
Triangles Class 10 important questions with answers PDF download
Are you looking for important questions to help you master Chapter 6 - Triangles for CBSE Class 10 Maths? This chapter covers essential concepts like the similarity of triangles, proportionality theorems, and properties of triangles. By practising key questions, you can strengthen your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills. Whether it's finding the missing sides, applying similarity criteria (AA, SSS, SAS), or solving real-life problems, this chapter is crucial for scoring well in your exams according to the latest Class 10 Maths Syllabus.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentTo help you prepare, we’re offering a FREE PDF of the most important questions from Chapter 6 - Triangles. This resource is designed to provide you with a wide variety of problems to practise and improve your skills, making sure you're fully prepared for the upcoming exam. Download the PDF for Class 10 Maths Important Questions now and boost your preparation with high-quality questions for your success.
Important Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles - 2025-26



Access Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles Important Questions
1 Mark Question
1. In the figure \[\mathbf{\vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle EDC,}\]if we have \[\mathbf{\text{AB}=4~\text{cm},\text{ED}=3~\text{cm},\text{CE}=4.2~\text{cm}}\]and \[\mathbf{\text{CD}=4.8~\text{cm},}\]then the values of \[\mathbf{\text{CA}\,\,and\,\,\text{CB}}\] are
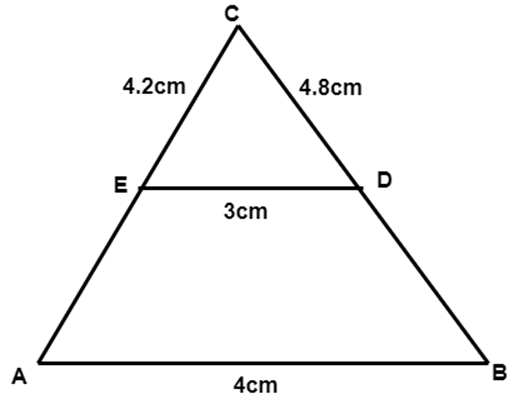
\[\mathbf{6~\text{cm},6.4~\text{cm}}\]
\[\mathbf{4.8~\text{cm},6.4~\text{cm}}\]
\[\mathbf{5.4~\text{cm},6.4~\text{cm}}\]
\[\mathbf{5.6~\text{cm},6.4~\text{cm}}\]
Ans: (d) $ 5.6~\text{cm},6.4~\text{cm} $
As the triangles are similar,
$ \dfrac{AB}{ED}=\dfrac{CA}{CE}=\dfrac{CB}{CD}=\dfrac{4}{3} $
$ \dfrac{CA}{CE}=\dfrac{CA}{4.2}=\dfrac{4}{3} $
$ CA=5.6 $
Then,
$ \dfrac{CB}{CD}=\dfrac{CB}{4.8}=\dfrac{4}{3} $
$ CB=6.4 $
2. The areas of two similar triangles are respectively $ \mathbf{9~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} }$ and $ \mathbf{16~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}} $ . Then ratio of the corresponding sides are
3:4
4:3
2:3
4:5
Ans: (a) $ 3:4 $
Ratio of area of triangle is equal to the square the ratio of the corresponding sides
Therefore, $ \sqrt{\dfrac{9}{16}}=\dfrac{3}{4} $
3. Two isosceles triangles have equal angles and their areas are in the ratio \[\mathbf{16:\text{ }25,}\]then the ratio of their corresponding heights is
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{4}{5} }$
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{5}{4}} $
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{3}{6} }$
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{5}{7}} $
Ans: (a) $ \dfrac{4}{5} $
Ratio of area of triangle is equal to the square the ratio of the corresponding sides
Therefore, $ \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{25}}=\dfrac{4}{5} $
4. If $ \mathbf{\vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle DEF} $ and $ \mathbf{AB=5~\text{cm}, }$ area $ \mathbf{(\Delta ABC)=20~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}, }$ area $\mathbf{ (\Delta DEF)=45~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}, }$ then $ \mathbf{\text{DE}= }$
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{4}{5}~\text{cm}} $
$ \mathbf{7.5~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{8.5~\text{cm}} $
$ \mathbf{7.2~\text{cm}} $
Ans: (b) $ 7.5~\text{cm} $
Ratio of area of triangle is equal to the square the ratio of the corresponding sides
Therefore, $ \sqrt{\dfrac{(\Delta ABC)}{(\Delta DEF)}}=\dfrac{AB}{DE} $
$ \sqrt{\dfrac{20}{45}}=\dfrac{5}{DE}\Rightarrow DE=7.5 $
$ \dfrac{(\Delta ABC)}{(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{20}{45}=\dfrac{5}{7.5} $
5. A man goes $ 15~\text{m} $ due west and then $ 8~\text{m} $ due north. Find distance from the starting point.
17
18
16
7
Ans: (A) $ 17~\text{m} $
Square of the distance = square of the sum of two distances.
$ =\sqrt{{{15}^{2}}+{{8}^{2}}}=\sqrt{225+64}=\sqrt{289}=17m $
6. In a triangle $ \text{ABC}, $ if $ \text{AB}=12~\text{cm},\text{BC}=16~\text{cm},\text{CA}=20~\text{cm}, $ then $ \vartriangle ABC $ is
Acute angled
Right angled
Isosceles triangle
Equilateral triangle
Ans: (b) Right angled
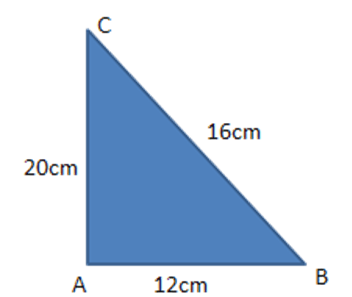
By law of Pythagoras triangle,
$ A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( 16 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}=400 $
$ AC=20 $
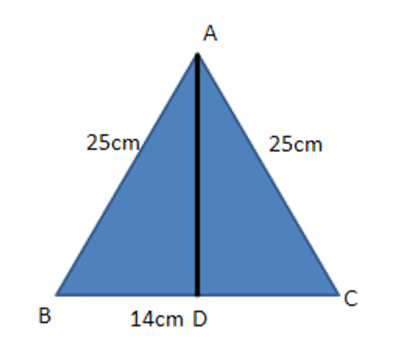
7. In an isosceles triangle $ \text{ABC},\text{AB}=\text{AC}=25~\text{cm} $ and $ \text{BC}=14~\text{cm}, $ then altitude from $ \text{A} $ on $ \text{BC}= $
20
24
12
None of these
Ans: (b) $ 24~\text{cm} $
8. The side of square who's diagonal is $ 16~\text{cm} $ is
$\mathbf{ 16~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{8\sqrt{2}~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{5\sqrt{2}~\text{cm} }$
None of these
Ans: (a) \[8\sqrt{2}~\text{cm}\]
Length of diagonal = sum of both sides of square.
