




What is Networking?
It feels like there are networks everywhere, isn’t it? There isn't much you can do with data that doesn't include a network. Computer networks enable us to exchange information and resources, much like the human networks of which we are all a part.
Networks not only help businesses and individuals save money, but they also assist generate revenue. A computer network is a collection of computers that are spread out geographically yet are linked together to allow for the meaningful transmission and exchange of data.
Purpose of Networking
Networking allows us to get the knowledge we require to advance our profession or business and share our activities and interests with others. Additionally, networking is becoming more and more vital for achieving both personal and professional goals. For instance, our personal network consists of our friends, family, and acquaintances.
One of our most valuable sources of information for networking is provided by today's information technology.
A computer network is made up of a number of connected computers, printers, and other devices that can interact with one another. An illustration of a network at a school might be a LAN, or local area network, which links computers together.
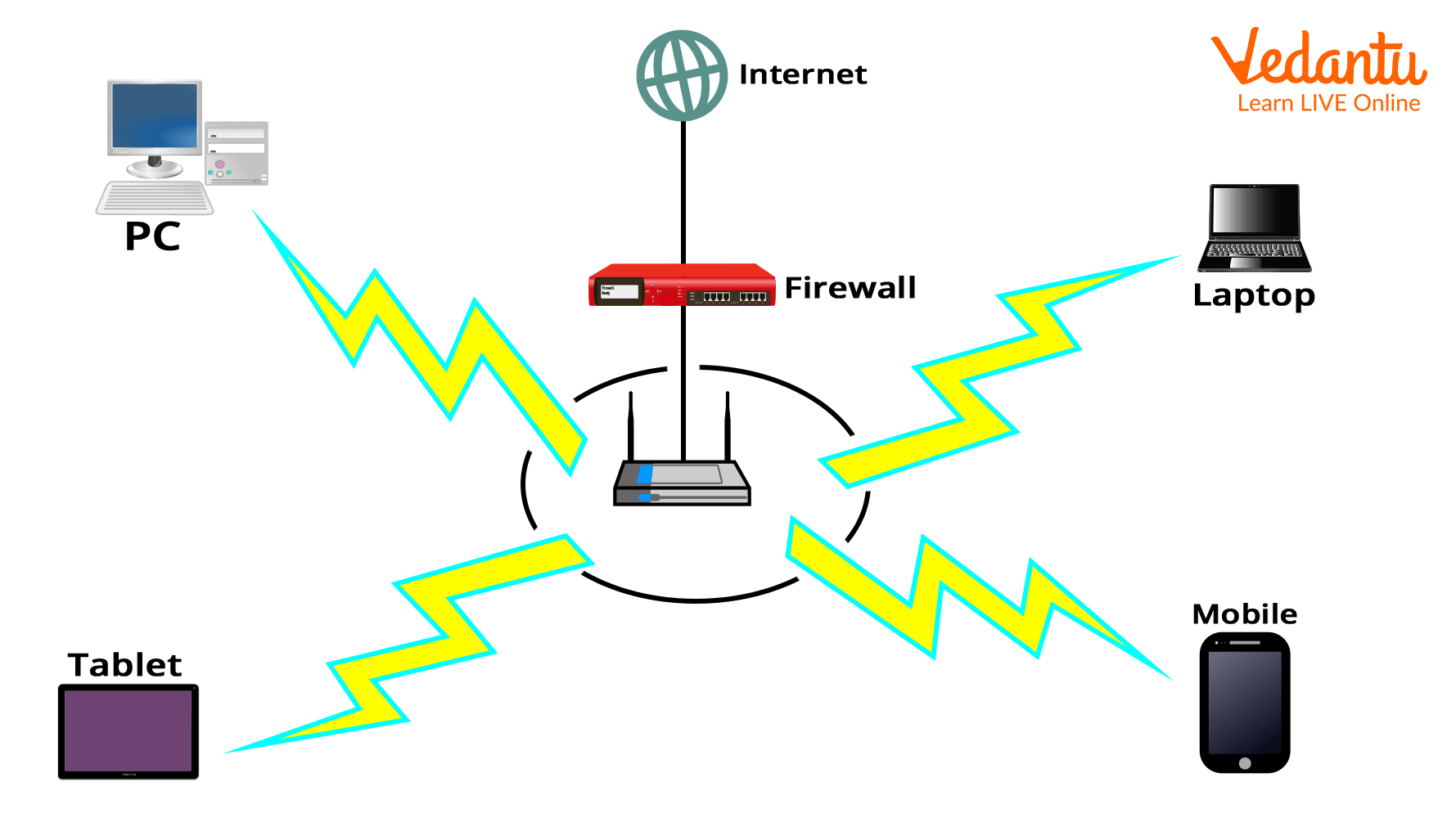
Computer Network
Type of Networks
