How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce? - 2025-26



FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce? - 2025-26
1. What are the key differences between sexual and asexual reproduction that are important for the CBSE exam?
For the Class 10 board exam, it's crucial to know the main differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. Here are the key points:
- Parents Involved: Asexual reproduction involves only one parent, while sexual reproduction typically involves two parents.
- Gamete Formation: There is no formation or fusion of gametes (like sperm and egg) in asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is defined by the fusion of male and female gametes.
- Genetic Variation: Offspring from asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent (clones). Sexual reproduction leads to genetic variation in offspring because genetic material from two different parents is combined.
- Speed: Asexual reproduction is a much faster method of producing offspring compared to sexual reproduction.
2. Which topics from 'How do Organisms Reproduce?' are most frequently asked in Class 10 board exams?
Based on previous years' papers for the CBSE Class 10 Science exam, the most important topics from this chapter are:
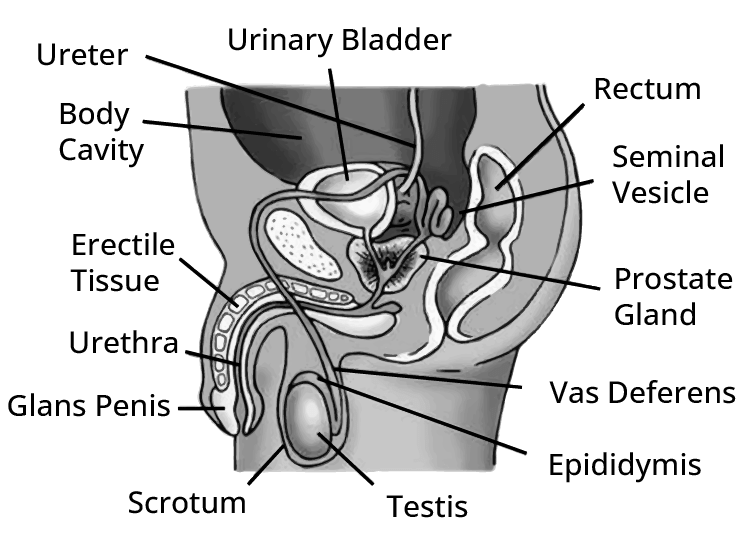
- Human Reproductive Systems: Labelled diagrams and functions of the male and female reproductive systems are frequently asked as 5-mark questions.
- Contraceptive Methods: Questions on different methods of contraception and their role in preventing pregnancy and STDs are common.
- Reproduction in Plants: Structure of a flower (diagram-based), pollination vs. fertilisation, and post-fertilisation changes are key areas.
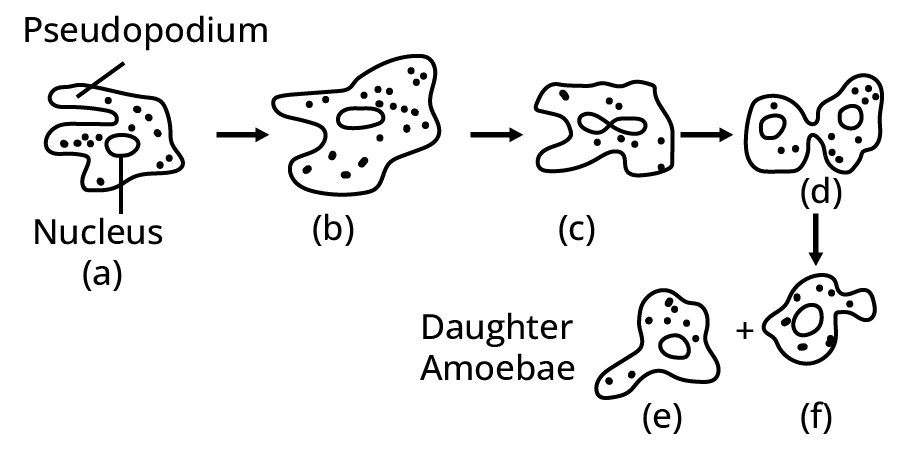
- Asexual Reproduction: Different modes like binary fission, budding, and vegetative propagation are often asked as 1 or 2-mark questions.
- Puberty and Menstrual Cycle: Changes during puberty and the process of menstruation are important for 3-mark questions.
3. Explain the process of double fertilisation in flowering plants.
Double fertilisation is a unique process in flowering plants. After the pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube grows down to the ovule. This tube carries two male gametes. Inside the ovule's embryo sac:
- Syngamy: One male gamete fuses with the female gamete (egg cell) to form the zygote, which develops into the embryo.
- Triple Fusion: The second male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei present in the centre of the embryo sac. This results in the formation of the primary endosperm nucleus (PEN), which develops into the endosperm, providing nourishment to the growing embryo.
Because two fusion events (syngamy and triple fusion) occur, this process is called double fertilisation.
