




How Are Gamma Rays Used in Everyday Life and Healthcare?
Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves with a very high frequency; they are the most energetic form of electromagnetic waves. In the early 1900s, scientists discovered gamma rays and their properties. Gamma radiation is emitted from radioactive substances when they undergo nuclear decay or nuclear fission.

Gamma Rays
This radiation can be harmful to live organisms. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation, like light and X-rays. They come from radioactive substances, such as uranium and plutonium. In this article, we are going to discuss gamma rays in detail. We will learn about their various uses and much more. So, let’s read further!
Uses of Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are used in a variety of fields, but they are most commonly used in the medical field. They are used to diagnose and treat cancer patients.
These rays are produced by radioactive nuclei and can be used to treat cancer. They can also be used in the production of food and other products like silicon chips, plastics, and paints.
Gamma Rays are high-energy, short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation. They can be used to treat cancer and other diseases by killing the cells that need to be eliminated.
Gamma Rays Examples
Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. They are high in energy, like X-rays, but with even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies.
Gamma rays are produced from nuclear reactions in stars and other high-energy events such as supernovas. Gamma rays can also be produced by particle accelerators, neutron stars and pulsars, supernova explosions, and regions around black holes.
The radiation that we call "gamma" comes from the Greek letter gamma (γ).
How are Gamma Rays Used for Cancer Treatment?

Gamma Rays
The process named Gamma Knife Surgery is used to treat cancer. High beams of concentrated gamma rays are directed towards the tumour cells. When gamma rays are used in high doses, they can kill the cancer or tumour cells. They first spot the tumour cells and slow them down, ultimately killing them by damaging their DNA. The dead cells are then removed by the body.
How are Gamma Rays Used for Sterilisation?
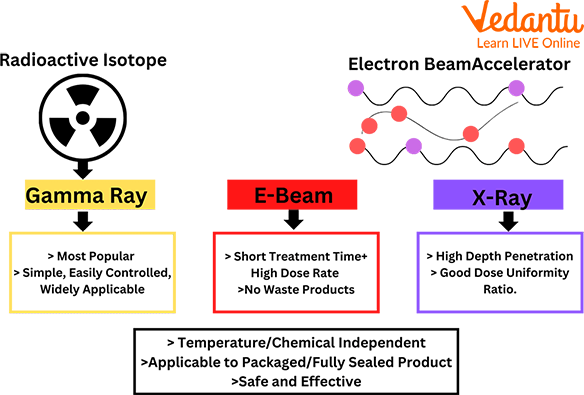
Radiation Sterilisation
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation. They have the ability to penetrate materials and destroy living cells. Gamma-ray sterilisation is used to get rid of microorganisms and other pathogens that may be present in a medical device or instrument.
Gamma rays are generated by radioactive isotopes like cobalt-60, cesium-137, and iridium-192. These isotopes are sealed in a container which is then placed inside a lead shield. The radiation passes through the lead shield to reach the object which needs sterilisation.
Gamma Rays Uses in Medicine
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation and are used in medicine to treat cancer. These rays have the ability to penetrate deep into the human body, which makes them great for targeting specific tumours.
Gamma rays are also used in medical imaging, such as Computed Tomography (CT). This is a process that is performed by doctors to get an accurate view of a patient's brain or another part of the body. Doctors use CT scans to diagnose many diseases and conditions. Gamma rays are a form of radiation that can be emitted by radioactive substances such as uranium, plutonium and cobalt. They can also be produced artificially from radioactive isotopes.
Gamma Rays Uses in Everyday Life
Gamma rays are an important part of modern life. They are used to provide a safe environment for people and the environment.
Gamma rays have many uses in everyday life. We use them to find out if food is safe, scan our bodies, see what is happening inside volcanoes, and they are even used to find out if there are any cracks in buildings and bridges. Gamma rays are the most powerful form of electromagnetic radiation. They are emitted from radioactive materials and nuclear reactions. Gamma rays are used in everyday life for medical imaging, sterilisation, and food processing.
Summary
In this article, we learnt that gamma ray is a type of radiation that is made up of high-energy photons. Gamma rays are produced by radioactive materials and can be used to scan for cancerous tumours. We also learnt that gamma Rays were first discovered by Paul Villard when he was investigating radiation from radium. These rays have shorter wavelengths than X-rays ranging between 1 and 10 nanometers. We also discussed uses of gamma rays in various medical fields. Apart from the medical arena, gamma rays are used to scan structures and examine them like buildings, bridges and even volcanoes.
FAQs on Uses of Gamma Rays: Applications & Benefits
1. What are the main applications of gamma rays across different fields?
Gamma rays have several important applications due to their high energy and penetrating power. The primary uses include:
Medicine: Used in a procedure called Gamma Knife radiosurgery to treat brain tumours by focusing beams to destroy cancerous cells. They are also used to sterilise medical equipment because they can kill pathogens without high heat.
Industry: Utilised for industrial radiography to inspect metal castings and welds for flaws. They are also used for food irradiation to kill bacteria and prolong shelf life.
Scientific Research: In astronomy, gamma-ray telescopes study high-energy phenomena in the universe like supernovae and black holes.
2. What makes gamma rays unique within the electromagnetic spectrum?
Gamma rays are unique because they have the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency of all waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. This means they carry the most energy. Unlike other forms of radiation, they are typically produced by subatomic particle interactions such as radioactive decay, nuclear fission, or nuclear fusion, originating from the nucleus of an atom.
3. How dangerous are gamma rays to living organisms?
Gamma rays are extremely dangerous to living organisms because they are a form of ionizing radiation. Their high energy allows them to penetrate deep into tissues and damage cells by breaking down chemical bonds and creating free radicals. This can destroy or mutate a cell's DNA, leading to severe health effects like radiation sickness, cancer, and genetic damage.
4. How can a person be shielded from gamma radiation?
Due to their high penetrating power, shielding from gamma rays requires very dense materials. The most common and effective shielding materials are thick layers of lead or high-density concrete. The principle of protection involves increasing the distance from the source, limiting the time of exposure, and using appropriate shielding to absorb the energy of the rays.
5. Why are gamma rays so effective for sterilizing medical equipment and food?
Gamma rays are effective for sterilization because their high energy can penetrate packaging and the product itself to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and moulds by destroying their DNA and cellular structure. This process, known as irradiation, is a form of 'cold sterilization' because it does not use high heat, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials like plastics and certain foods.
6. How do the medical uses of gamma rays differ from X-rays?
While both are high-energy forms of radiation, their medical uses differ based on their energy levels and origin. X-rays have lower energy and are primarily used for diagnostic imaging, as they are absorbed differently by tissues like bone and muscle. Gamma rays, with their higher energy, are primarily used for therapeutic purposes, such as in radiotherapy, where their ability to destroy cells is harnessed to target and eliminate cancer tumours.
7. Are the gamma rays discussed in physics the same as gamma waves produced by the brain?
No, they are completely different concepts. Gamma rays are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. In contrast, gamma brain waves are high-frequency electrical patterns (oscillations) generated by neurons in the brain, associated with cognitive functions like focus, memory, and perception. They are related to neuroscience, not nuclear physics.
8. What are the natural sources of gamma rays in the universe?
Gamma rays are produced naturally by some of the most energetic events in the universe. Key natural sources include:
Radioactive Decay: The natural decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and soil on Earth.
Lightning: Terrestrial gamma-ray flashes can be produced during thunderstorms.
Cosmic Events: Events like supernovae (exploding stars), neutron stars, pulsars, and regions around black holes are significant sources of cosmic gamma rays.