A computer network is a collection of connected computers that allows one computer to talk with another and share resources, data, and software. The size of a computer network can be used to classify it. Most computer networks consist of 3 type:
LAN (Local Area Network)
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
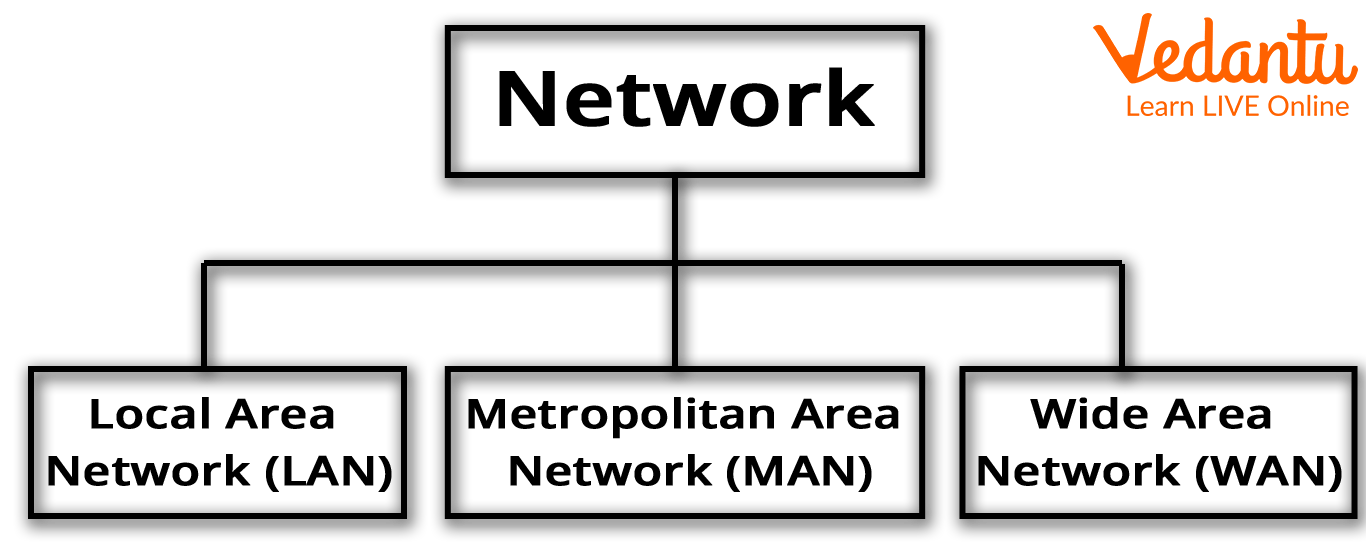
Types of Network
LAN (Local Area Network)
A local area network (LAN) is used to connect two or more personal computers using a communication means like coaxial cable or twisted pair.
It is less expensive since hubs, network adapters, and ethernet cables were used in its construction.
In a local area network, data is exchanged at an incredibly quick rate.
Greater security is provided by local area networks.
Advantages
It allows sharing of software and hardware resources.
Network loss might not affect a single workstation.
System and component evolution is conceivable.
Support for hardware and software in diverse forms.
Access to other LANs and WANs
Private possession.
Secure transfers performed at rapid speeds and with little mistake.
Disadvantages
Equipment and assistance might be expensive.
Hardware may not function together in some cases.
Power: A reliable LAN must always be running.
A network frequently uses a single internet connection, which might slow down individual computers if they are all running at once.
