Water Class 7 important questions with answers PDF download
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 7 Social Science Our Environment Water - 2025-26
1. What types of short-answer questions are typically asked from the CBSE Class 7 'Water' chapter?
From the 'Water' chapter, you can expect short-answer questions, usually for 1 or 2 marks, that test your knowledge of key definitions. Be ready to define terms like precipitation, tides, ocean currents, and the water cycle. Questions might also ask you to list the factors that affect the height of waves.
2. How should I structure an answer explaining the three main types of ocean movements for a 5-mark question?
To score full marks on a 5-mark question about ocean movements, follow this structure:
- Begin with a brief introduction stating the three movements: waves, tides, and currents.
- Use a separate short paragraph to explain each one.
- For waves, describe them as the rise and fall of water on the surface, mainly caused by wind.
- For tides, explain them as the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water due to the gravitational pull of the sun and moon. Mention high and low tides.
- For currents, define them as streams of water flowing in specific paths, and mention they can be warm or cold.
3. What is the difference between warm and cold ocean currents? Why is this concept important for exams?
The key difference is their point of origin. Warm currents start near the equator and flow towards the poles (e.g., the Gulf Stream), while cold currents start near the poles and flow towards the equator (e.g., the Labrador Current). This topic is important for exams because ocean currents have a major impact on the climate and temperature of nearby land areas, which is often a basis for reasoning-based questions.
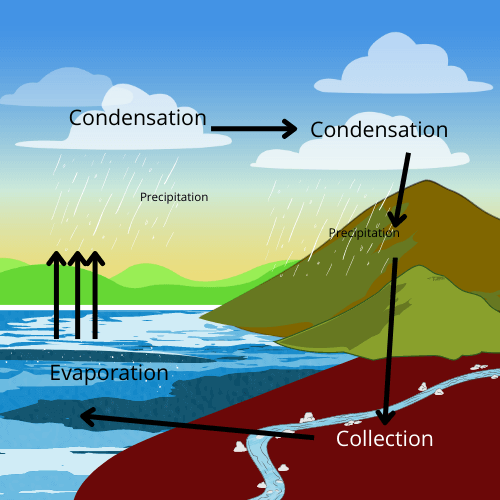
4. What is the best way to answer a question on the water cycle to score full marks?
To ensure you get full marks, explain the water cycle step-by-step using the correct scientific terms. You must include and briefly explain evaporation (water turns to vapour), condensation (vapour forms clouds), and precipitation (water falls back to Earth). For a 3 or 5-mark question, drawing a simple, labelled diagram of the cycle is an excellent way to impress the examiner.
5. Are Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) expected from Chapter 5, Water?
Yes, you can expect MCQs from this chapter in your Social Science exam. These questions usually check your understanding of basic facts and definitions. For instance, an MCQ could ask, "The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice a day is called a _____" with the correct answer being 'tide'.
6. Tides are caused by gravity, so what makes waves different? Why is it important to know this for an exam?
This is a crucial point of distinction. The main cause for tides is the massive gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on Earth's water. In contrast, waves are surface movements primarily caused by the friction of wind blowing across the water. Knowing this difference is important for exams because it shows a deeper understanding of the different forces that shape our oceans.
7. Why do we say 'Earth is a blue planet, but we still face water scarcity'? How could this be asked as an important question?
This statement highlights a critical fact: although about 71% of Earth is covered in water, over 97% of it is saltwater in oceans, which is unusable for drinking or farming. Only a very small amount is freshwater. In an exam, this concept could form a value-based question asking for your thoughts on the importance of conserving freshwater or suggesting ways to avoid wasting it.
8. What is the key difference between condensation and precipitation to remember for a 1-mark question?
The simplest way to remember is: Condensation is the process where water vapour cools down and turns into liquid droplets to form clouds. Precipitation is the next step, where these droplets in the clouds become heavy and fall to the Earth as rain, snow, or hail. So, condensation makes clouds, and precipitation is what falls from them.
9. How do ocean movements like tides and currents affect human life? Give two examples for a 3-mark question.
Ocean movements are vital for many human activities. For a 3-mark answer, you can provide these two examples:
- Navigation and Trade: High tides help large ships enter and leave ports safely. Ocean currents also act like sea-highways, helping ships save time and fuel.
- Fishing: Areas where warm and cold currents meet are some of the world's best fishing grounds because the mixing of water brings up rich nutrients for fish to eat.