$ {{\left( 16 \right)}^{2}}={{s}^{2}}+{{s}^{2}} $
$ 2{{s}^{2}}=16*16 $
$ {{s}^{2}}=8\left( 16 \right) $
$ s=8\sqrt{2} $
9.In an isosceles triangle $ \text{ABC}, $ if $ \text{AC}=\text{BC} $ and $ A{{B}^{2}}=2A{{C}^{2}}, $ then $ \angle C= $
$ \mathbf{{{45}^{{}^\circ }}} $
$ \mathbf{{{60}^{{}^\circ }} }$
$\mathbf{ {{90}^{{}^\circ }} }$
$ \mathbf{{{30}^{{}^\circ }} }$
Ans: (c) $ {{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
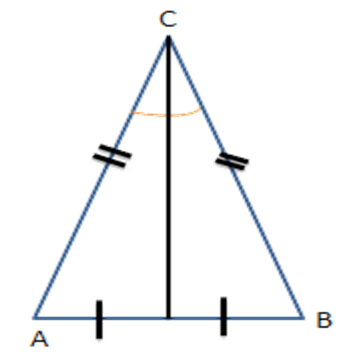
If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then angles opposite to those sides are congruent.
So $ \angle C=90{}^\circ $
10. If $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\Delta EDF $ and $ \vartriangle ABC $ is not similar to $ \vartriangle DEF, $ then which of the following is not true?
$\mathbf{ BC\times EF=AC\times FD }$
$ \mathbf{AB\times EF=AC\times DE }$
$ \mathbf{BC\times DE=AB\times EF }$
$ \mathbf{BC\times DE=AB\times FD }$
Ans: c) $ BC\times DE=AB\times EF $
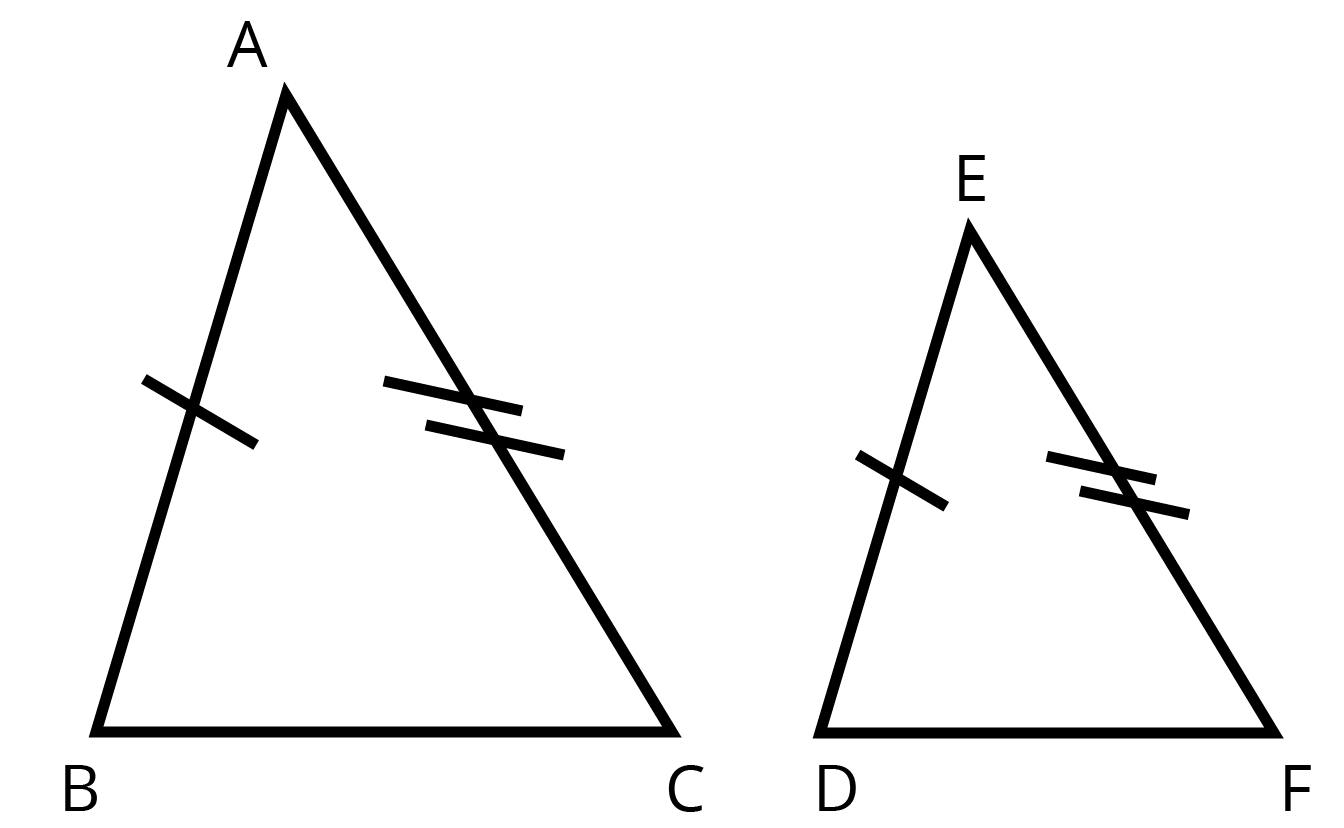
11.A certain right-angled triangle has its area numerically equal to its perimeter. The length of each side is an even integer, what is the perimeter?