Limited area is covered.
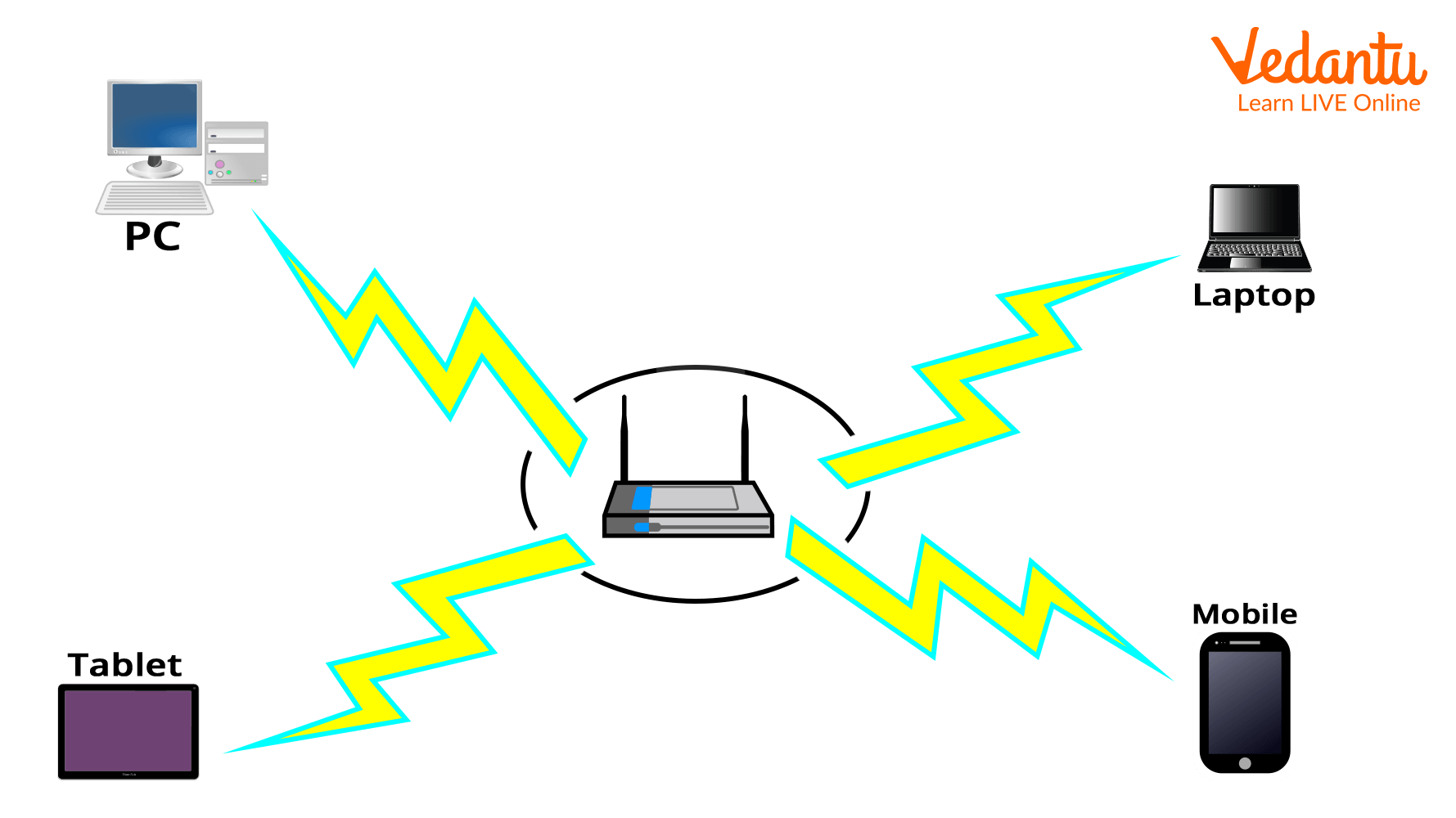

LAN
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A wide area network is a communication system. Simply said, a wide area network is a network of networks or a LAN of LANs. WAN links LANs that may be on different sides of a building, on different continents, or even on different planets.
