
Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
The Class 10 Science Chapter 1, Chemical Reactions and Equations, introduces students to the basics of chemical reactions, types of reactions, and how to represent them with balanced chemical equations. Many Class 10 students struggle to remember reaction types or balance equations, which is why these NCERT solutions are carefully curated by Vedantu experts according to the Class 10 Science syllabus, ensuring every question is explained clearly and accurately.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentThese Class 10 Science Chapter 1 question answer solutions cover all exercises from NCERT, helping students understand concepts like combination, decomposition, displacement, and redox reactions in a simple, step-by-step way. By using these solutions, students can revise efficiently and prepare confidently for exams.
Whether it’s balancing equations, identifying reaction types, or solving tricky numerical problems, these NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 provide clear guidance. Students can also download the Science Class 10 Chapter 1 PDF for quick reference and revision before tests.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations (2025-26)
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Intext Exercise 1
1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Ans: Magnesium is a reactive metal. It will react with oxygen and form a white layer of magnesium oxide (MgO) on its surface. Magnesium oxide is a stable compound and will prevent the further reaction of the metal. So, a magnesium ribbon is cleaned before burning in air to remove the layer of magnesium oxide from its surface.
2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
i) Hydrogen + Chlorine $\to $ Hydrogen chloride
Ans: A balanced equation consists of the same number of moles on the reactants and the products side. The balanced equation for the given reaction is:${{H}_{2(g)}}+C{{l}_{2(g)}}\to 2HC{{l}_{(g)}}$
ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate $\to $ Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
Ans: A balanced equation consists of the same number of moles on the reactants and the products side. The balanced equation for the given reaction is:$3BaC{{l}_{2(s)}}+A{{l}_{2}}{{(S{{O}_{4}})}_{3(s)}}\to 3BaS{{O}_{4(s)}}+2AlC{{l}_{3(s)}}$
iii) Sodium + Water $\to $ Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Ans:
A balanced equation consists of the same number of moles on the reactants and the products side. The balanced equations for the given reaction is $2N{{a}_{(s)}}+2{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}\to 2NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}+{{H}_{2}}_{(g)}$
3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
Ans: A balanced chemical equation has the same number of moles of reactants and products. The balanced chemical equation is:$BaC{{l}_{2(aq)}}+N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4(aq)}}\to BaS{{O}_{4(s)}}+2NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}$
ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Ans: A balanced chemical equation has the same number of moles of reactants and products. The balanced chemical equation is:$NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}+HC{{l}_{(aq)}}\to NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}$
Intext Exercise 2
1. A solution of a substance 'X ' is used for white washing.
i) Name the substance 'X' and write its formula.
Ans: Substance ‘X’ is calcium oxide also known as quicklime that is used in white washing. Its chemical formula is CaO.
ii) Write the reaction of the substance 'X' named in (i) above with water.
Ans:Calcium oxide reacts with water in a combination reaction to from calcium hydroxide also called slaked lime, the reaction is:
$Ca{{O}_{(s)}}+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}\to Ca{{(OH)}_{2(aq)}}$
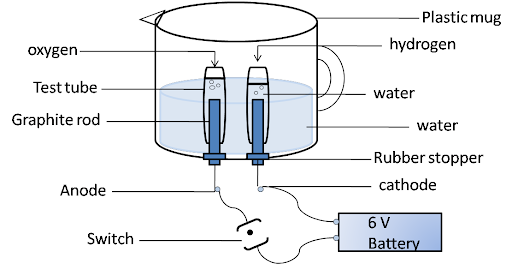
2. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Ans:
Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. It is a combination of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom. In electrolysis, hydrogen moves towards the cathode and oxygen towards the anode. So, the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen is 2:1. And hydrogen is double the amount of oxygen.
