An Overview of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 14



FAQs on Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 14
1. What are the key characteristics that define a good or an ideal source of energy for the board exam?
For an exam question on an ideal energy source, you should list the following qualities:
- High Calorific Value: It should produce a large amount of heat per unit mass.
- Easy Availability: The source should be readily and easily accessible.
- Economical: It must be inexpensive and affordable for widespread use.
- Safe to Store and Transport: It should not pose significant risks during storage or transportation.
- Low Pollution: It should burn cleanly without producing harmful gases or residue.
2. Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy with two examples of each, as per the CBSE syllabus.
The key distinction between renewable and non-renewable energy sources is based on their rate of replenishment.
- Renewable Sources: These are energy sources that can be replenished naturally over a short period. They are considered inexhaustible. Important examples include solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, and biomass.
- Non-Renewable Sources: These are sources that have accumulated over millions of years and cannot be replenished quickly once consumed. Their reserves are finite. Key examples are coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
3. Explain the working principle of a box-type solar cooker. What is the significance of the black-painted surface and the glass cover?
A box-type solar cooker works by trapping solar heat through the greenhouse effect.
- Working Principle: It uses a concave or plane mirror reflector to concentrate sunlight into an insulated black box covered with a glass sheet. The light enters the box and is absorbed by the black surfaces.
- Black-Painted Surface: Black surfaces are excellent absorbers of heat. This maximises the absorption of incoming solar radiation, causing the temperature inside the cooker to rise significantly.
- Glass Cover: The glass sheet allows shorter-wavelength infrared radiation from the sun to pass through but traps the longer-wavelength heat radiated by the black surfaces inside. This prevents heat from escaping, leading to a gradual increase in temperature (the greenhouse effect).
4. What are fossil fuels? State three major disadvantages of our increasing dependency on them.
Fossil fuels are energy-rich substances formed from the decomposed remains of ancient plants and animals over millions of years. The main disadvantages of using them are:
- Pollution: Burning fossil fuels releases harmful gases like carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, which cause air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory problems.
- Greenhouse Effect: The release of carbon dioxide (a major greenhouse gas) contributes to a rise in the Earth's average temperature, leading to global warming and climate change.
- Non-Renewable: Fossil fuels are finite resources. Their rapid consumption is depleting the reserves, which cannot be replaced in our lifetime, leading to a future energy crisis.
5. Why is charcoal considered a better fuel than wood? Give three important reasons.
Charcoal is considered superior to wood as a fuel for several important reasons:
- Higher Calorific Value: Charcoal produces more heat per unit mass compared to wood.
- Smokeless Flame: It burns without producing smoke, making it a cleaner fuel and reducing air pollution.
- Compact and Easy to Handle: It is lighter and more compact than wood, making storage and transport more convenient.
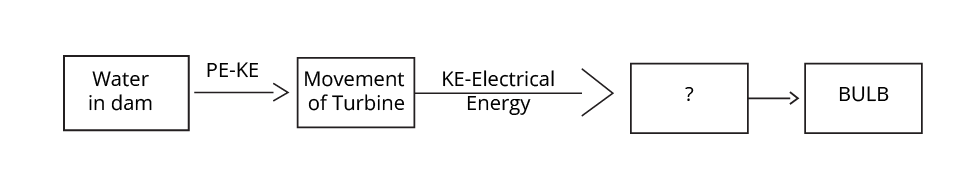
6. Explain how electricity is generated in a hydroelectric power plant. Why is the construction of large dams often opposed?
In a hydroelectric power plant, the potential energy of stored water is converted into electrical energy.
- Generation: Water stored at a height in a dam is allowed to fall through pipes. The force of the falling water turns the blades of a turbine. This turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy of rotation into electrical energy.
- Opposition to Dams: Large dams are opposed due to significant environmental and social problems, including the submergence of large areas of agricultural land and forests, the displacement of local populations, and negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
7. What are the main limitations of harnessing wind energy for commercial electricity generation?
While wind energy is a clean source, it has several limitations for large-scale use:
- Variable Wind Speed: Wind farms require a consistent wind speed of at least 15 km/h to operate efficiently. This is not available in all locations or at all times.
- Large Land Area: A wind farm requires a very large expanse of land to produce a significant amount of electricity.
- High Setup and Maintenance Costs: The initial cost of establishing a wind farm and the subsequent maintenance of the turbines are very high.
- Noise Pollution: The rotation of the blades can create considerable noise pollution for nearby residents.
8. What is biogas? Explain why it is considered a more efficient and useful fuel than cow dung cakes.
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily methane (up to 75%), carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulphide, produced by the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter like animal dung and plant waste. Biogas is superior to cow dung cakes because:
- Higher Calorific Value: It produces more heat than dung cakes.
- Clean Fuel: It burns without smoke, unlike dung cakes which cause air pollution.
- No Residue: Biogas leaves no ash after burning.
- Valuable Slurry: The leftover slurry is an excellent nitrogen and phosphorus-rich manure, whereas burning dung cakes destroys these nutrients.
9. What are the major advantages and disadvantages of using nuclear energy for generating electricity?
Nuclear energy offers significant benefits but also poses serious risks.
- Advantages: A small amount of nuclear fuel (like uranium) can produce a vast amount of energy. It does not produce greenhouse gases during operation, making it a clean energy source in that respect.
- Disadvantages: The major challenges are the high cost of building nuclear power plants, the immense risk associated with accidental radiation leaks, and the critical problem of safely storing and disposing of hazardous nuclear waste, which remains radioactive for thousands of years.
10. Can any source of energy be considered completely pollution-free in its entire lifecycle? Justify your answer with an example.
No source of energy can be considered completely pollution-free when analysing its entire lifecycle. While a source might be non-polluting during operation, the manufacturing and installation of the device that harnesses the energy often cause environmental damage. For example, solar cells generate electricity without any emissions, but the industrial process of manufacturing them requires significant energy and can release pollutants. Therefore, every energy source has some environmental impact at some stage.
11. Why are most conventional energy sources, like fossil fuels and biomass, considered indirect forms of solar energy, while geothermal and nuclear energy are not?
This is because the energy in most sources originates from the Sun.
- Solar-derived sources: Fossil fuels were formed from ancient plants and animals that depended on the sun for life. Wind is created by the uneven heating of the Earth by the sun. Biomass is direct plant matter that grows via photosynthesis using sunlight.
- Non-solar sources: Geothermal energy comes from the heat within the Earth's core, produced by the radioactive decay of elements. Nuclear energy is released from the nucleus of atoms, a process independent of solar energy.
12. Hydrogen is often called a cleaner fuel than CNG. As a Class 10 student, how would you justify this claim and also point out the major practical challenge in using hydrogen as a common fuel?
Hydrogen is considered a cleaner fuel because its combustion product is only water, which is non-polluting.
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water + Heat
In contrast, the combustion of CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), which is mainly methane (CH₄), produces carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, along with water.
The main practical challenge in using hydrogen is its safe storage and transportation. Hydrogen is highly inflammable and has a very low density, making it difficult to store in a compact and safe manner for use in vehicles or homes.