24 units
36 units
32 units
30 units
Ans: 24 units
Length of each side is even integer amd also area is numerically equal its perimeter.
$ \therefore \left( 6,8,10 \right) $ make a Pythagorean triplet.
$ {{8}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}={{10}^{2}} $
Sum of all sides =perimeter
$ 6+8+10=24 $
12. In the given figure, if $ \text{AB}||\text{CD}, $ then $ x= $
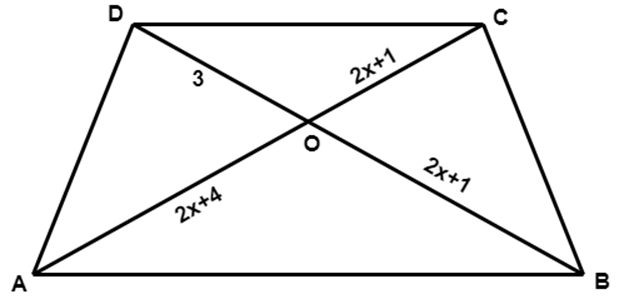
3
4
5
6
Ans: (a) 3
From the figure it is clear that the triangles $ \text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ OAB}\sim \text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ OCD} $ because all the corresponding angles are equal.
So, we have,
$ \dfrac{OA}{OC}=\dfrac{OB}{OD} $
$ \dfrac{2x+4}{2x+1}=\dfrac{2x+1}{3} $
$ 3\left( 2x+4 \right)=\left( 2x+1 \right)\left( 2x+1 \right) $
$ 6x+12=4{{x}^{2}}+4x+1 $
Now, by rearranging the terms to one side of the equation we get,
$ 4{{x}^{2}}-2x-11=0 $ …….(1)
Now, by using the formula of finding roots of quadratic equation
$ \text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=0} $ we get,
$ X = \dfrac {{-b}\pm{(\sqrt{{b^2} - 4ac)}}}{2a} $
By using this formula for equation (1) we get,
\[x=\dfrac{-\left( -2 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}} + 4\left( -11 \right)\left( 4 \right)}}{2\left( 4 \right)}\]
$ \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{2 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ 6}\sqrt{\text{5}}}{\text{8}} $
Here, the two values of $ \text{x} $ are,
$ \text{x=1}\text{.92} $
$ \text{x=-1}\text{.42} $
As the length cannot be negative so, the required value of $ \text{x} $ is $ 1.92 $ .
13.Length of an altitude of an equilateral triangle of side ' $ 2\text{a} $ ' $ \text{cm} $ is
$\mathbf{ 3\text{acm}} $
$ \mathbf{\sqrt{3}a~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a~\text{cm}} $
$\mathbf{ 2\sqrt{3}a~\text{cm} }$
Ans: (b) $ \sqrt{3}a~\text{cm} $
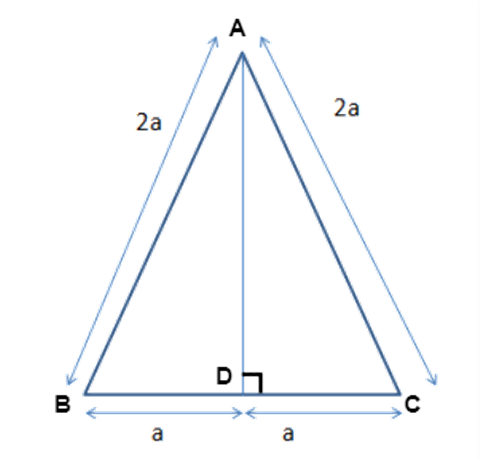
In the right angled $ \vartriangle ABC $
$ A{{B}^{2}}=A{{D}^{2}}+D{{B}^{2}} $
$ A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-D{{B}^{2}}=4{{a}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} $
$ AD=\sqrt{3}acm $
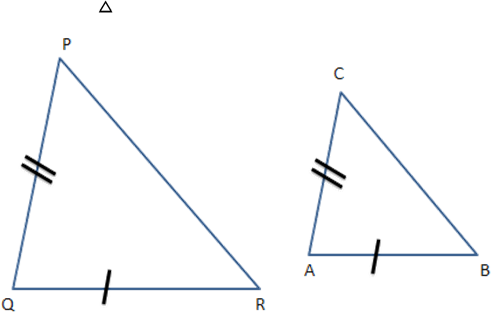
14. If in two triangles $ \text{ABC} $ and $ \text{PQR},\dfrac{AB}{QR}=\dfrac{BC}{PR}=\dfrac{CA}{PQ} $
$ \mathbf{\vartriangle PQR\sim\vartriangle CAB} $
$\mathbf{ \vartriangle PQR\sim\Delta ABC }$
$ \mathbf{\Delta CBA=\vartriangle PQR }$
$ \mathbf{\Delta BCA\sim\Delta PQR }$
Ans: a) $ \vartriangle PQR\sim\Delta CAB $
15. The area of two similar triangles are $ 81~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} $ and $ 49~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} $ respectively. If the altitude of the bigger triangle is $ 4.5~\text{cm}, $ then the corresponding altitude of the smaller triangle is
$ \mathbf{2.5~\text{cm}} $
$ \mathbf{2.8~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{3.5~\text{cm}} $
$ \mathbf{3.7~\text{cm} }$
Ans: c) $ 3.5~\text{cm} $
$ \dfrac{Area\,\,of\,\,l\arg er\vartriangle }{Area\,\,of\,\,smaller\vartriangle }={{\left( \dfrac{altitude\,\,\,of\,\,l\arg er\vartriangle }{altitude\,\,\,of\,\,smaller\vartriangle } \right)}^{2}} $
$ \dfrac{81}{49}=\dfrac{{{\left( 4.5 \right)}^{2}}}{{{x}^{2}}} $
