




What is Surfing on a Computer?
Surfing the World Wide Web is the act of moving aimlessly from one Web website to another. It is the act of looking up information on the World Wide Web. When browsing, a user normally chooses which pages to view based on what interests them at the time. In this article, we will discuss World Wide Web surfing in detail.
World Wide Web Surfing
With the introduction of the World Wide Web, surfing became a popular pastime. With the use of hypertext links, users may navigate between different sections of a document and between various documents, even those housed on different websites. Millions of individuals who have access to the Internet across the world enjoy surfing as a hobby. Many people are addicted to it and spend countless hours engaging in Internet browsing or other activities. Some do it to pass the time.
World Wide Web Surfing
How to Surf the Internet?
The term "Internet surfing" refers to navigating from one web page to another while looking up relevant information.
Internet browsing often entails:
Launching a web browser.
Browsers are computer applications that let you switch between pages on the Internet.
Put the URL of a website in the browser's address or location field.
Recognising and employing standard browser toolbar buttons, such as Back, Forward, and Home.
Getting around on or between websites.

Launching Web browser
The Advantages of Internet Surfing
This generation's everyday routine now includes Internet browsing. We can do many things on the Internet, such as clothing shopping, chatting with others, and finding out information. We frequently turn to the Internet to find solutions to issues.
The majority of individuals enjoy shopping for clothing online the most. We may pick from a wide variety of clothing by looking through websites.
There are many different types of buddies we may find online. We may meet people from other countries through the Internet and learn about their experiences, cultures, jobs, and other things.
The Internet offers a wealth of knowledge. Without the Internet, we would need to spend much time looking up information.
Functioning of Buttons on Internet Explorer
Each button on the toolbar has a distinct function and application.
Back
Navigate to the website's previous page.
Forward
Navigates to the website's next page.
Stop
It stops the web page from loading.
Refresh
Initiates the reopening of a Web page. You may access a website's home page by clicking on it.
Search
Facilitates information search.
Favourites
Enables you to "bookmark" your preferred Web pages in a specific folder.
History
Displays a list of recently viewed pages.
Mail
Displays a drop-down menu with several email sending and receiving options.
Print
It prints the page you are now reading.
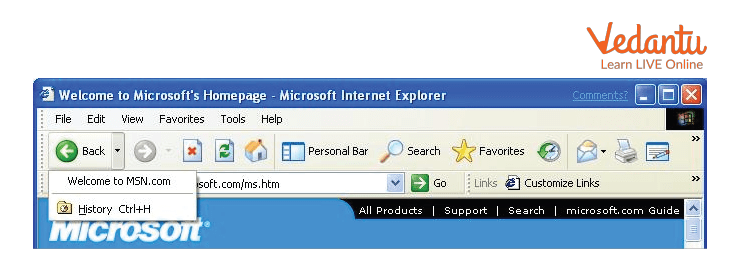
Buttons on IE
Sample Questions
1. What distinguishes the Internet from the World Wide Web?
Ans: The sites you see when online on a device are known as the world wide web, or simply the web. However, the Internet is the collection of interconnected computers that powers the Internet and facilitates the transfer of information and emails. Consider the Internet as the highway that links cities and towns.
2. How is the Internet connection to the World Wide Web?
Ans: To connect to the Internet, you must have an Internet service provider (ISP) to connect to the Internet. You must pay the ISP a fee in exchange for them allowing your device to connect to the Internet through their network.
Learning by Doing
1. When your computer is permanently linked to the Internet, which of the following should you do first to start the Internet?
Start-> Programs-internet Explorer
Start -> Internet Explorer-> Programs
Internet Explorer-> Start->Programs
Internet Explorer-> Programs-> Start
None of these
Ans: Correct Choice is (A) When your computer is permanently linked to the Internet, the proper order to launch the Internet is Programs -> Internet Explorer under Start
2. You must first _________ if your computer is not always connected to the Internet.
Give your username.
Dial up a connection to the computer of your access provider.
Give your password.
None of these.
All of these.
Ans: Correct Choice is (B) You must dial up a connection to the computer of your access provider if your computer is not always linked to the Internet.
Summary
A system for creating wireless, wired, and cable connections between any two computers anywhere in the world is the Internet, also referred to as "the net." If your computer is not always online, you must dial up a connection to your access provider's computer.
The Internet evolved from the Cold War to the Facebook era. We can download movies, music, videos, games, photographs, and files from the internet.
FAQs on World Wide Web Surfing
1. What is meant by surfing the World Wide Web?
Surfing the World Wide Web means navigating from one webpage to another using a web browser. It is the process of exploring information online by clicking on hyperlinks, which take you to different pages or websites based on your interests.
2. What is the difference between the Internet and the World Wide Web?
The Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW) are related but not the same. The Internet is the global network of computers that allows digital information to be shared. The World Wide Web is the collection of websites and pages that you can access using the Internet. Think of the Internet as the road network and the Web as the houses and shops along those roads.
3. What do you need to start surfing the World Wide Web?
To surf the World Wide Web, you need three essential things:
- A computing device like a computer, tablet, or smartphone.
- An active Internet connection provided by an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- A web browser software application, such as Chrome, Firefox, or Edge, installed on your device.
4. Can you give some examples of web surfing?
Web surfing includes a wide variety of online activities. Common examples are:
- Reading news articles on a news website.
- Watching videos on platforms like YouTube.
- Shopping for products on an e-commerce site.
- Using a search engine like Google to find information for homework.
- Connecting with friends on social media platforms.
5. What are the functions of common buttons in a web browser like 'Back', 'Forward', and 'Refresh'?
Most web browsers have standard navigation buttons that help you surf the web. Key functions include:
- Back: Takes you to the previous webpage you visited.
- Forward: Takes you to the webpage you were on before you clicked 'Back'.
- Refresh/Reload: Loads the current webpage again to show the most up-to-date content.
- Home: Takes you to the browser's designated start page.
- Stop: Halts the loading of a webpage.
6. How does a web browser actually show you a webpage after you enter an address?
When you type a web address (URL) into a browser, it sends a request over the Internet to a specific computer called a web server where the website's files are stored. The server then sends these files (like HTML for structure, CSS for style, and images) back to your browser. Your browser reads these files and arranges the content to display the complete, interactive webpage on your screen.
7. What is the role of HTTP in the World Wide Web?
HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is the set of rules used for transferring files (like text, images, and videos) on the World Wide Web. When your browser requests a webpage, it uses HTTP to communicate with the web server. It is the fundamental protocol that enables you to 'surf' from one page to another by clicking hyperlinks.
8. Who invented the World Wide Web and why is it so important?
The World Wide Web was invented by Sir Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 while he was working at CERN. Its invention is incredibly important because it created a user-friendly way for people to share and access information globally. Before the Web, using the Internet was much more complicated. The WWW made the Internet accessible to everyone, not just technical experts, leading to the information age we live in today.
9. Is the World Wide Web controlled by a single company or organization?
No, the World Wide Web is not controlled by any single company, government, or organization. It is a decentralised system. While organisations like the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), co-founded by Tim Berners-Lee, develop standards and guidelines to ensure the web works uniformly for everyone, they do not own or control the content on it.