4. Why is DNA copying an essential part of reproduction and what is its significance?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) copying, or replication, is the most fundamental event in reproduction. Its significance is twofold:
- Inheritance: DNA contains the genetic blueprint for an organism's body design and functions. Copying this DNA ensures that the offspring receives a complete set of genetic instructions from the parent(s), allowing for the inheritance of traits.
- Creation of Variation: While the DNA copying mechanism is remarkably accurate, it is not perfect. Small errors or changes (mutations) can occur during replication. This creates variations among individuals, which is the basis for evolution and helps a species adapt to changing environments.
5. What is the role of the placenta in the development of an embryo?
The placenta is a vital disc-like organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy, connecting the mother and the foetus. Its primary roles are:
- Nutrition: It facilitates the transfer of essential nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and minerals from the mother's blood to the foetus.
- Respiration: It allows oxygen to pass from the mother to the foetus and carbon dioxide to pass from the foetus back to the mother's bloodstream to be exhaled.
- Excretion: It helps in removing metabolic waste products, such as urea, from the foetal blood into the mother's blood for disposal.
- Endocrine Function: The placenta also produces hormones like progesterone and oestrogen that are crucial for maintaining the pregnancy.
6. Why are the testes located in the scrotum, outside the abdominal cavity?
The testes are located in the scrotum outside the main abdominal cavity because the process of spermatogenesis (sperm production) requires a temperature slightly lower than the normal body temperature. The scrotum helps maintain this optimal temperature, which is about 2-2.5°C cooler than the core body temperature, ensuring the formation of viable sperm.
7. What are the main advantages of vegetative propagation in plants?
Vegetative propagation is a preferred method for growing certain plants due to several key advantages:
- Genetic Uniformity: Plants grown through this method are genetically identical to the parent plant, ensuring desirable traits like flower colour, fruit flavour, or disease resistance are preserved.
- Faster Growth: Plants produced by vegetative propagation mature and bear fruits and flowers much earlier than those grown from seeds.
- Propagation of Seedless Varieties: It is the only way to reproduce plants that have lost the ability to produce viable seeds, such as bananas, some varieties of grapes, and roses.
- High Success Rate: This method is often more reliable and has a higher success rate than growing plants from seeds.
8. What changes occur in a flower after fertilisation?
After fertilisation, several significant changes occur in the flower as it transitions to produce a fruit and seeds:
- The ovule develops a tough coat and transforms into the seed.
- The ovary grows and ripens to become the fruit. The wall of the ovary becomes the fruit wall (pericarp).
- The zygote inside the ovule divides multiple times to form the embryo.
- The other parts of the flower, such as the petals, sepals, stamens, style, and stigma, typically wither and fall off.
9. Why can't complex multicellular organisms, like humans, reproduce through regeneration?
Complex multicellular organisms like humans cannot reproduce through regeneration because their bodies are highly specialised and organised. Regeneration of a whole individual requires the ability to regrow all different types of cells, tissues, and organs and place them in their correct positions. In complex organisms:
- Cell Differentiation: Cells are highly differentiated to perform specific functions (e.g., nerve cells, muscle cells, bone cells) and cannot easily de-differentiate and re-form a whole organism.
- Organisational Complexity: The body is not just a random collection of cells. Tissues form organs, and organs form complex systems (like the nervous or circulatory system) that must be precisely integrated. Re-creating this entire complex structure from a small fragment is not possible. Simple organisms like Planaria have less complex structures and a higher proportion of stem-like cells that allow for complete regeneration.
10. What is menstruation, and why does it occur?
Menstruation is the periodic discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. It occurs as part of the monthly menstrual cycle in human females. Every month, the uterus prepares itself to receive a fertilised egg by developing a thick, spongy lining rich in blood vessels. If fertilisation does not happen, this lining is no longer needed. Consequently, the lining breaks down and is shed from the body, resulting in menstrual bleeding. This marks the start of a new cycle.
11. Why is sexual reproduction considered advantageous over asexual reproduction for the survival of a species?
Sexual reproduction is advantageous for species survival primarily because it creates genetic variation among offspring. This variation arises from the combination of DNA from two different parents. In contrast, asexual reproduction produces genetically identical clones. This variation is crucial because:
- Adaptation to Change: If the environment changes (e.g., a new disease appears or climate shifts), individuals with favourable variations may be better equipped to survive and reproduce.
- Long-Term Survival: A genetically diverse population has a higher chance of surviving drastic environmental challenges, preventing the entire species from being wiped out. Asexual populations lack this diversity, making them more vulnerable.
12. How can using a condom help in preventing pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
A condom is a barrier method of contraception. It works by physically preventing the male gametes (sperm) from entering the female reproductive tract during sexual intercourse.
It acts as a physical barrier that not only stops sperm but also prevents direct contact with genital fluids and sores. This is how it effectively reduces the transmission of pathogens that cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like HIV-AIDS, Syphilis, and Gonorrhoea.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video