$ \dfrac{9}{7}=\dfrac{4.5}{x} $
$ x=3.5 $
16.In figure, $ \text{DF}||\text{BC} $ and $ \text{AD}=1~\text{cm},\text{BD}=2~\text{m}. $ The ratio of the area of $ \vartriangle ABC $ to the area of $ \vartriangle ADE $ is
9:1
1: 9
3:1
none of these
Ans: (a) 9:1
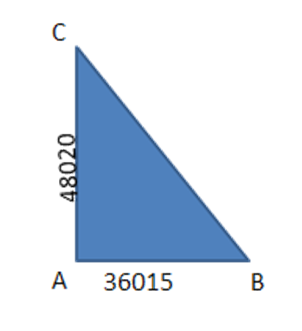
$ \dfrac{Area\,of\,\vartriangle ABC}{Area\,of\,\vartriangle ADF}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{A{{D}^{2}}} $
$ AB=AB+DB=1+2=3 $
$ \dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{A{{D}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{1}=\dfrac{9}{1} $
17.In the given figure, $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle PQR, $ then the value of $ x $ and $ y $ are
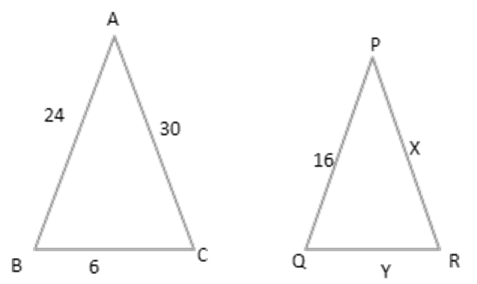
$\mathbf{ \left( x,y \right)=\left( 6,20 \right) }$
$ \mathbf{(20,60)} $
$ \mathbf{(x,y)=(3,10)} $
none of these
Ans: (d)none of these
$ \dfrac{AB}{PQ}=\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{BC}{QR} $
$ \dfrac{24}{16}=\dfrac{30}{x}=\dfrac{6}{y} $
$ \dfrac{24}{16}=\dfrac{30}{x}\Rightarrow x=20 $
$ \dfrac{24}{16}=\dfrac{6}{y}\Rightarrow y=4 $
$ \therefore \left( x,y \right)=\left( 20,4 \right) $
18.In figure, $ \text{P} $ and $ \text{Q} $ are points on the sides $ \text{AB} $ and AC respectively of $ \vartriangle ABC $ such that $ \text{AP}=3.5~\text{cm},\text{AQ}=3~\text{cm} $ and $ \text{QC}=6~\text{cm} $ . If $ \text{PQ}=4.5~\text{cm}, $ then $ \text{BC} $ is
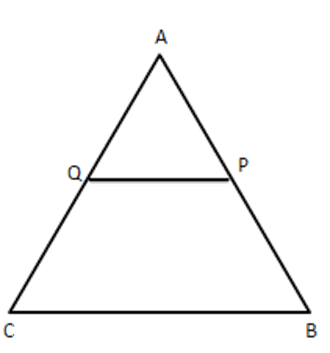
$\mathbf{ 12.5~\text{cm}} $
$ \mathbf{5.5~\text{cm} }$
$ \mathbf{13.5~\text{cm} }$
none of these
Ans: d)none of these.
$ \dfrac{AC}{AP}=\dfrac{CB}{PQ}=\dfrac{AB}{AQ} $
$ \dfrac{3+6}{3.5}=\dfrac{BC}{4.5}\Rightarrow BC=11.5 $
19.D, E, F are the mid-points of the sides $ \text{AB},\text{BC}, $ and CA respectively of $ \vartriangle ABC, $ then $ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEF)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)} $ is
1: 4
4: 1
1: 2
none of these
Ans: (a) 1: 4
$ AB=2AD $
$ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEF)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}={{\left( \dfrac{DE}{AB} \right)}^{2}} $
$ ={{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{4} $
2 Marks Questions
1. In the given figures, $ \vartriangle ODC\sim\vartriangle OBA,\angle BOC={{125}^{{}^\circ }} $ and $ \angle CDO={{70}^{{}^\circ }}. $ Find
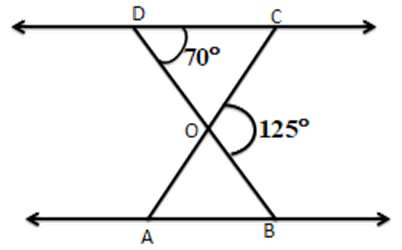
(i) $ \mathbf{\angle DOC }$
Ans: The sum of each interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle is equal to 180 degrees
$ \angle DOC={{180}^{{}^\circ }}-{{125}^{{}^\circ }}={{55}^{{}^\circ }} $
(ii) $\mathbf{ \angle DCO} $
Ans: $ \angle DCO={{180}^{{}^\circ }}-\left( {{70}^{{}^\circ }}+{{55}^{{}^\circ }} \right)[\because DOB $ is a straight line and OC stands on it]
$ ={{180}^{{}^\circ }}-{{125}^{{}^\circ }}={{55}^{{}^\circ }}\left[ \because \right. $ sum of angles of a triangle $ \left. ={{180}^{{}^\circ }} \right] $
(iii) $ \mathbf{\angle OAB }$
Ans: $ \left[ \begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \because \vartriangle ODC\sim\vartriangle OBA(\text{ given }) \\ \therefore \angle DOC=\angle AOB,\angle ODC=\angle OBA,\angle DCO=\angle OAB \\ \end{array} \right] $
(iv) $ \mathbf{\angle AOB }$
Ans: $ \angle AOB=\angle DOC={{55}^{{}^\circ }} $
