
Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 important questions with answers PDF download
Vedantu provides CBSE Class 10 Science important questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations to help students excel in their exams. This chapter covers key topics such as types of chemical reactions, balancing chemical equations, and understanding the effects of oxidation and reduction reactions. The questions are designed to test students' knowledge and ensure they grasp fundamental concepts. Download the FREE PDF for detailed answers, helping students prepare efficiently and confidently for their exams.
Vedantu provides CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions according to the CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus to help students prepare for their exams by focusing on key topics from each chapter.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations - 2025-26



Access Important Questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Some crystals of copper sulphate were dissolved in water. The colour of the solution obtain would be
Green
Red
Blue
Brown
Ans: (c) Blue
2. When dilute \[HCl\] is added to zinc pieces taken in a test tube
No change takes place
The colour of the solution becomes yellow.
A pungent smelling gas gets liberated
Small bubbles of \[{{H}_{2}}\] gas appear on the surface of zinc pieces
Ans: (d) Small bubbles of \[{{H}_{2}}\] gas appear on the surface of zinc pieces.
3. \[PbS\] reacts with ozone ( \[{{O}_{3}}\] ) and forms \[PbS{{O}_{4}}\] . As per the balanced equation, molecules of ozone required for every one molecule of \[PbS\] is/are
\[4\]
\[3\]
\[2\]
\[1\]
Ans: (a) \[4\]
4. Chemically rust is
Hydrated ferrous oxide
Hydrated ferric oxide
Only ferric oxide
None of these
Ans: (b) Hydrated ferric oxide
5. Which of the following reactions is not correct
\[Zn+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to ZnS{{O}_{4}}+Cu\]
\[2Ag+Cu{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}\to 2AgN{{O}_{3}}+Cu\]
\[Fe+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to FeS{{O}_{4}}+Cu\]
\[Mg+2HCl\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\]
Ans: (b) \[2Ag+Cu{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}\to 2AgN{{O}_{3}}+Cu\]
6. Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution:
\[ZnS{{O}_{4}}\]
\[FeS{{O}_{4}}\]
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}\]
\[NiS{{O}_{4}}\]
Ans: (c) \[AgN{{O}_{3}}\]
7. In an electrolytic cell where electrolysis is carried, anode has:
Positive change
Negative charge
Connected to negative terminal of the battery
None of these is correct.
Ans: (a) Positive change
8. The reaction \[{{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to 2HCl\] represents:
Oxidation
Reduction
Decomposition
Combination
Ans: (d) combination
9. In the reaction \[PbO+C\to Pb+CO\]
\[PbO\] is oxidised
\[C\] acts as an oxidising agent
\[C\] acts as a reduction agent
Reaction does not represent redox reaction.
Ans: (c) \[C\] acts as a reduction agent.
10. A substance which oxidizes itself and reduces other is known as
Oxidising agent
reducing agent
Both (a) and (b)
None of these.
Ans: (b) Reducing agent
11. Take about \[5\] ml of dil. \[HCl\] in a test tube and add a few pieces of fine granules to it. Which gas is evolved?
Chlorine
Hydrogen
\[HCl\]
Nitrogen
Ans: (b) Hydrogen
12. Dissolving sugar is an example of-
Physical change
Chemical change
Redox Reaction
None of these.
Ans: (a) Physical change
13. Heat is evolved diving
Endothermic Reaction
Displacement Reaction
Combustion Reaction
Combination Reaction
Ans: (c) Combustion Reaction
14. Which of the following is not a balanced equation?
\[Fe+C{{l}_{2}}\to FeC{{l}_{3}}\]
\[Mg+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to MgS{{O}_{4}}+{{C}_{4}}\]
\[NaOH+HCl\to NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
\[Zn+S\to ZnS\]
Ans: (a) \[Fe+C{{l}_{2}}\to FeC{{l}_{3}}\]
15. The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide present in aqueous solutions is an example of
Decomposition Reaction
Displacement Reaction
Double Displacement Reaction
Neutralisation Reaction
Ans: (c) Double Displacement Reaction
16. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filling? Tick the correct answer
Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced
No reaction takes place
Iron salt and water are produced
Ans: (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. Identify the type of chemical reaction
i. \[A\to B+C\]
Ans: \[A\to B+C\] is a decomposition reaction.
ii. \[AD+CD\to AD+CB\]
Ans: \[AD+CD\to AD+CB\] is a double displacement reaction.
2. Why does not silver evolve hydrogen on reacting with dil \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] ?
Ans: Silver does not evolve hydrogen on reacting with dil. \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] as silver is a less reactive metal than hydrogen.
