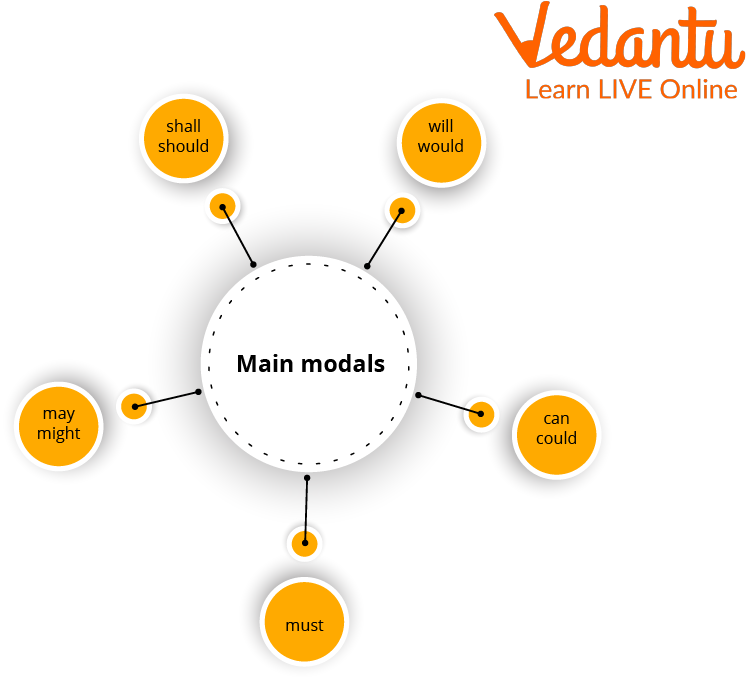
Master the Tense: Key Concepts and Practice Questions for Class 7 English Grammar 2025-26
FAQs on The Tense in English Grammar: Complete Class 7 Guide for 2025-26
1. What are the most common types of important questions on Tenses for the Class 7 English exam?
Based on the CBSE pattern for the 2025-26 session, students can expect the following types of important questions on Tenses:
- Fill in the blanks: You will be given a sentence with a blank and a verb in brackets, and you must use the correct tense of the verb.
- Sentence Conversion: You may be asked to change a sentence from one tense to another, for example, from Simple Present to Simple Past.
- Error Correction: This involves identifying and correcting the incorrect tense used in a given sentence.
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): You will need to choose the correct verb form from a list of options to complete a sentence.
2. How do you identify the specific tense used in a sentence? Provide examples.
To identify the tense, you need to look at the main verb and any auxiliary (helping) verbs. Here are some examples:
- "She is writing a letter." – The structure 'is + verb-ing' indicates the Present Continuous Tense.
- "They had finished their homework." – The structure 'had + past participle (V3)' indicates the Past Perfect Tense.
- "We will have completed the project by next Monday." – The structure 'will have + past participle (V3)' indicates the Future Perfect Tense.
- "He plays cricket every evening." – The base form of the verb with an '-s' indicates the Simple Present Tense.
3. Why is it important to distinguish between the Simple Past and Present Perfect Tense in exams?
Correctly distinguishing between the Simple Past and Present Perfect tenses is crucial as they signal different time connections, a common area for marks deduction. The key difference is:
- Simple Past Tense (e.g., "I visited Delhi in 2020") describes an action completed at a specific time in the past. The connection to the present is cut off.
- Present Perfect Tense (e.g., "I have visited Delhi") describes an action that happened at an unspecified time in the past but has relevance or impact on the present. Using one for the other changes the entire meaning.
4. How can auxiliary verbs like 'be', 'do', and 'have' change the meaning of a sentence when forming tenses?
Auxiliary verbs are essential for forming different tenses and moods. They add specific meanings that the main verb cannot convey on its own:
- 'To be' (is, am, are, was, were): Used to form the continuous tenses, showing an action in progress. For example, "He reads" (a habit) versus "He is reading" (an action happening now).
- 'To have' (has, have, had): Used to form the perfect tenses, showing that an action is completed in relation to another point in time. For instance, "I wrote the essay" (past action) versus "I have written the essay" (completed, and the essay is now ready).
- 'To do' (do, does, did): Used to form questions and negative sentences in simple tenses, like "Did he go?" or "He did not go."
5. What is a common mistake Class 7 students make when using future tenses like 'will' vs. 'be going to'?
A frequent error is using 'will' and 'be going to' interchangeably. While both refer to the future, they have different uses:
- Use 'will' for spontaneous decisions made at the moment of speaking (e.g., "I think I will have a glass of water"), for promises, or for predictions without evidence.
- Use 'be going to' for plans and intentions made before the moment of speaking (e.g., "I am going to visit my grandparents this weekend") or for predictions based on present evidence (e.g., "Look at those dark clouds. It is going to rain").
6. How do tenses help in constructing a clear narrative or story?
Tenses are the backbone of storytelling, as they establish a clear timeline for the reader. Using them correctly is important for narrative writing questions.
- Past Tense: Most stories are told in the past tense (e.g., "The princess lived in a tower"). It grounds the story in a time that has already occurred.
- Sequence of Events: Using different past tenses like Simple Past and Past Perfect helps to order events. For example, "The team celebrated because they had won the match." This clearly shows the winning happened before the celebration.
- Building Suspense: Shifting to the Present Tense can make action feel more immediate and exciting, pulling the reader into the moment.
7. For exam practice, fill in the blanks with the correct tense of the verb given in brackets.
Here are some practice questions typical for a Class 7 exam:
- After the students ____________ (complete) the assignment, the teacher collected the papers.
Answer: After the students had completed the assignment, the teacher collected the papers. - I ____________ (read) this book for three hours now.
Answer: I have been reading this book for three hours now. - By this time next year, my brother ____________ (finish) his high school education.
Answer: By this time next year, my brother will have finished his high school education.