(v) $\mathbf{ \angle OBA }$
Ans: $ \angle OBA=\angle ODC={{70}^{{}^\circ }} $
2. $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle DEF $ and their areas are respectively $ 64~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} $ and $ 121~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}. $ If $ \text{EF}=15.4~\text{cm}, $ find $ \text{BC}. $
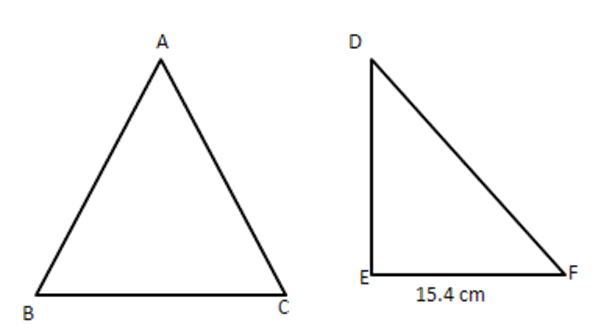
Ans: $ \text{ Since }\vartriangle ABC\sim\Delta DEF\therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{area}(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{area}(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}} $
$ [\because $ the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of the corresponding sides]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{64}{121}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{{{(15.4)}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=\dfrac{64\times 154\times 154}{121\times 10\times 10}=\dfrac{64\times 14\times 14}{100} $
$ \Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{8\times 14}{10}=11.2~\text{cm} $
3. $ \text{ABC} $ is an isosceles right triangle right-angled at $ \text{B}\text{.} $ Prove that $ A{{C}^{2}}=2A{{B}^{2}} $
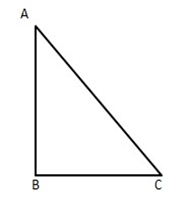
Ans: In right-angled $ \vartriangle ABC, $ right $ \angle A\,\,at\,\,B $
$ A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}[ $ By Pythagoras theorem]
$ =A{{B}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}}=2A{{B}^{2}}\quad [\because BC=AB(given)] $
$ =A{{C}^{2}}=2A{{B}^{2}} $
4. In the figure, $ \text{DE}||\text{AC} $ and $ \dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}, $ prove that
Ans: In $ \Delta ABC,DE\|AC $
$ \therefore \dfrac{BD}{DA}=\dfrac{BE}{EC}\ldots \ldots (i) $ [By Thales's Theorem]
Also $ \dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}(given)\ldots \ldots .(ii) $
$ \therefore $ from (i) and (ii), we get
$ \dfrac{BD}{DA}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}\therefore DC\|AP $
(By the converse of Thales's Theorem)
5.The hypotenuse of a right triangle is $ 6~\text{m} $ more than twice of the shortest side. If the third side is $ 2~\text{m} $ less than the hypotenuse. Find the side of the triangle.
Ans: Let shortest side be $ Xm $ in length
Then hypotenuse $ =(2x+6)m $
And third side $ =(2x+4)m $
We have,
$ {{(2x+6)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{(2x+4)}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+24x+36={{x}^{2}}+4{{x}^{2}}+16+16x $
$ \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-8x-20=0 $
$ \Rightarrow x=10\text{ or }x=-2\text{ } $
$ \Rightarrow x=10 $
Hence, the sides of triangle are $ 10~\text{m},26~\text{m} $ and $ 24~\text{m}. $
6. PQR is a right triangle right angled at P and M is a point on QR such that \[\text{PM}\bot \]QR. Show that \[P{{M}^{2}}=QM.MR\]
Ans: Given PQR is a right triangle right angled at P and $ PM\bot QR $
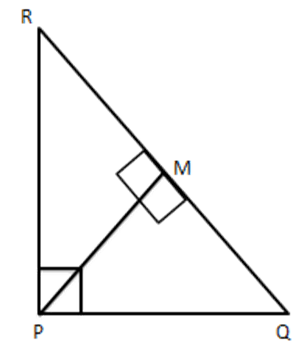
$ \therefore \vartriangle PMR\sim\vartriangle PMQ $
$ \therefore \dfrac{PR}{PQ}=\dfrac{PM}{QM}=\dfrac{MR}{PM} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{PM}{QM}=\dfrac{MR}{PM} $
$ \text{ i}\text{. e}\text{., }P{{M}^{2}}=QM.MR $
