Heat Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 7 Science Heat - 2025-26
1. What are some frequently asked 2-mark questions from the 'Heat' chapter for Class 7 Science exams?
For the CBSE Class 7 Science exam, some expected short-answer questions from Chapter 3, Heat, include:
- Defining heat and stating its SI unit.
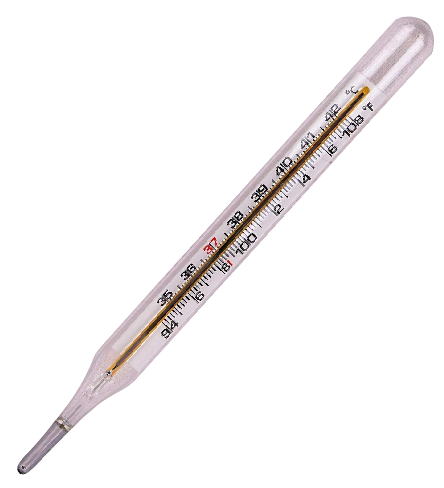
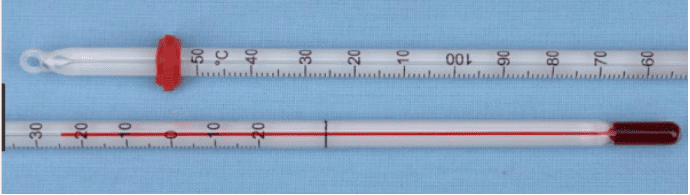
- Explaining why a clinical thermometer has a temperature range of 35°C to 42°C.
- Naming the device used to measure temperature and the liquid commonly used in it.
- Stating the normal temperature of a healthy human body on the Celsius scale.
2. How should I answer a question on the differences between a clinical and a laboratory thermometer to score full marks?
To score full marks on this important question, structure your answer in a comparative table format. Key differences to mention are:
- Temperature Range: A clinical thermometer measures from 35°C to 42°C, while a laboratory thermometer has a wider range, typically -10°C to 110°C.
- Purpose: Clinical thermometers are exclusively for measuring human body temperature, whereas laboratory thermometers are used for experiments and measuring the temperature of other objects.
- Kink/Constriction: A clinical thermometer has a kink to prevent the mercury level from falling back immediately, which is absent in a laboratory thermometer.
- Reading Method: A clinical thermometer is read after taking it out of the mouth, while a laboratory thermometer must be read while it is still in contact with the substance.
3. Which questions on the modes of heat transfer are most important for the 2025-26 exam?
For the Class 7 exams, questions on all three modes of heat transfer—conduction, convection, and radiation—are crucial. However, application-based questions are frequently asked. Focus on:
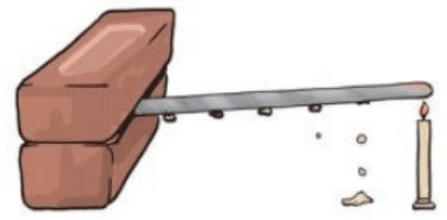
- Conduction: Defining conductors and insulators with examples (e.g., Why are pan handles made of plastic?).
- Convection: Explaining the real-world phenomena of sea breeze and land breeze is a high-yield topic.
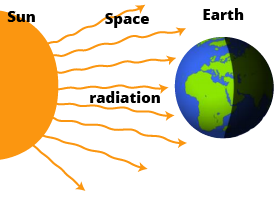
- Radiation: The reasoning behind wearing light-coloured clothes in summer and dark-coloured clothes in winter is an expected question.