3. Why do diamond and graphite, the two allotropic forms of carbon, evolve different amounts of heat on combustion?
Ans: Diamond and graphite are the two allotropes of carbon but they evolve different amounts of heat on combustion because the arrangement of carbon atoms and thus their shapes are different from one another.
4. What is the role of oxidizing agent in a reaction?
Ans: The role of oxidizing agent in a reaction is that it supplies the oxygen or removes the hydrogen in the reaction.
5. What happens chemically when quick lime is added to water?
Ans: When quick lime is added to water a lot of heat is evolved and calcium hydroxide (or slaked lime) is formed with a hissing sound. The chemical reaction involved is
\[CaO(s)+{{H}_{2}}O(\text{quicklime})\to Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}+\text{Heat(shakedLime)}\]
6. Why a combustion reaction an oxidation reaction?
Ans: Combustion reaction is an oxidation reaction because it is always carried out in the presence of oxygen. The chemical reaction involved is:
\[C{{H}_{4}}(g)+2{{O}_{2}}(g)\to C{{O}_{2}}(g)+2{{H}_{2}}O(l)\]
7. Why are food particle preferably packed in aluminium foil?
Ans: Food particles are preferably packed in aluminium foil because it does not corrode in atmosphere. A protective coating of aluminium oxide ( \[A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\] ) is formed on the surface of the foil and it stops any further reaction of the metal with air and water so even if it is kept for a long time food particles do not get spoiled.
8. What happens to lime water when \[C{{O}_{2}}\] gas is bubbled through it in excess?
Ans: When \[C{{O}_{2}}\] gas is bubbled through lime water in excess then initially it becomes milky but after some time its milkiness disappears. This is because initially calcium carbonate is formed which causes the lime water to turn milky and when further \[C{{O}_{2}}\] is passed calcium bicarbonate is formed which turns the solution colourless.
9. Why is a Combustion reaction an oxidation reaction?
Ans: Combustion is an oxidation reaction as it is always carried out in the presence of oxygen. In an oxidation reaction, oxygen is added to or removed from a compound. For example,
\[C{{H}_{4}}+2{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
10. Identify the type of chemical reaction
i. \[A+B\to C\]
Ans: This is a combination reaction in which a single product is formed from multiple reactants.
ii. \[A+BC\to AC+B\]
Ans: It is a displacement reaction in which a more reactive reactant displaces a less reactive element in the compound.
11. Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed?
Ans: Chemical change cannot be normally reversed because products so formed in a chemical reaction are quite different from the reactants.
12. Identify the substance oxidized and reduced in the reaction.
\[CuO(s)+Zn(s)\to ZnO(s)+Cu(s)\]
Ans: The substance oxidized is Zinc and the substance reduced is copper oxide.
13. A student took two-three g of a substance $X$ in a glass beaker & poured water over it slowly. He observed bubbles along with hissing noise. The beaker becomes quite hot. Identify $X$ . What type of reaction is it?
Ans: In the given experiment where the student took two-three g of a substance $X$ in a glass beaker and poured water over it slowly. He observed bubbles along with hissing noise and the beaker became quite hot after the reaction. Therefore, here $X$ is Calcium oxide (or Quick lime) and the reaction is a type of combination reaction.
14. A substance $X$ used for coating iron articles is added to a blue solution of a reddish-brown metal $Y$ , the colour of the solution gets discharged. Identify $X$ and $Y$ & also the type of reaction.
Ans: Here, a substance $X$ used for coating iron articles is added to a blue solution of a reddish-brown metal $Y$ , the colour of the solution gets discharged. Therefore, $X$ is Iron ( \[Fe\] ) $Y$ is Copper ( \[Cu\] ). Also, it is a type of a displacement reaction.
15. A student burnt a metal \[A\] found in the form of ribbon. The ribbon burnt with a dazzling Flame & a white powder \[B\] is formed which is basic in nature. Identify \[A\] & \[B\] . Write the Balanced chemical equation.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction for the given experiment is:
$X=Mg,Y=MgO,Mg+{{O}_{2}}\to 2MgO$
16. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Ans: A magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning in air in order to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from the surface of magnesium ribbon.
17. Write the balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions?
Ans: Balance chemical reaction with state symbols are:
i. $BaC{{l}_{2}}(aq)+N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}(aq)\to BaS{{O}_{4}}(s)+2NaCl(aq)$
ii. $NaOH(aq)+HCl(aq)\to NaCl(aq)+{{H}_{2}}O$
18. A solution of a substance ‘ $X$ ’ is used for white washing
i. Name the substance ‘ $X$ ’ and writes its formula.
Ans: The substance used for white washing is calcium oxide and its formula is $CaO$
ii. Write the reaction of the substance ‘ $X$ ’ named in (i) above with water.