$2{{H}_{2}}O\to 2{{H}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}$
Intext Exercise 3
1. Why does the color of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans:
When an iron nail is dipped in a solution of copper sulphate, then the more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal. As a result the blue solution of copper sulphate gets faded and forms a green compound known as ferrous sulphate.
\[\underset{\text{Iron}}{\mathop{F{{e}_{(s)}}}}\,+\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}\text{ Copper sulphate } \\ (\text{Blue}) \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{CuS{{O}_{4(aq)}}}}\,\to \underset{\text{Ferrous sulphate}}{\mathop{FeS{{O}_{4(aq)}}}}\,+\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} \text {Copper} \\ (\text{Green})
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C{{u}_{(s)}}}}\,\]
2. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Ans:
A double displacement reaction consists of two ions replacing each other’s position from the reactants to form new compounds in the products. A double displacement reaction occurs when Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to form lead iodide (yellow precipitate) and potassium nitrate.
\[2KI+Pb{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}\to Pb{{I}_{2}}\downarrow +2KN{{O}_{3}}\]
3. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions
i) $\text{4N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{(s)}}}\text{+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2(g)}}}\to \text{2N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{(s)}}}$
Ans: Any species is said to be oxidised when it loses electrons and increases the oxidation state, while any species is said to be reduced when it gains electrons and decreases the oxidation state. Sodium (Na) is oxidised and oxygen gets reduced.
\[4\text{Na}+{{\text{O}}_{2}}\to 2\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}\text{O}\]
ii) $\text{Cu}{{\text{O}}_{\text{(s)}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2(g)}}}\to \text{Cu(s)+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{(l)}}}$
Ans: Any species is said to be oxidised when it loses electrons and increases the oxidation state, while any species is said to be reduced when it gains electrons and decreases the oxidation state. Copper oxide (CuO) is reduced to copper (Cu) as it loses oxygen and hydrogen $\left( {{H}_{2}} \right)$is oxidized to water $({{H}_{2}}O)$
\[CuO+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }Cu+{{H}_{2}}O\]
NCERT exercises
1. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
$\text{2Pb}{{\text{O}}_{\text{(s)}}}\text{+}{{\text{C}}_{\text{(s)}}}\to \text{2P}{{\text{b}}_{\text{(s)}}}\text{+C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2(g)}}}$
a. Lead is getting reduced.
b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
c. Carbon is getting oxidised.
d. Lead oxide is getting reduced.
Options
i) (a) and (b)
ii) (a) and (c)
iii) (a),(b) and (c)
iv) all
Ans:
Incorrect option is (i) (a) and (b)
Explanation:
(a) Oxygen is being removed
(b) The Oxygen removed from lead is transferred to the elemental Carbon.
2. $\text{F}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+2Al}\to \text{A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+2Fe}$
The above reaction is an example of a _______________
Options:
a) Combination reaction.
b) Double displacement reaction.
c) Decomposition reaction.
d) Displacement reaction.
Ans:
(d) The given reaction is an example of a single displacement reaction.
Explanation: The oxygen from ferrous oxide is transferred to aluminum metal, forming aluminum oxide. In this reaction, aluminum, being more reactive than iron, displaces iron from its oxide. This process is known as a displacement reaction, where a more reactive element replaces a less reactive one.
3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings? Tick the correct answer.
a. Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
b. Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
c. No reaction takes place,
d. Iron salt and water are produced.
Ans:
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced. The reaction is as follows:
\[F{{e}_{(s)}}+2HC{{l}_{(aq)}}\to FeC{{l}_{2(aq)}}+{{H}_{2}}\uparrow \]
4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Ans:
A balanced chemical equation consists of the equal number of moles of the elements in the reactants and that in the products.
Chemical equations should be balanced, as according to the law of conservation of mass, mass can neither be created nor can be destroyed. Therefore, in a chemical reaction, the total mass of reactant should be equal to the total mass of products. Hence, a balanced chemical equation has total mass of reactants equal to total mass of products.