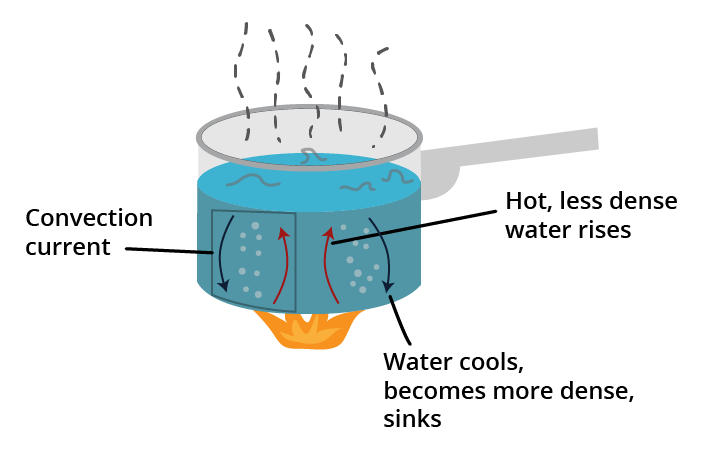
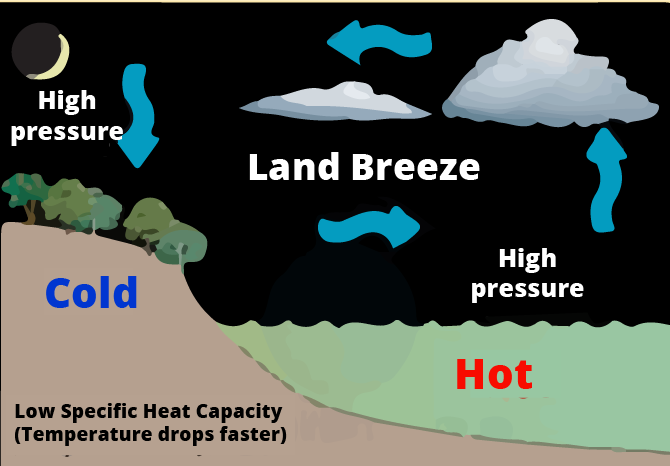
4. Why are questions about sea breeze and land breeze considered important for understanding convection?
These questions are considered important because they test your ability to apply the concept of convection to a real-world scenario. Answering them correctly shows a deeper understanding beyond just defining the term. You need to explain how the unequal heating of land and water by the sun creates a pressure difference, which in turn sets up convection currents in the air, resulting in the flow of a sea breeze during the day and a land breeze at night. This is a classic example of a HOTS (High Order Thinking Skills) question.
5. From an exam perspective, what is the scientific principle to explain why we wear light-coloured clothes in summer?
The scientific principle is based on heat radiation. For a high-scoring answer, you must state that light-coloured surfaces are poor absorbers and good reflectors of heat. During summer, wearing white or light-coloured clothes helps in reflecting most of the sun's heat, keeping our bodies cool. In contrast, dark-coloured surfaces are good absorbers of heat, which is why they are preferred in winter.
6. What kind of objective-type questions (MCQs) can be expected from the Class 7 Science Chapter on Heat?
Objective-type questions from this chapter often test specific values and concepts. Be prepared for MCQs on topics such as:
- The normal temperature of the human body (37°C).
- The material that does not allow heat to pass through it easily (an insulator).
- The mode of heat transfer that does not require any medium (radiation).
- Identifying the correct range of a clinical thermometer.
7. My textbook mentions mercury in thermometers. Why is it important to know the properties of mercury for exam questions?
Understanding the properties of mercury is crucial for answering 'Give Reason' or 'Why' type questions, which often carry higher marks. Important properties to know for your exam include:
- It is a liquid at room temperature and expands uniformly on heating.
- It is shiny and opaque, making it easy to see in a glass tube.
- It does not stick to the glass.
- It has a high boiling point and a low freezing point, allowing it to measure a wide range of temperatures.
8. How do I define and differentiate between conductors and insulators of heat for a 3-mark question?
For a 3-mark question, first provide clear definitions and then give at least two examples for each.
Conductors: These are materials that allow heat to pass through them easily. They transfer heat energy quickly.
Examples: Metals like iron, copper, and aluminium.
Insulators: These are materials that do not allow heat to pass through them easily. They are poor conductors of heat.
Examples: Materials like wood, plastic, glass, and air.