WANs are distinguished by the longest distances and the slowest data transmission speeds. Computers linked to WANs frequently connect over open networks, such as the telephone network.
The Internet is the current biggest WAN.
Benefits of WAN
Long-distance or rural firms may join on one network, which covers a very big geographic region.
WAN has an extremely fast speed.
Drawbacks of WAN
The cost of the network increases with network size.
The price of technology and equipment is quite high.
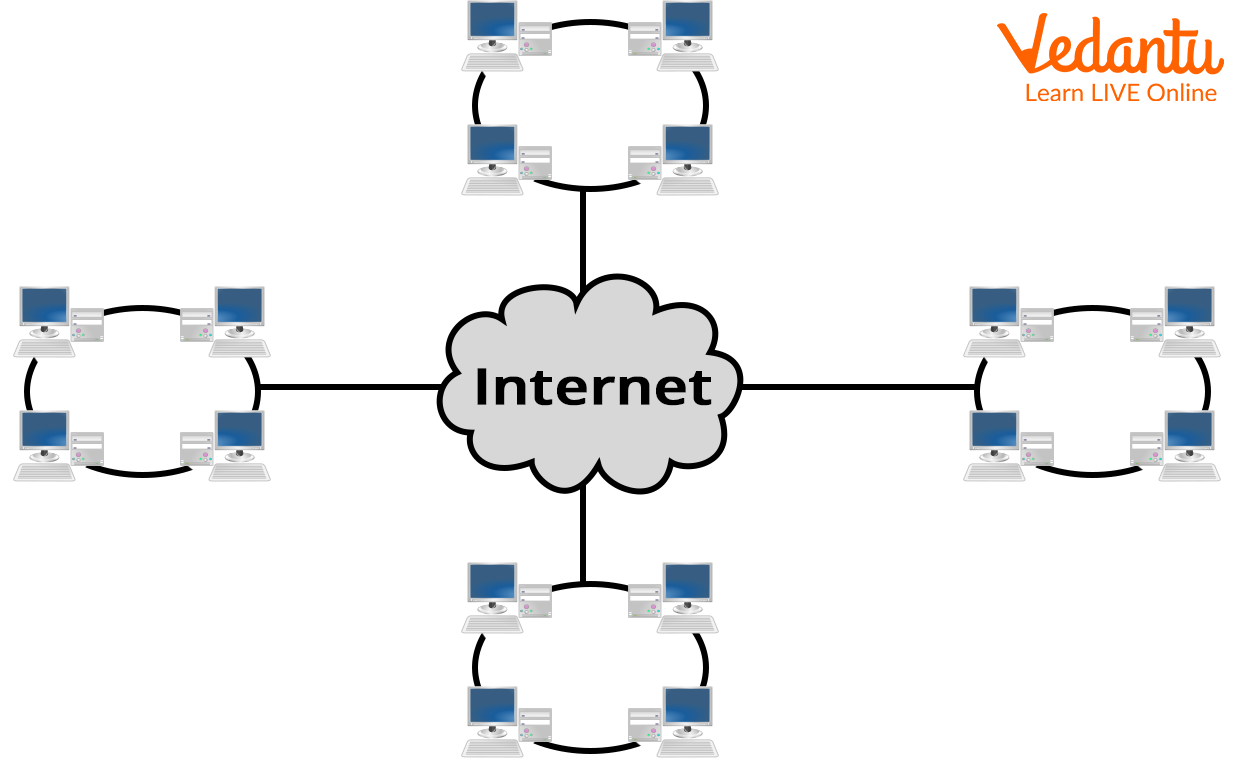
WAN
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
MAN is a data network created for a city or residence. MAN’s networks cover a wider geographic region than LANs but less than WANs in terms of geographic breadth. MAN's are typically distinguished by their extremely fast connections across cable or digital media.
Benefits of MAN
It offers more security than WAN.
Greater than LAN in size
It facilitates the economical sharing of shared resources like printers and other things.
It facilitates the quick LAN interfacing of users. This is because links are simple to implement.
Drawbacks of MAN
For a MAN connection from one location to another, more cable is needed.