7. In the given figure, \[\mathbf{D}\text{ }\mathbf{E}\text{ }\left\| \mathbf{O}\text{ }\mathbf{Q}\text{ }\mathbf{and}\text{ }\mathbf{D}\text{ }\mathbf{F}\text{ }\left\| OR \right. \right.\text{ },\]Prove that \[\mathbf{E}\text{ }\mathbf{F}\text{ }\left\| OQ \right.\]
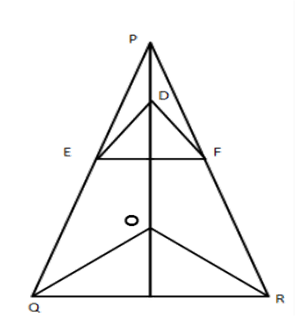
Ans: In $ \vartriangle OQR,DE\|OQ $
$ \dfrac{PE}{EQ}=\dfrac{PD}{DO}\,\,\,\,.....\left( 1 \right) $
In $ \vartriangle OPR,DF\|OR $
$ \dfrac{PD}{DO}=\dfrac{PF}{FR}\ldots \left( ii \right) $
From (i) and (ii), we get
$ \dfrac{PE}{EQ}=\dfrac{PF}{FR} $
$ \therefore From\,\,\vartriangle PQR $
$ EF\|QR $
8. In figure, $ \text{DE}||\text{BC} $ . Find EC
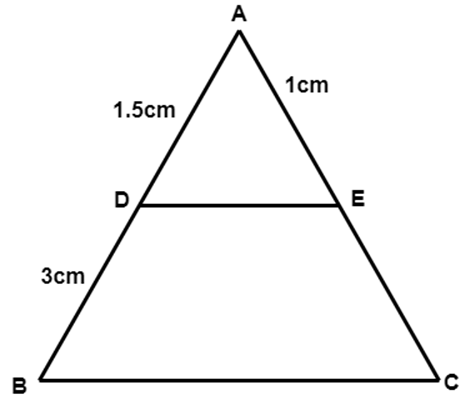
Ans: $ \because DE\|BC $
$ \therefore \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{AE}{EC} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{3}=\dfrac{1}{EC} $
$ \therefore EC=2~\text{cm} $
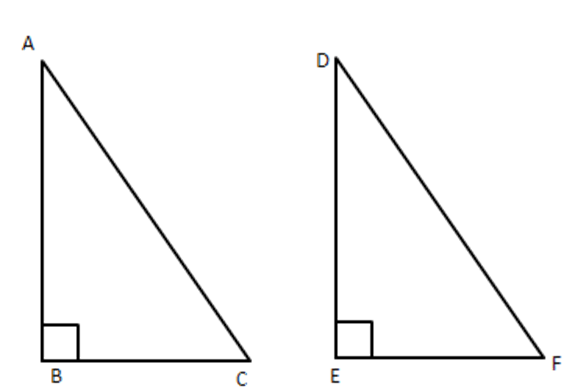
9. In the given figure, $ \text{ABC} $ and AMP are two right-angled triangles, right angled at $ \text{B} $ and M respectively, prove that
$ (i)\vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle AMP $
(ii) $ \dfrac{CA}{PA}=\dfrac{BC}{MP} $
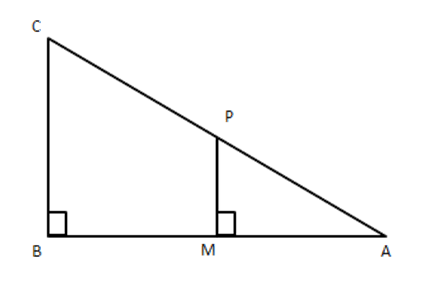
Ans: In $ \vartriangle ABC $ and DAMP,
$ \angle B=\angle M\left( {} \right. $
Each $ \left. {{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right) $
$ \angle A=\angle A(\text{common}) $
$ \therefore \angle ACB=\angle APM $
$ \therefore \Delta S $ are equiangular
i.e., $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle AMP $
$ \therefore \dfrac{BC}{MP}=\dfrac{CA}{PA} $
10. In the given figure, $ \text{OA}\times \text{OB}=\text{OC}\times OD $ or $ \dfrac{OA}{OC}=\dfrac{OD}{OB} $ , prove that $ \angle A=\angle C\,\,and\,\,\angle B=\angle D $
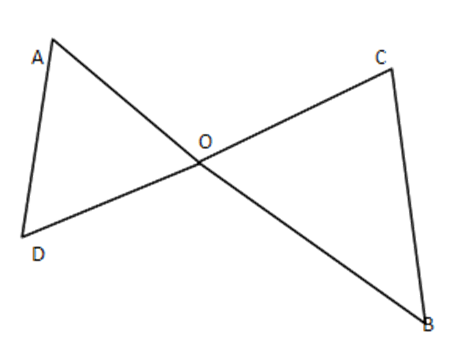
Ans: In $ \vartriangle AOD\,\, $ and $ \vartriangle BOC, $
$ OA\times OB=OC\times OD $
$ \text{ i}\text{.e }\dfrac{OA}{OC}=\dfrac{OD}{OB} $
And $ \angle AOD=\angle BOC $ (Vertically opposite Angles)
$ \therefore \vartriangle AOD\sim\Delta BOC(BySAS) $
$ \therefore \angle A=\angle C $ and $ \angle B=\angle D $ (Corresponding angles of similar $ \Delta $ )
11. In the given figure,
$ \text{DE}\|\text{BC} $ and $ \text{AD}=1~\text{cm},\text{BD}=2~\text{cm}. $ What is the ratio of the area of $ \vartriangle ABC $ to the area of $ \vartriangle ADE $ ?
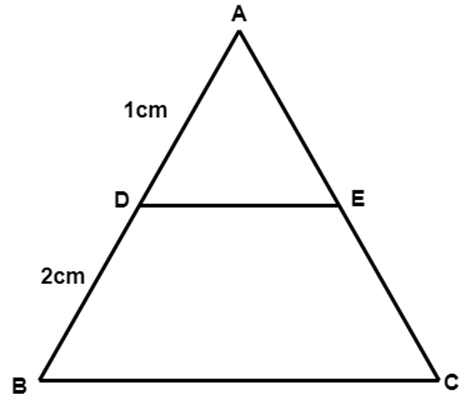
Ans: $ \because DE\|BC $ in $ \vartriangle ABC $ $ \therefore \angle ADE=\angle ABC $
$ \angle AED=\angle ACB $
Also $ \angle DAE=\angle DAC $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ADE\sim\Delta ABC $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ADE\sim\vartriangle ABC $
$ \therefore\dfrac{A{{D}^{2}}}{A{{B}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\operatorname{area}(\vartriangle ADE)}{\operatorname{area}(\vartriangle ABC)} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{1}^{2}}}{{{3}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\operatorname{area}(\Delta ADE)}{\text{ area }(\Delta ABC)}[\because AB=AD+OB=1+2=3] $
$ \text{ Hence, }\dfrac{\operatorname{area}(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{area}(\Delta ADE)}=\dfrac{9}{1} $
12. A right-angle triangle has hypotenuse of length $ \text{p }cm $ and one side of length $ \text{qcm}. $ If $ \mathbf{p}-q=1, $ Find the length of third side of the triangle.