Ans: The reaction for $CaO$ with water is: $CaO(s)+{{H}_{2}}O\to Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}(s)$
19. Which of the following statement about the reaction below are incorrect? $2PbO(s)+C(s)\to 2Pb(s)+C{{O}_{2}}(g)$
Lead is getting reduced.
Carbon dioxide is getting oxidized
Carbon is getting oxidized
Lead oxide is getting reduced
i. (a) and (b)
ii. (a) and (c)
iii. (a), (b) and (c)
iv. All
Ans: (i) Gain of oxygen is oxidation and loss of oxygen is reduction. Therefore, the statements (a) and (b) are incorrect and thus option (i) is correct.
20. In refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans: The reaction involved in refining of silver is $Cu(s)+2AgN{{O}_{3}}(aq)\to Cu{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}(aq)+2Ag(s)$
21. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Ans: A chemical reaction occurring in an aqueous solution in which an insoluble substance (precipitate) is formed is called precipitation reaction. For example, precipitation of silver chloride when aqueous silver nitrate is added to a solution containing potassium chloride.
$AgN{{O}_{3}}+NaCl\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}$
22. A shiny brown coloured element ‘ $X$ ’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘ $X$ ’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans: The shiny brown coloured element ‘ $X$ ’ is copper. On heating in air, it forms copper oxide, which is black in colour. The chemical reaction for the above situation is:
$2CuS+{{O}_{2}}\to 2CuO$
23. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Ans: We apply paint on iron articles in order to prevent rusting. Due to this layer of paint, iron articles do not come in contact of atmospheric oxygen and react with it to form iron oxide. Thus, rusting is prevented.
24. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans: Oil and fat containing food items get rancid due to oxidation with atmospheric oxygen due to which the food gets an odour because of the formation of small volatile fatty acid molecules. To prevent this rancidity, food items are flushed with nitrogen. Nitrogen, being an inert gas, does not react with oil and fat containing items and therefore, acts as an antioxidant.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1.
a). Define Rusting.
Ans: The formation of reddish-brown ferric oxides on the surface of iron when exposed to air for a long period of time in the presence of water at low temperature is called rusting.
b). Why do you apply paint on iron articles?
Ans: We apply paint on iron articles so that it forms a protective coating on the surface of iron and not come in contact directly with oxygen and water. It protects them against rusting.
2. White the balanced reactions for the following
A. \[\text{PotassiumBromide(aq)+Bariumiodide(aq)}\to \text{Potassiumiodide(aq)+BariumBromide(aq)}\]
Ans: $2KBr(aq)+Ba{{I}_{2}}(aq)\to 2KI(aq)+BaB{{r}_{2}}(aq)$
B. $\text{Zinccarbonate(s)}\to \text{Zincoxide(s)+carbondioxide(g)}$
Ans: $ZnC{{O}_{3}}(s)\to ZnO(s)+C{{O}_{2}}(g)$
C. $\text{Hydrogen(g)+chlorine(g)}\to \text{Hydrogenchloride}$
Ans: ${{H}_{2}}(g)+C{{l}_{2}}(g)\to 2HCl(g)$
3. The reaction is given by
$Zn+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to ZnS{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}$
i. White the ionic equation for the reaction.
Ans: The ionic equation is: \[Zn+2{{H}^{+}}\to Z{{n}^{2+}}+{{H}_{2}}\]
ii. The ionic equations can be represented by two half equations. Write these equations.
Ans: The two halves of the ionic equation representing one at cathode and another at anode are:\[Zn\to Z{{n}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\] \[2{{H}^{+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\]
iii. Explain why this is a redox reaction.
Ans: A redox reaction is the one in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. Here, from Zinc there is loss of electrons representing oxidation process and gain of electrons in hydrogen represent reduction. Therefore, this is a redox reaction.
4. What are neutralization reactions? Why are they named so? Give one example?
Ans: A neutralization reaction is the chemical reaction between an acid and a base. The products formed are water and salt.
Neutralization reactions are named so because acid and base neutralize each other in this type of reaction. For example, formation of sodium chloride and water by the reaction of \[HCl\] and \[NaOH\] .
\[HCl+NaOH\to NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
5. Identify the type of reaction in the following
a). $ZnC{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\left( aq \right)\to ZnC{{l}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\left( aq \right)$
Ans: Double decomposition reaction.
b). $2NaBr\left( aq \right)+Cl\left( g \right)\to 2NaCl\left( aq \right)+B{{r}_{2}}\left( aq \right)$
Ans: Displacement reaction.
c). $2CuO\left( s \right)\underrightarrow{Heat}2Cu\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)$
Ans: Decomposition reaction.
6. A student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was then passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write balanced chemical equation for both the change observed?