5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
Ans: $3{{H}_{2(g)}}+{{N}_{2(g)}}\to 2N{{H}_{3(g)}}$
b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
Ans:$2{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{(g)}}+3{{O}_{2(g)}}\to 2{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}+2S{{O}_{2(g)}}$
c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
Ans:$3BaC{{l}_{2(aq)}}+A{{l}_{2}}{{(S{{O}_{4}})}_{3(aq)}}\to 2AlC{{l}_{3(aq)}}+3BaS{{O}_{4(s)}}$
d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Ans:$2{{K}_{(s)}}+2{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}\to 2KO{{H}_{(aq)}}+{{H}_{2(g)}}$
6. Balance the following chemical equations
a)$\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{3}}+\text{Ca}{{(\text{OH})}_{2}}\to \text{Ca}{{\left( \text{N}{{\text{O}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$
Ans: $2HN{{O}_{3}}+Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\to Ca{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O$
b)$\text{NaOH}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}\to \text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$
Ans: $2NaOH+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}O$
c)$\text{NaCl}+\text{AgN}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\to \text{AgCl}+\text{NaN}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$
Ans: \[NaCl+AgN{{O}_{3}}\to AgCl+NaN{{O}_{3}}\]
d)$\text{BaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\to \text{BaS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+HCl}$
Ans:$BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to BaS{{O}_{4}}+2HCl$
7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide $\to $ Calcium carbonate + Water
Ans: $Ca(OH)2 + CO2 \to CaCO3 +H2O$
b) Zinc + Silver nitrate $\to $Zinc nitrate +Silver
Ans: $Zn+2AgN{{O}_{3}}\to Zn{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2Ag$
c) Aluminium + Copper chloride $\to $Aluminium chloride + Copper
Ans: $2Al+3CuC{{l}_{2}}\to 2AlC{{l}_{3}}+3Cu$
d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate$\to $Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Ans:$BaC{{l}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to BaS{{O}_{4}}+2KCl$
8. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
a) Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (aq) $\to $Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium bromide(s)
Ans: $2KB{{r}_{(aq)}}+Ba{{I}_{2(aq)}}\to 2K{{I}_{(aq)}}+BaB{{r}_{2(aq)}}$ ; Double displacement reaction
b) Zinc carbonate (s) $\to $Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
Ans: $ZnC{{O}_{3(s)}}\to Zn{{O}_{(s)}}+C{{O}_{2(g)}}$ ; Decomposition reaction
c) Hydrogen (g)+ Chlorine (g)$\to $Hydrogen chloride (g)
Ans: ${{H}_{2(g)}}+C{{l}_{2(g)}}\to 2HC{{l}_{(g)}}$ ; Combination reaction
d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) $\to $Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Ans:$M{{g}_{(s)}}+2HC{{l}_{(aq)}}\to MgC{{l}_{2}}_{(aq)}+{{H}_{2}}_{(g)}$ ; Single displacement reaction
9. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Ans:
Exothermic Reaction: The reactions in which heat is evolved along with the formation of new products are called exothermic reactions. In these reactions the energy of the reactants is more than that of the products, so energy is released to complete the reaction.
Energy of reactants > Energy of products
Example: Complete combustion of methane gas produces carbon dioxide and water along with heat and light.
\[C{{H}_{4}}(~g)+2{{O}_{2}}(~g)\to C{{O}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+heat+light\]
Another example of exothermic reactions is respiration and decomposition of vegetable matter.
Endothermic Reaction: The reactions in which energy is absorbed by the reactants to carry on the reaction are called endothermic reactions. In this type of reaction, the energy of the reactants is less than that of the products, so energy is needed and absorbed.
Energy of reactants <Energy of products
Example: Process of Photosynthesis, where plants absorb sunlight in the presence of carbon dioxide and water and make their food in the form of glucose and release oxygen.
\[6C{{O}_{2(g)}}+6{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}\xrightarrow{sunlight}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{4(aq)\text{ }}}+6{{O}_{2(g)}}\]
10. Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Ans:
Exothermic reactions are the reactions in which heat is going to be released. These reactions result in the formation of energy as the energy of reactants is greater than that of products. Respiration is the process in which the glucose from our body combines with oxygen in the cells to provide us with energy. The glucose is broken down through the process of digestion that along with oxygen provides us with energy and hence respiration is an exothermic reaction. The reaction that happens is as follows:
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6(aq)}}+6{{O}_{2(g)}}\to 6C{{O}_{2(g)}}+6{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}+energy\]
11. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans:
A decomposition reaction consists of a single reactant that breaks down into two or more simpler products.
Example: Decomposition of calcium carbonate to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide as,
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}+\text{ }Energy\text{ }\to CaO+C{{O}_{2}}\]
A combination reaction consists of two reactants that combine or mix together to form a single product.
Example: Combination of Calcium oxide and carbon dioxide to form one single product calcium carbonate
\[CaO+C{{O}_{2}}\to CaC{{O}_{3}}+\text{ }energy\text{ }\]
Hence, decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions.