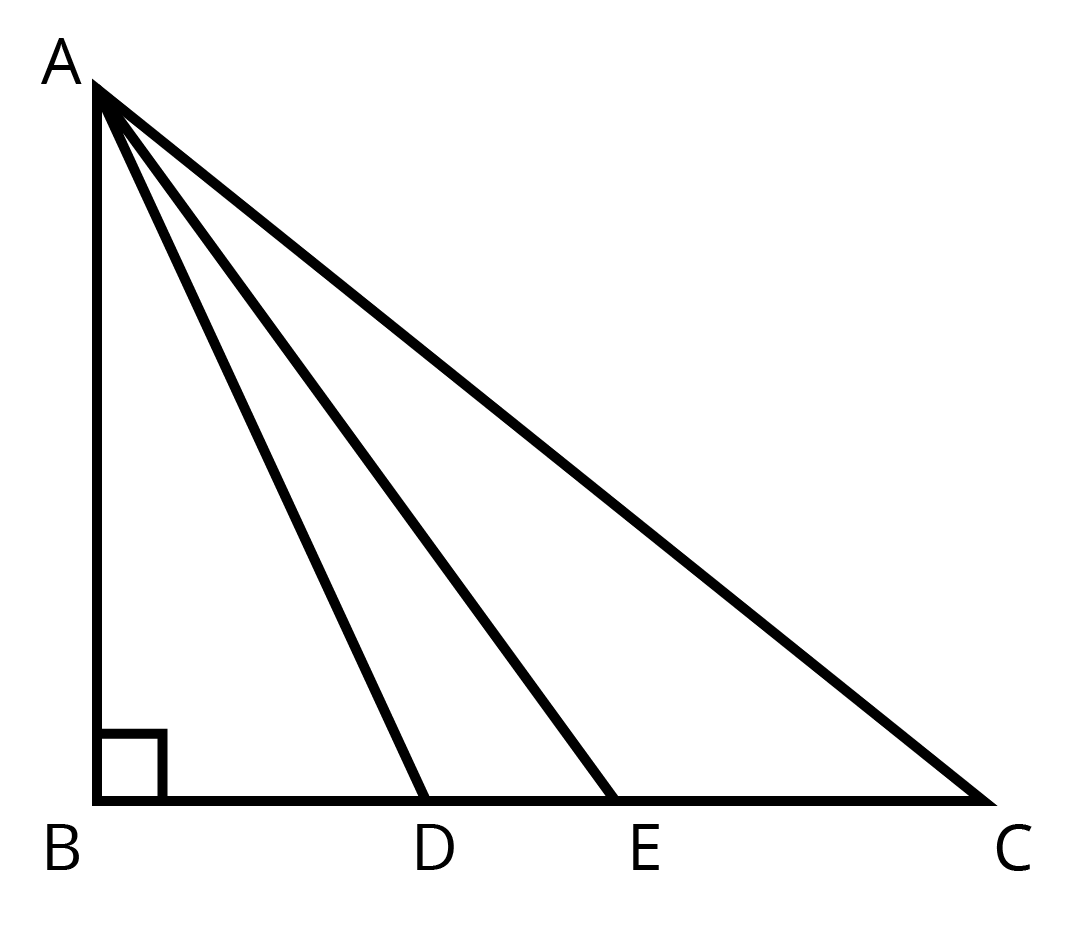
Ans: Let third side $ =\text{xcm} $
Then by Pythagoras theorem.
$ {{p}^{2}}={{q}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} $
$ {{x}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}-{{q}^{2}} $
$ =(p+q)\times 1(\because p-q=1) $
\[=q+1+q\]
\[=2\text{ }q+1\]
$ \therefore x=\sqrt{2q+1} $
13. The length of the diagonals of a rhombus are $ 24~\text{cm} $ and $ 10~\text{cm} $ . Find each side of rhombus.
Ans: $ AC=24~\text{cm}\therefore AO=12~\text{cm} $
$ BD=10~\text{cm}\therefore OD=5~\text{cm} $
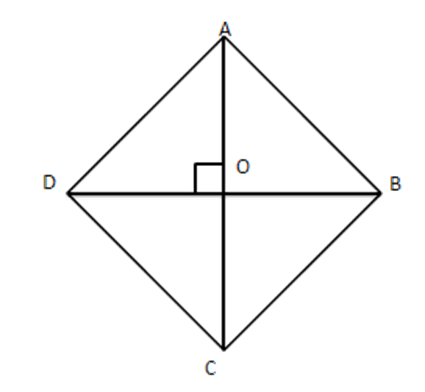
From right-angled $ \vartriangle AOD\,\,\,A{{D}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+O{{D}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=169 $
$ \Rightarrow AD=13~\text{cm} $
Hence each side $ =13~\text{cm} $
14. In an isosceles right-angled triangle, prove that hypotenuse is $ \sqrt{2} $ times
Ans: Let hypotenuse of right-angled $ \Delta =h $ units and equal sides of triangle $ x $ units
$ \therefore $ By Pythagoras theorem,
$ {{h}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=2{{x}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{2}x $
15. In figure, express $ \text{x} $ in terms of $ \mathbf{a},\mathbf{b},\mathbf{c}. $
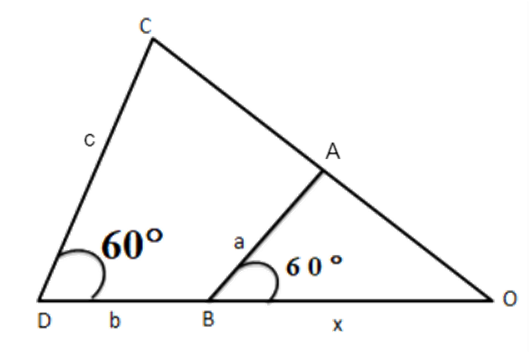
Ans: $ \vartriangle ABO\sim\vartriangle OCD $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}=\dfrac{x+b}{c} $
$ \Rightarrow x=ax+ab $
$ \Rightarrow x(c-a)=ab $
$ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{ab}{c-a} $
16. The perimeter of two similar triangle ABC and PQR are respectively $ 36~\text{cm} $ and $ 24\text{cm}. $ If $ \text{PQ}=10~\text{cm}, $ find $ \text{AB}. $
Ans: $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\Delta PQR $
$ \therefore \dfrac{AB}{PQ}=\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{AC}{PR} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB+BC+AC}{PQ+QR+PR}=\dfrac{\text{ perimeter of }\Delta ABC}{\text{ perimeter of }\Delta PQR} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{10}=\dfrac{36}{24} $
$ \Rightarrow AB=\dfrac{36\times 10}{24}=15~\text{cm} $
17. In the given figure, $ \text{DE}||\text{BC}. $ If $ AD=x,DB=x-2,AE=x+2,EC=x-1 $ find the value of \[\mathbf{x}.\]
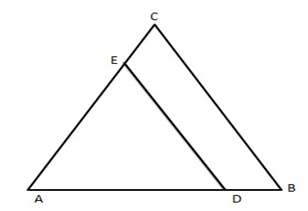
Ans: In the given figure,
\[D\text{ }E\text{ }\left\| BC \right.\]
$ \therefore \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{AE}{EC} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{x-2}=\dfrac{x+2}{x-1} $
$ \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-x={{x}^{2}}-4 $
$ \Rightarrow x=4 $
18. In the given figure, $ \dfrac{AO}{OC}=\dfrac{BO}{OD}=\dfrac{1}{2} $ and $ \text{AB}=5~\text{cm}, $ find the value of $ \text{DC}. $