Ans: If a student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. Carbon dioxide gas is evolved. If this gas is passed through lime water insoluble Calcium carbonate is formed which turns the lime water milky. The solution will turn colourless after some time due to the formation of Calcium bicarbonate. The reactions involved are: \[CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)+2HCl\left( aq \right)\to CaC{{l}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
\[Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to CaC{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\]
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\to Ca{{\left( HC{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)\]
7. In the reaction $Mn{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\to MnC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}$
a) Name the substance oxidised.
Ans: In the given reaction \[HCl\] is oxidised to \[C{{l}_{2}}\] .
b) Name the oxidising agent.
Ans: The oxidising agent is \[Mn{{O}_{2}}\]
c) Name the reducing agent and the substance reduced.
Ans: The reducing agent is \[HCl\] and here, \[Mn{{O}_{2}}\] is oxidised to \[MnC{{l}_{2}}\].
8. Give one example each of
a) Thermal decomposition
Ans: An example of Thermal decomposition is
\[MgC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\underrightarrow{Heat}MgO\left( s \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
b) Electrolytic decomposition
Ans: An example of Electrolytic decomposition is \[2{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\underrightarrow{ElectricCurrent}2{{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
c) Photo decomposition
Ans: An example of Photo decomposition is \[2{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\left( l \right)\underrightarrow{Light}{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
9. Write three equations for decomposition reaction where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity?
Ans: The three equations for decomposition reaction where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity are:
i. \[MgC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\underrightarrow{Heat}MgO\left( s \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
ii. \[2AgCl\underrightarrow{Light}2Ag+C{{l}_{2}}\]
iii. \[2NaCl\underrightarrow{Electricity}2Na+C{{l}_{2}}\]
10. When you mix solutions of lead (II) nitrate and potassium iodide,
i. What is the colour of the precipitate formed? Name the compound evolved?
Ans: The precipitate formed here is lead(II) Iodide which is yellow in colour.
ii. Write a balanced chemical reaction?
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is: \[Pb{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+2KI\left( aq \right)\to Pb{{I}_{2}}\left( s \right)+2KN{{O}_{3}}\left( aq \right)\]
iii. Is this a double displacement reaction?
Ans: Yes, this is a double displacement reaction because both the compounds are getting displaced.
11. Transfer the following into chemical equations and balance them.
i. Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to from ammonia.
Ans: \[3{{H}_{2}}+{{N}_{2}}\to 2N{{H}_{3}}\]
ii. Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
Ans: \[2{{H}_{2}}S+3{{O}_{2}}\to 2{{H}_{2}}O+2S{{O}_{2}}\]
iii. Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans: \[2K+2{{H}_{2}}O\to 2KOH+{{H}_{2}}\].
12. Balance the equations
i. $HN{{O}_{3}}+Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\to Ca{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
Ans: $2HN{{O}_{3}}+Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\to Ca{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O$
ii. $NaCl+AgN{{O}_{3}}\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}$
Ans: $NaCl+AgN{{O}_{3}}\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}$
iii. $BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to BaS{{O}_{4}}+HCl$
Ans: $BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to BaS{{O}_{4}}+2HCl$
13. A compound ‘ $X$ ’ is used for drinking, has $pH=7$ . Its acidified solution undergoes decomposition in presence of electricity to produce gases ‘ $Y$ ’ and ‘ $Z$ ’. The volume of $Y$ is double than $Z$ . $Y$ is highly combustible whereas $Z$ is supporter of combustion. Identify $X$ , $Y$ & $Z$ and write the chemical reactions involved.
Ans: In the given situation, $X={{H}_{2}}O$ , $Y={{H}_{2}}$ and $Z={{O}_{2}}$ . The chemical reaction involved is: $2{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)$
14. An aqueous solution of metal nitrate $P$ reacts with sodium bromide solution to form yellow ppt of compound $Q$ which is used in photography. $Q$ on exposure to sunlight undergoes decomposition reaction to form metal present in $P$ along with reddish brown gas. Identify $P$ & $Q$ . Write the chemical reaction & type of chemical reaction.
Ans: In the given situation, $P=AgN{{O}_{3}}$ , $Q=AgBr$ . The chemical reaction involved is a photochemical reaction which is as follows: $2AgBr\left( s \right)\to 2Ag\left( s \right)+B{{r}_{2}}\left( g \right)$
15. Bhawana took a pale green substance $A$ in a test tube. And heated it over the flame of a burner. A brown coloured residue $B$ was formed along with evolution of two gases with burning smell of sulphur. Identify $A$ & $B$ . Write the chemical reaction involved.