12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Ans:
Decomposition reactions are the reactions where a reactant breaks down into two or more products.
a) Decomposition by heat:
Ferrous sulphate decomposes to give ferrous oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide as,
\[2FeS{{O}_{4(s)}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3(s)}}+S{{O}_{2(g)}}+S{{O}_{3(g)}}\]
b) Decomposition by light:
Silver chloride decomposes in light to form silver and chlorine as,
\[2AgC{{l}_{(s)}}\xrightarrow{Light}2A{{g}_{(s)}}+C{{l}_{2(g)}}\]
c) Decomposition by electricity:
Water decomposes in presence of electricity to form hydrogen and oxygen gases as,
\[2{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{Electricity}2{{H}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}\]
13. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans:
A displacement reaction is a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. The elements at the top in the activity series can replace the elements at the bottom.
Example: Zinc is more reactive than copper and replaces copper from copper sulphate as:
\[CuS{{O}_{4(aq)}}+Z{{n}_{(s)}}\to ZnS{{O}_{4(aq)}}+C{{u}_{(s)}}\]
Double displacement reaction is the type of reaction where two compounds react in the way that there is exchange of positive and negative ions and new compounds are formed as products.
Example: On mixing sodium sulphate solution with barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed as:
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4(aq)}}+BaC{{l}_{2(aq)}}\to BaS{{O}_{4(s)}}+2NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}\]
14. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans:
The equation of recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution in silver refining is as follows:
\[2AgN{{O}_{3(aq)}}+C{{u}_{(s)}}\to Cu{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2(aq)}}+2A{{g}_{(s)}}\]
Here displacement of silver by copper happens as copper is more reactive than silver.
15. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Ans:
The type of reaction where an insoluble substance called a precipitate is formed when there is exchange of ions between the reactants is called a precipitation reaction.
Example 1: On mixing sodium carbonate solution with calcium chloride solution, a white precipitate of calcium carbonate is formed.
\[N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3(aq)}}+CaC{{l}_{2(aq)}}\to CaC{{O}_{3(s)}}\downarrow +2NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}\]
Example 2: On mixing sodium sulphate solution with barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4(aq)}}+BaC{{l}_{2(aq)}}\to BaS{{O}_{4(s)}}\downarrow +2NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}\]
16. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
a) Oxidation
Ans: Oxidation: A type of reaction in which oxygen or an electronegative species is added to a substance or there is removal of hydrogen or a positive species from a substance is called oxidation.
For Example:
$C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\to CO+{{H}_{2}}O$ (Addition of oxygen to${{H}_{2}}$)
$2Cu+{{O}_{2}}\to 2CuO$ (Addition of oxygen to Cu)
b) Reduction
Ans: Reduction: A type of reaction in which hydrogen or an electropositive species is added to a substance or oxygen or an electronegative species is removed, is called reduction.
For Example:
$C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\to CO+{{H}_{2}}O$ (Oxygen is removed from$C{{O}_{2}}$)
$CuO+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }Cu+{{H}_{2}}O$ (Oxygen is removed from CuO)
17. A shiny brown-coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black-coloured compound formed.
Ans:
Copper (Cu) is ‘X’ and the black colour compound is copper (II) oxide (CuO). Copper reacts with oxygen to form a black colour compound called copper (II) oxide as:
\[2Cu+{{O}_{2}}\to 2CuO\]
18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Ans:
Iron is a reactive metal and can react with moisture and air. Iron articles, if exposed for a long time in moisture or air, can get corroded and form rust. So, paint is applied on iron articles to prevent rusting and form a protective layer for exposure to air and moisture.
19. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans:
Oils and fat containing items are perishable and can be spoiled when exposed to oxygen. This is because oil and fats are reactive and can react with oxygen easily and get oxidised. To prevent oxidation, these items are flushed with nitrogen gas. Nitrogen is an inert gas and cannot react with oils or fats easily. So, food items with oils and fats are kept in packets having nitrogen gas that increases the shelf life and makes these items last for a long time.
20. Explain the following terms with one example each.
a) Corrosion
Ans: Corrosion: Corrosion is defined as a process where a substance, generally metal deteriorates and forms a layer of oxide on its surface. Metals get converted into their hydrated oxides or sulphides. Ex; Iron, Cu, Ag
\[4Fe+3{{O}_{2}}+n{{H}_{2}}O\to \underset{Hydrated\,iron\,oxide}{\mathop{2F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}.n{{H}_{2}}O}}\,$\]
\[2Ag+{{H}_{2}}~S\to A{{g}_{2}}~S+{{H}_{2}}\]
b) Rancidity
Ans: Rancidity: It is a process in which food items like fats and oils are oxidised. This results in the change in taste and smell of the food item and is called rancidity. For example, when any fried food is exposed to air for a long time then it has a change in smell and taste and it becomes rancid.