When compared to LAN, the data rate is minimal.
Making a system secure against hackers is challenging.
Managing the extensive network is challenging.
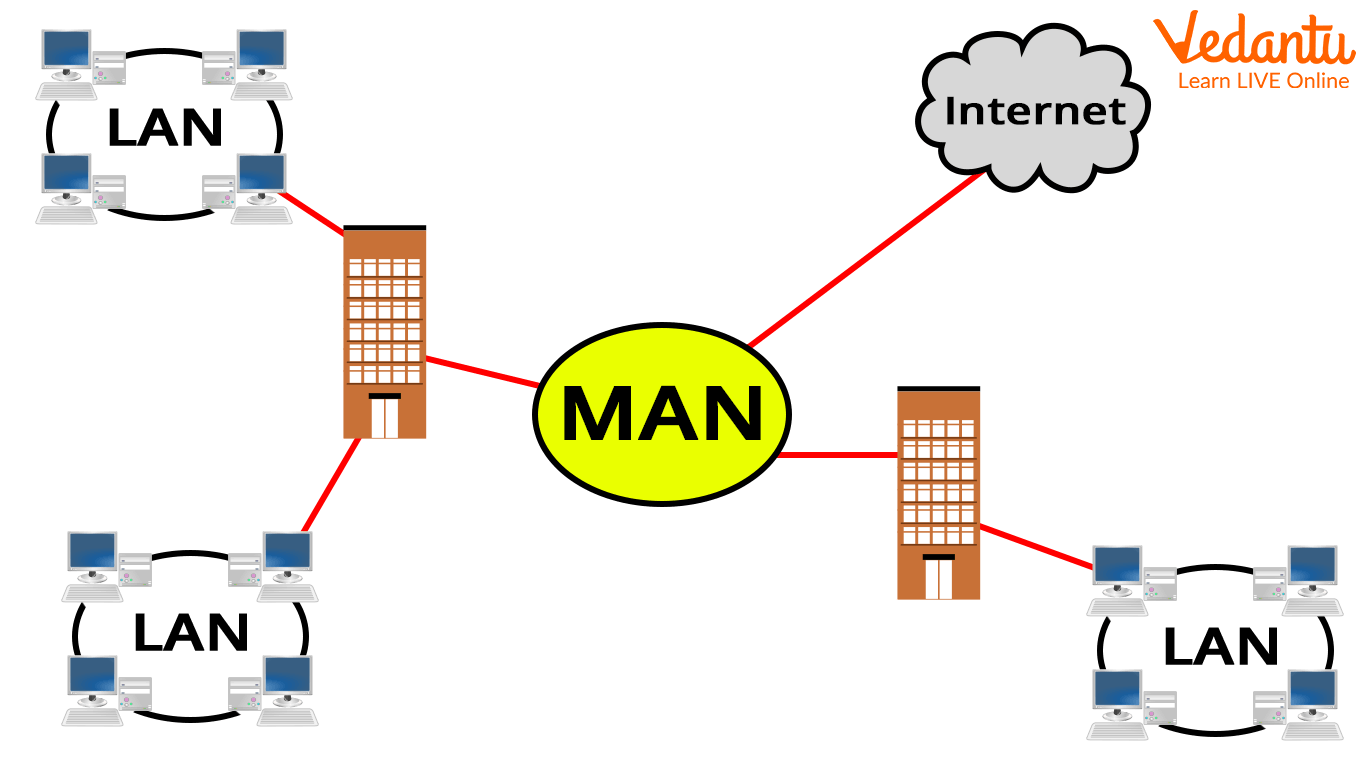
MAN
Points to Remember
Tracking files and folders allows you to gather all of your key papers in one location.
Editing, keeping, and sharing your work all depend on saving a file.
Since a lot of data builds up on your hard disc over time, removing outdated files helps make room for more items you might desire.
The Recycle Bin serves as a "holding area" for objects that have been removed, such files and folders.
Learning by Doing
Local area networks (LAN) are more expensive. (True/False)
_______ is the current biggest WAN. (Fill in the blank).
Sample Questions
1. What is the LAN acronym?
Local Area Network
Local Access Network
Line And Networking
Line-less Networking
Ans: Correct Choice- (A)
Two or more personal computers can be connected through a local area network (LAN).