Ans: In the given situation, $A=FeS{{O}_{4}}$ , $B=F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ . The chemical reaction involved is: $2FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( s \right)\to F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)+S{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)+S{{O}_{3}}\left( g \right)$
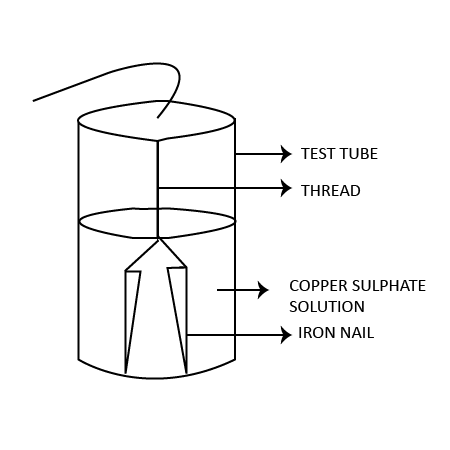
16. A reddish-brown vessel developed a green-colored solid $X$ .When left open in air for a long time. When reacted with $dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ , it forms a blue-colored solution along with brisk efficient due to colourless & odourless gas $Z$ . $X$ decomposes to form black-colored oxide $Y$ of a reddish-brown metal along with gas $Z$ , Identify $X$ , $Y$ , & $Z$ .
Ans: In the given situation, $X=CuC{{O}_{3}}$ , $Y=CuO$ and $Z=C{{O}_{2}}$ .
17. A student has mixed the solutions of lead (II) nitrate and potassium iodide.
i. What was the colour of the precipitate formed? Can you name the compound?
Ans: The precipitate formed here is lead(II) Iodide which is yellow in colour.
ii. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is: \[Pb{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+2KI\left( aq \right)\to Pb{{I}_{2}}\left( s \right)+2KN{{O}_{3}}\left( aq \right)\]
iii. What type of reaction is it?
Ans: This is a double displacement reaction because both the compounds are getting displaced.
18. Name the type of reaction seen in the diagram below. Write the reaction for the same.
Ans: The type of reaction is displacement reaction. \[Fe\left( s \right)+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)+Cu\]
19. A student dropped few pieces of marble in $dil.HCl$contained in a test tube. The gas evolved was passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write chemical reactions for both the changes observed.
Ans: If a student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. Carbon dioxide gas is evolved. If this gas is passed through lime water insoluble Calcium carbonate is formed which turns the lime water milky. The solution will turn colourless after some time due to the formation of Calcium bicarbonate. The reactions involved are: \[CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)+2HCl\left( aq \right)\to CaC{{l}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
\[Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to CaC{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\]
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\to Ca{{\left( HC{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)\]
20. Astha has been collecting silver coins and copper coins. One day she observed a black Coating on silver coins and a green coating on copper coins. Which chemical phenomenon is responsible for these coatings? Write the chemical name of black and green coatings?
Ans: Corrosion is responsible for the black coating on silver and green coating on copper. The chemical name of the black coating formed is $A{{g}_{2}}S$ and the green coating formed is due to $CuC{{O}_{3}}.Cu{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}$ .
21. Write the balance equation for the following reactions.
i. Hydrogen + Chlorine -> Hydrogen chloride
Ans: ${{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to 2HCl$
ii. Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate -> Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
Ans: $3BaC{{l}_{2}}+A{{l}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}\to 3BaS{{O}_{4}}+2AlC{{l}_{3}}$
iii. Sodium + water -> Sodium hydroxide + water
Ans: $2Na+2{{H}_{2}}O\to 2NaOH+{{H}_{2}}$
22. $F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2Al\to A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2Fe$
The above reaction is an example of a
combination reaction
double displacement reaction
decomposition reaction
displacement reaction
Ans: (d) This is an example of displacement reaction because $Fe$ in $Fe{{O}_{3}}$ has been displaced by $Al$ .
23. What is balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equation be balanced?
Ans: The representation of a chemical reaction in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on the reactant side and product side is called balanced chemical equation. Chemical reaction should be balanced because only a balanced equation tells us the relative quantities of different reactants and products involved in the reaction.
24. Why respiration is considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Ans: Reactions which release heat or energy are called exothermic reactions. Respiration is considered an exothermic reaction because when we breathe out heat is liberated. During respiration, we inhale oxygen from the atmosphere which reacts with glucose in your body cells to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. You are given with
Iron Nails
$CuS{{O}_{4}}$ solution
$BaC{{l}_{2}}$
$Cu$ Powder
Ferrous sulphate crystal
Quick lime.
Make five reactions that can take place from these materials.
