




Overview: Sneak Peek into the Topic
You've probably experienced the warming heat transfer if you've ever stood close to a campfire or in front of a fireplace. Your body also gets warm on the side closest to the fire, but the opposite side is untouched by the heat. Even though the air surrounds you, it is not responsible for this heat transmission. The same principles apply to heat lamps used to keep meals warm.
Radiation is the electromagnetic transmission of heat energy from the sun. The heat coming from the sun to earth is because of these radiations too. Let’s learn more about solar radiation and energy emission from the sun in depth.
The Heat in Solar Radiation is Mainly Due to?
Solar radiation is a broad word for the electromagnetic energy that the sun emits. It is also sometimes called the solar resource or just sunshine. The heat in solar radiation is mainly due to infrared radiation (infrared radiation is waves that have longer wavelengths than visible light). These infrared radiations present in solar radiations give us a warm feeling.
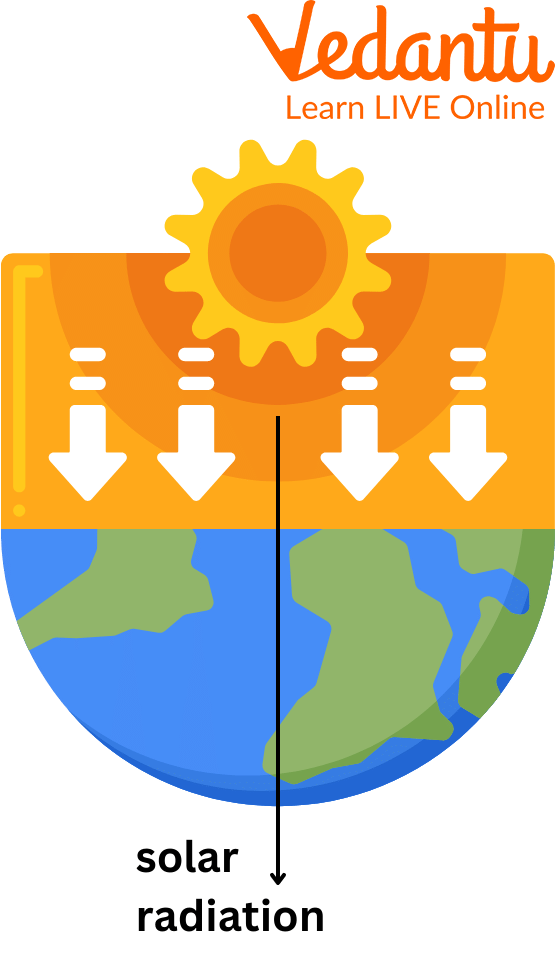
Solar Radiation
Energy in the form of Waves
The primary source of energy and heat is our sun. It generates solar energy or fuel for the weather and environmental processes. The term "solar radiation" refers to the sun's energy. Isolation is the term for the incoming radiation to the earth, which travels there as short waves.
Magnetic and electric field vibrations transfer energy in electromagnetic waves. Heat energy reaches the earth in the form of electromagnetic waves. Since there is no medium in space for the waves to travel, these waves reach the earth by radiation (it is the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic radiation).
How Does Energy Come From the Sun?
There is a reason why Earth is the only known location in the Solar System where life may exist and flourish.
The fact that the Earth is located in the Habitable Zone of our Sun, often known as the "Goldilocks Zone," is one of the causes. The sun, like all stars, is essentially a big nuclear fusion reaction, hence it has the power to produce energy. According to the Nebula Theory, scientists think this started when a massive cloud of gas and particles, or nebula, fell under the weight of its gravity.
This led to the formation of the large ball of light in the centre of our solar system as well as the beginning of a process when hydrogen that had gathered in the centre started to fuse to produce solar energy. The energy generated by the sun reaches earth in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Solar Panel
Facts About Solar Energy
Some interesting facts about solar energy are as follows:
The world's most accessible energy source is solar electricity.