2. MAN networks cover a larger geographic region than LAN, spanning whole cities to single-story building blocks.
True
False
Ans: Correct Option:(A)
A MAN is more suited than a LAN for covering greater geographic areas, such as entire cities or several building blocks. Its geographic range is in the middle between a WAN and a LAN. MANs link LANs to larger networks, such as the Internet.
Summary
In this chapter, you were introduced to the concept of networking, purpose and types of networking. A computer network is a collection of computers that are spread out geographically yet are linked together to allow for the meaningful transmission and exchange of data. Computer networks enable us to exchange information and resources, much like the human networks of which we are all a part.
FAQs on Networking
1. What is meant by computer networking?
A computer network is a collection of two or more interconnected computers and other hardware devices, linked together to enable the sharing of resources and information. The primary purpose of networking is to facilitate communication and allow for the seamless exchange of data, such as files, and shared use of devices like printers and servers.
2. What are the four main types of computer networks based on their geographical scope?
Computer networks are primarily classified based on the geographical area they cover. The four main types are:
- PAN (Personal Area Network): Covers a very small area, typically for connecting personal devices like a laptop, smartphone, and wireless headphones.
- LAN (Local Area Network): Connects devices within a limited area such as a school, office building, or home. It offers high-speed data transfer.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Spans a larger area than a LAN, such as an entire city or a large campus. It often interconnects several LANs.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): Extends over a large geographical area, like a country or a continent. The internet is the largest example of a WAN.
3. What is the difference between a 'network' and 'networking'?
While often used interchangeably, a 'network' and 'networking' refer to different concepts. A network refers to the physical infrastructure itself—the collection of computers, cables, routers, switches, and other hardware. In contrast, networking is the active process of designing, implementing, managing, and using that network to establish communication and share resources.
4. How do a hub, switch, and router differ in their roles within a network?
These are fundamental networking devices with distinct functions:
- A Hub is a basic device that operates at the physical layer. When it receives a data packet, it broadcasts it to every connected device, which can cause unnecessary traffic.
- A Switch is smarter than a hub and operates at the data link layer. It learns the MAC addresses of connected devices and forwards data packets only to the specific device they are intended for, improving efficiency and reducing congestion.
- A Router is the most intelligent of the three, operating at the network layer. Its main job is to connect different networks together (e.g., your home LAN to the internet WAN) and direct traffic between them using IP addresses.
5. Can you explain the importance of a network topology with an example?
A network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of nodes and connections in a network. It's important because it affects the network's performance, stability, and cost. For example, in a Star Topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. The main advantage is that if one cable fails, only that one device is disconnected. However, if the central switch fails, the entire network goes down.
6. What are the key advantages of using a computer network in a school or office?
Implementing a computer network offers several significant benefits for an organisation:
- Resource Sharing: Allows multiple users to share expensive hardware like printers, scanners, and servers, reducing costs.
- Centralised Data Storage: Files can be stored on a central server, making them easier to manage, back up, and access for all authorised users.
- Improved Communication: Facilitates quick and efficient communication through tools like email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Enables teams to work on the same documents and projects simultaneously, improving productivity.
7. Why is a layered protocol architecture, like the TCP/IP model, important for network communication?
A layered architecture like the TCP/IP model is crucial because it breaks down the complex process of network communication into smaller, manageable, and standardised parts called layers. This approach provides several key benefits: it promotes interoperability between different vendors' hardware and software, simplifies troubleshooting by isolating problems to a specific layer, and allows for easier development and modification of network functionalities without affecting the entire system.
8. Provide a real-world example of how LAN, MAN, and WAN work together.
Imagine a large bank. Each branch office operates its own Local Area Network (LAN) to connect computers, printers, and servers within that single building. To connect all the branches across a single city, the bank uses a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). Finally, to connect its offices nationwide and internationally, and to link to the global financial system, the bank uses a Wide Area Network (WAN), which is essentially the internet, to tie all its MANs and LANs together.











