarity is fundamental to the operation of electric motors.