Ans: Five reactions possible from the given materials are:
i. $BaC{{l}_{2}}\left( aq \right)+CuS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)\to BaS{{O}_{4}}\left( s \right)+CuC{{l}_{2}}\left( aq \right)$
ii. $2Cu\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2CuO\left( s \right)$
iii. $2FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( s \right)\underrightarrow{heat}F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+S{{O}_{2}}+S{{O}_{3}}$
iv. $2FeS{{O}_{4}}.7{{H}_{2}}O\underrightarrow{heat}Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\left( s \right)+Heat$
v. $CaO\left( s \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\to Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\left( s \right)+Heat$
2. A metal is heated with $dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ . The gas evolved is collected by the method shown in the figure: Answer the following
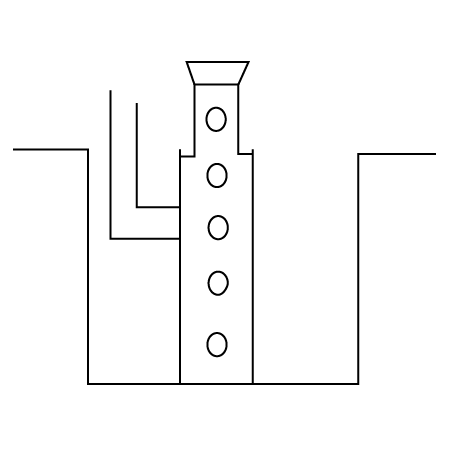
Name the gas.
Ans: The gas evolved is ${{H}_{2}}$ .
Name the method of collection of gas.
Ans: Gas is collected by downward displacement method.
Is the gas soluble or insoluble in water?
Ans: The gas is insoluble in water since it is collected over water and does not get dissolved.
Is the gas lighter or heavier than air?
Ans: The gas is lighter than air as it floats above.
3. With the help of an activity show that iron is more reactive than copper?
Ans: To show that iron is more reactive than copper, take a test tube and pour some copper sulphate solution into it. Now, drop some iron nails into this solution and wait for some time. You will notice that the solution turns blue and the nails become reddish-brown. This is because of the displacement of copper from copper sulphate solution. The brown deposit is of copper. The chemical reaction involved in this experiment is:
\[Fe\left( s \right)+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)+Cu\]
4. Observe the following activity & answer the questions
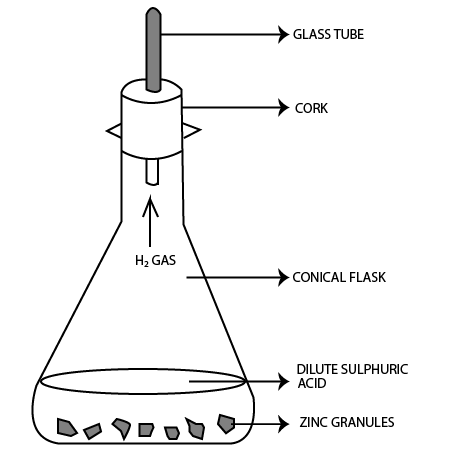

Do you observe anything happening around the zinc granules?
Ans: Bubbles of hydrogen gas evolve around zinc granules.
Is there any change in its temperature?
Ans: Yes, temperature will increase after reaction.
Why is glass tube not dipped in $dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ ?
Ans: If glass tube is dipped in $dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ , then the level of ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ will rise in the glass tube preventing hydrogen gas to evolve.
How is ${{H}_{2}}$ gas collected by downward displacement or upward displacement of water?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is collected by downward displacement of water.
Is ${{H}_{2}}$ gas soluble or insoluble in water?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is insoluble in water.
Is ${{H}_{2}}$ gas heavier or lighter than air?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is lighter than air.
5. A reddish-brown metal $X$ when heated in presence of oxygen forms a black compound $Y$ Which is basic in nature when heated with hydrogen gas gives back X. Identify $X$ & $Y$ . Write the chemical reaction between $Y$ & ${{H}_{2}}$ . Identify the substance being oxidized & reduced.
Ans: Here, $X=Cu$ and $Y=CuO$ .
Chemical reaction between copper oxide and hydrogen is
\[2Cu\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2CuO\left( s \right)\]
\[CuO+{{H}_{2}}\underrightarrow{heat}Cu+{{H}_{2}}O\]
During this reaction, copper oxide is getting reduced as it is losing oxygen and hydrogen is getting oxidised as it is gaining oxygen.
6. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans: The colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it because of the displacement of copper from copper sulphate solution and formation of iron sulphate solution. The brown deposit is of copper. The chemical reaction involved in this experiment is: \[Fe\left( s \right)+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)+Cu\]
7. Identify the substances that are oxidized and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions.
a. $4Na\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2N{{a}_{2}}O\left( s \right)$
Ans: In this reaction, sodium is oxidised because it is combined with oxygen and oxygen molecule is reduced because it is losing an oxygen atom to convert into sodium oxide.
b. $CuO\left( s \right)+{{H}_{2}}\to Cu\left( s \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)$
Ans: In this reaction, hydrogen is getting oxidised because it is combined with oxygen to form water and copper oxide is reduced because it is losing an oxygen atom to convert into copper.
8. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[3{{H}_{2}}+{{N}_{2}}\to 2N{{H}_{3}}\]
b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and Sulphur dioxide.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[2{{H}_{2}}S+3{{O}_{2}}\to 2{{H}_{2}}O+2S{{O}_{2}}\]
c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and precipitate of barium sulphate.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[3BaC{{l}_{2}}+A{{l}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}\to 2AlC{{l}_{3}}+3BaS{{O}_{4}}\]
9. Balance the following chemical equations:
a) $HN{{O}_{3}}+Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\to Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}.Ca{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$2HN{{O}_{3}}+Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\to Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}.Ca{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O$
c) $NaOH+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$2NaOH+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}O$
d) $NaCl+AgN{{O}_{3}}\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}$
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$NaCl+AgN{{O}_{3}}\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}$
e) $BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to B{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+HCl$
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to B{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2HCl$
10. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide -> Calcium carbonate + Water
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to CaC{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\]
b) Zinc + Silver nitrate -> Zinc nitrate + Silver
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$Zn+2AgN{{O}_{3}}\to Zn{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2Ag$
c) Aluminum + Copper chloride -> Aluminum chloride +Copper
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
$2Al+3C{{l}_{2}}\to 2AlC{{l}_{3}}+3Cu$
d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate -> Barium sulphate + potassium chloride
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to BaS{{O}_{4}}+2KCl\]
11. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
a) Potassium bromide (s) + Barium iodide (aq) -> Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium bromide(s)
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[2KBr\left( aq \right)+Ba{{I}_{2}}\to 2KI\left( aq \right)+B{{r}_{2}}\]
This is a displacement reaction.
b) Zinc carbonate (s) -> Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[Zn{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\to ZnO\left( s \right)+C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
This is a decomposition reaction.
c) Hydrogen (g) + Chlorine (g) -> Hydrogen chloride (g)
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[{{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)+C{{l}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2HCl\]
This is a combination reaction.
d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) -> Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is:
\[Mg\left( s \right)+2HCl\left( aq \right)\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
This is a displacement reaction.
12. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Ans: A reaction in which energy is released in the form of heat or light is called exothermic reaction. For example,
\[C{{H}_{4}}+2{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+heat\]
\[2Al+Fe{{O}_{3}}\to A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+Fe+heat\]
A reaction in which energy is absorbed from the surrounding and cooling is produced is called endothermic reaction. For example,
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}\to CaO+C{{O}_{2}}\]
\[{{N}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}\to 2NO\]
13. Why decomposition reactions are called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans: In a decomposition reaction, a single substance breaks down into two or more substances while in a combination reaction, two or more substances react to produce one substance. Therefore, decomposition reactions are called opposite of combination reactions.
For example,
Decomposition reaction: \[CaC{{O}_{3}}+CuS{{O}_{4}}\to ZnS{{O}_{4}}+Cu\]
Combination reaction: \[CaO+{{H}_{2}}O\to Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\]
14. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Ans: The equation for decomposition reaction by heat is:
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}+heat\to CaO+C{{O}_{2}}\]
The equation for decomposition reaction by light is:
\[2AgBr+light\to 2Ag+B{{r}_{2}}\]
The equation for decomposition reaction by electricity is:
\[2{{H}_{2}}O+electricity\to 2{{H}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}\]
15. What is difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans: In displacement reaction, more reactive element displaces the less reactive element from its compound. For example,
$Zn(s)+CuS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)\to ZnS{{O}_{4}}(aq)+Cu(s)$
Whereas in double displacement reaction, exchange of ions takes place between the compounds. For example,
$HCl\left( aq \right)+AgN{{O}_{3}}\left( aq \right)\to AgCl\left( s \right)+HN{{O}_{3}}\left( aq \right)$
16. Explain the following in terms of gain and loss of oxygen with two examples each?
a) Oxidation
Ans: The process of addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen in a chemical reaction is called oxidation reaction. For example,
\[2Cu\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2CuO\left( s \right)\] , here copper is oxidised into copper oxide
\[2Mg\left( s \right)+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to 2MgO\left( s \right)\] , here magnesium is oxidised into magnesium oxide
b) Reduction
Ans: The process of addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen in a chemical reaction is called oxidation reaction. For example,
\[CuO+{{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to Cu+{{H}_{2}}O\] , here copper oxide is reduced to copper
\[{{H}_{2}}S+C{{l}_{2}}\to 2HCl+S\] , here chloride is reduced to hydrogen chloride
17. Explain the following terms with one example each.
a) Corrosion
Ans: Corrosion is defined as a process where a metal reacts with water, air or acid to form oxides and carbonates. This is also known as rusting. For example, black coating on silver in the presence of air or atmosphere.
b) Rancidity
Ans: Rancidity is the process of oxidation of fats and oils when kept in open or in presence of oxygen for a long time. Due to this change in taste and odour of food can be observed. To prevent rancidity food items are flushed with nitrogen or kept in airtight containers. For example, the taste and smell of butter changes when kept for long.