The most rapidly expanding source of energy is solar electricity.
There is no pollution produced while generating solar energy.
It is the fastest source of energy to deploy.
Solar energy users save up to 35 tons of carbon dioxide and 75 million barrels of oil each year.
Plants and animals have been using solar energy since the beginning of time.
200 homes can be powered by 1MW of solar energy.
Summary
From the article, how does the sun warm the earth, we have learnt about the heat coming from the sun and about solar radiation, which is a broad word for the electromagnetic radiation that the sun emits. It is also sometimes referred to as the solar resource or just sunshine. A variety of devices can be used to catch solar radiation and transform it into useful forms of energy, such as heat and electricity.
Solar power is the key future production technology in the shift to clean energy, and as prices decline due to economies of scale, its significance will only grow. The fact that it is a clean, renewable source of electricity is its greatest benefit. Solar energy can be expanded.
FAQs on How Does the Sun Warm the Earth?
1. How does the sun warm the Earth?
The Sun warms the Earth primarily through a process called radiation. The Sun releases a vast amount of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, including visible light and infrared radiation (heat). These waves travel through the vacuum of space and, upon reaching Earth, are absorbed by the atmosphere, land, and oceans, causing their molecules to vibrate faster and generate heat.
2. What is solar radiation?
Solar radiation is the energy emitted by the Sun that travels outward in all directions. It is a mixture of different types of electromagnetic waves. The main components of solar radiation that reach Earth are:
- Visible Light: The light that we can see with our eyes.
- Infrared Radiation: This is felt as heat and is the primary component that warms the Earth.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: This is mostly absorbed by the Earth's ozone layer.
3. Why does the sun's heat warm the Earth but not the vast emptiness of space?
This is a great question that highlights how radiation works. Space is mostly a vacuum, meaning it has very few atoms or molecules. The Sun's energy waves travel through space without having much to interact with. However, when these waves hit the Earth, they strike the dense collection of particles in our atmosphere, oceans, and land. These particles absorb the energy, get excited, and heat up. So, it's not the space that gets hot, but the objects within it that absorb the radiation.
4. Does the sun heat the Earth through conduction or convection?
The primary method the Sun uses to transfer heat to Earth is radiation. Conduction (heat transfer by direct contact) and convection (heat transfer through the movement of fluids) require a medium or particles to travel through. Since the vast distance between the Sun and Earth is a vacuum, radiation is the only process that can effectively transfer heat across space.
5. What happens to the sun's energy when it reaches Earth's atmosphere?
When solar energy reaches Earth's atmosphere, it doesn't all reach the ground. Three main things happen:
- Reflection: About 30% of the energy is reflected back into space by clouds, ice, and the atmosphere.
- Absorption: About 20% is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere, such as ozone, which warms the upper atmospheric layers.
- Transmission: The remaining 50% passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface (land and water), which is the main source of surface warming.
6. What is the importance of the sun's energy for life on Earth?
The sun's energy is crucial for almost all life on Earth. Its importance extends far beyond just providing warmth. It drives key processes such as:
- Photosynthesis: Plants use sunlight to create their own food, which forms the base of most food chains.
- The Water Cycle: The sun's heat evaporates water from oceans and lakes, leading to cloud formation and rain, which is essential for fresh water.
- Climate and Weather: The uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun creates wind and ocean currents, which define our climate and weather patterns.
- Vision: Visible light from the sun allows humans and animals to see.
7. If the sun heats the ground by radiation, why does the air feel warm on a sunny day?
This happens in a two-step process. First, the sun's radiation passes through the air and directly heats the solid ground and water. Then, the warmed ground heats the layer of air that is in direct contact with it through a process called conduction. As this layer of air becomes warm and less dense, it rises, and cooler, denser air sinks to take its place. This movement creates convection currents, which distribute the heat throughout the lower atmosphere, making the air we feel warm.