Rancidity can be avoided by:
Adding antioxidants like BHA (Butylated tri hydroxy anisole)
Refrigerate the food items
keep food items in airtight containers
Adding nitrogen to food packets to prevent oxidation.
Science Chapter 1 Class 10 - Quick Overview on Chemical Reaction and Equations
Topics of Chemical Reaction and Equation | Subtopics of Chemical Reaction and Equation |
Chemical Equations |
|
Types of Chemical Reactions |
|
Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday Life |
|
Important Concepts Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 1
Ch 1 Science Class 10 covers the following concepts which are very important from an exam point of view:
Types of Chemical Reactions:
Combination Reactions: Reactions where two or more substances combine to form a single product.
Decomposition Reactions: Reactions where a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
Displacement Reactions: Reactions where an element displaces another element from its compound. This includes:
Single Displacement Reactions: A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
Double Displacement Reactions: The ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds.
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions: Understanding redox reactions, where oxidation involves electrons' loss and reduction involves electrons' gain.
Corrosion and Rancidity: Learning about the chemical processes involved in the corrosion of metals and rancidity of food, and methods to prevent them.
Benefits Referring NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Below are some of the benefits of Chapter 1 of Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions.
Students will get a clear idea of balancing various types of equations.
Chapter 1 Science Class 10 solutions make it easier for the students to formulate chemical equations.
To get more insights on Ch 1 Chemistry Class 10, Vedantu provides many practice questions of varying difficulty levels so that board examinations may be taken without worry.
Every question from ch 1 chemistry class 10 is explained in a step-by-step manner and these solutions are provided keeping in mind CBSE patterns.
Related Study Materials for Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10
Students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for Chemistry Class 10, Chapter 1–
S.No. | Study Material Links For Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 |
1. | Class 10 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions |
2. | |
3. | Class 10 Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Exemplar Solutions |
4. |
Conclusion
Class 10 Science Ch 1, "Chemical Reactions and Equations," solutions are presented straightforwardly, containing all essential details to help students understand chemical reactions and equations. With completely revised solutions and critical points aligned with exam specifications, students can rely on these solutions for effective exam preparation. NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 1 introduces numerous new concepts, making comprehending challenging. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 are prepared by Vedantu's experts to provide students with an ideal resource for practice, enhancing the learning process and ultimately helping students achieve better exam marks.
Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
S.No. | Links to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | |
9. | Chapter 10 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World Solutions |
10. | |
11. | |
12. |
Related Links for Class 10 Science
S.No. | Related Links for Class 10 Science |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations (2025-26)
1. Are chemical reactions and equations Class 10 questions and answers available?
Yes, chemical reactions and equations Class 10 questions and answers are provided in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 on Vedantu.
2. Do the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 question answers follow the NCERT textbook order?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 question answers on Vedantu follow the same sequence and questions as given in the NCERT textbook.
3. Can chemical reactions and equations Class 10 answers be used for homework?
Yes, chemical reactions and equations Class 10 answers from Vedantu can be used for homework and written practice.
4. Are the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions useful for school exams?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions on Vedantu are written in an exam-appropriate format that helps in school and board exam preparation.
5. Is there a PDF for class 10 science chemical reactions and equations solutions?
Yes, you can access a PDF for Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations solutions via the NCERT Solutions section on Vedantu.
6. Do Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions include step-by-step explanations?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions on Vedantu include clear, step-by-step explanations wherever required.
7. Can private candidates use Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations solutions?
Yes, private candidates following the NCERT curriculum can use Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations solutions available on Vedantu.
8. Are the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions aligned with the latest syllabus?
Yes, the Class 10 Science Chapter 1 solutions on Vedantu are aligned with the latest NCERT and CBSE curriculum.
9. Are the chemical reactions and equations Class 10 answers written in easy language?
Yes, chemical reactions and equations Class 10 answers on Vedantu are written in simple, student-friendly language.














 Watch Video
Watch Video

