Important Topics of Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
S. No | Important Topics |
1 | Introduction to Chemical Reactions |
2 | Types of Chemical Reactions (Combination, Decomposition, Displacement, Double Displacement, and Redox Reactions) |
3 | Balancing Chemical Equations |
4 | Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions |
5 | Oxidation and Reduction Reactions |
6 | Corrosion and its Prevention |
7 | Rancidity and its Effects |
8 | Applications of Chemical Reactions in Daily Life |
Benefits of Class 10 Science Important Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Covers All Reaction Types: Focuses on important reaction types like combination, decomposition, and redox reactions.
Improves Balancing Skills: Helps students practice balancing complex chemical equations, an essential exam skill.
Enhances Conceptual Understanding: Simplifies difficult concepts such as oxidation and reduction reactions for better clarity.
Strengthens Practical Knowledge: Encourages application-based learning by relating chemical reactions to real-life examples like corrosion and rancidity.
Exam-Focused Preparation: Questions are based on frequently asked topics, aiding students in scoring well.
Detailed Explanations: Provides clear, step-by-step solutions to all questions, improving understanding.
Prepares for Numerical Problems: Includes practice questions on calculating reactants and products, improving numeracy in chemistry.
Time Management: Enhances students' ability to solve questions quickly and efficiently during exams.
Boosts Confidence: Familiarizes students with the exam pattern, building confidence for answering chemical reactions and equations questions.
Clears Doubts: Clarifies doubts related to reaction mechanisms, making learning easier and more effective.
Important Study Materials for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
S. No | Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 |
1 | Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Solutions |
2 | Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-wise Important Questions
S. No | CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Links |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 |
Additional Study Materials for Class 10 Science
S. No | Important Links for Science Class 10 |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations - 2025-26
1. What types of questions are most frequently asked from Chapter 1, Chemical Reactions and Equations, in the CBSE Class 10 board exams?
For this chapter, you can expect questions focused on balancing chemical equations, identifying the different types of reactions, and explaining real-world examples like corrosion. These are often asked as MCQs, 2-mark, and 3-mark questions in the board exams.
2. Which topics in 'Chemical Reactions and Equations' are most important for scoring well in the 2025-26 exam?
To score high marks, concentrate on balancing equations and identifying reaction types with proper justification. Also, prepare for application-based questions on oxidation and reduction, as these concepts are often tested in 3-mark or 5-mark questions.
3. How should I structure my answer for a 3-mark question about identifying a chemical reaction?
A perfect answer for a 3-mark question should include three key parts:
- State the correct type of reaction (e.g., displacement reaction).
- Write the complete, balanced chemical equation.
- Give a short, clear explanation of why it is that type of reaction, for instance, by stating which element is displacing another.
4. Are there any Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) questions I should prepare from this chapter?
Yes, HOTS questions from this chapter usually connect concepts to real life. For example, you might be asked to identify the chemical reaction when a silver anklet tarnishes (corrosion) or when an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution (displacement reaction). Focus on explaining the 'why' behind the observation.
5. Why is balancing a chemical equation so important? What fundamental law does it relate to?
Balancing a chemical equation is essential because it must obey the Law of Conservation of Mass. This law states that in any chemical reaction, mass is not created or destroyed. A balanced equation ensures the number of atoms for each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides, upholding this law.
6. How can I quickly tell the difference between a displacement and a double displacement reaction?
Look at the reactants. A displacement reaction usually involves an element reacting with a compound (e.g., Zn + CuSO₄). In contrast, a double displacement reaction involves two compounds reacting and exchanging ions to form two new compounds (e.g., AgNO₃ + NaCl).
7. What is a common mistake students make when answering questions about redox reactions?
A very common error is only identifying the substance that gets oxidised or reduced. To get full marks, you must also correctly identify the oxidising agent (the substance that gets reduced) and the reducing agent (the substance that gets oxidised). They are always the entire compound, not just the element.
8. Can one reaction be classified as both a decomposition and a redox reaction?
Yes, a reaction can be both. For instance, the decomposition of lead(II) nitrate when heated is a classic example. It breaks down into simpler substances (decomposition), but the oxidation states of nitrogen and oxygen also change, making it a redox reaction as well.














 Watch Video
Watch Video
