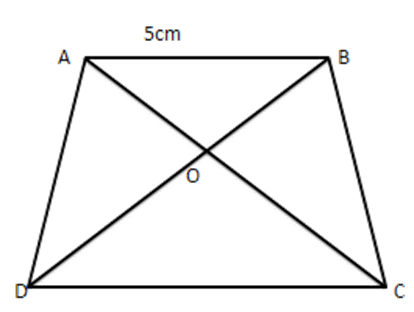
Ans: In $ \vartriangle AOB $ and $ \vartriangle COD, $
$ \angle AOB=\angle COD $ [Vertically opposite angles]
$ \dfrac{AO}{OC}=\dfrac{BO}{OD}\Rightarrow \dfrac{AO}{OB}=\dfrac{OC}{OD} $ [Given]
$ \therefore \vartriangle AOB\sim\vartriangle COD $ [By SAS similarity]
$ \therefore \dfrac{AO}{CO}=\dfrac{BO}{DO}=\dfrac{AB}{CD} $
$ \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{AB}{DC}\left[ \dfrac{AO}{OC}=\dfrac{BO}{OD}=\dfrac{1}{2} \right.is\,\,\,given] $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{DC} $
$ \Rightarrow DC=10~\text{cm} $
19. In $ \vartriangle ABC,AB=AC $ and $ \text{D} $ is a point on side $ \text{AC}, $ such that $ \text{B}{{\text{C}}^{2}}=AC\times CD\cdot $ Prove that $ \text{BD}=\mathbf{BC}. $
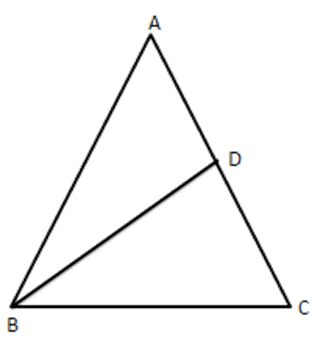
Ans: Given: $ \Delta ABC $ in which $ AB=AC,D $ is a point on $ BC $
To prove: $ \text{BD}=\text{BC } $
Proof: $ B{{C}^{2}}=AC\times CD $ [given]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{DC}{BC} $
$ \text{ In }\vartriangle ABC\text{ and }\vartriangle BDC, $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{BC}{CA}=\dfrac{DC}{CB}\text{ and }\angle C=\angle C[\text{ Common }] $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle BDC[\text{SASsimilarity}] $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{BD}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\Rightarrow \dfrac{AC}{BD}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}[\because AB=AC] $
$ \Rightarrow BD=BC $
3 Marks Questions
1. In the given figure, $ \dfrac{QT}{PR}=\dfrac{QR}{QS} $ and $ \angle 1=\angle2 $ . Prove that $ \Delta PQS\sim\Delta TQR $
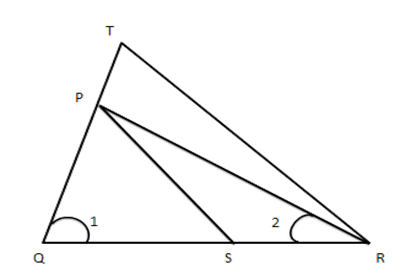
Ans: Since $ \dfrac{QT}{PR}=\dfrac{QR}{QS} $ [Given]
$ \therefore \dfrac{QT}{QR}=\dfrac{PR}{QS} $
Since $ \angle 1=\angle 2\,\,\,[Given] $
$ PQ=PR $
(In $ \Delta PQR $ sides opposites to opposite angles are equal)
$ \therefore \dfrac{QT}{QR}=\dfrac{PQ}{QS}\ldots \ldots .(iii)[\operatorname{Form}(i)\text{ and }(ii)] $
Now in $ \vartriangle PQS $ and $ \vartriangle TQR $
From (iii), \[\dfrac{PQ}{QS}=\dfrac{QT}{QR}i.e.\dfrac{PQ}{QT}=\dfrac{QS}{QR}\]
And $ \angle Q=\angle Q $ [Common]
$ \therefore \Delta PQS\sim\Delta TQR $ [By S.A.S. Rule of similarity]
2. In the given figure, PA, QB and RC are each perpendicular to AC. Prove that $ \dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{y} $
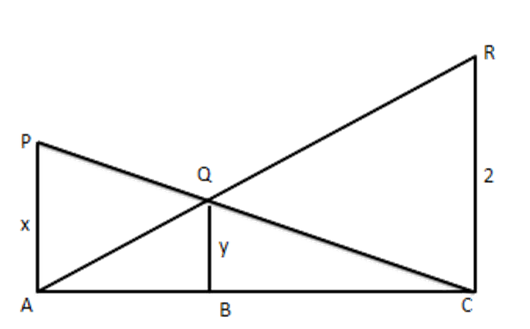
Ans: In $ \vartriangle PAC\text{ and }\Delta QBC\text{ } $
$ \angle PAC=\angle QBC\left[ \text{ Each }={{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right] $
$ \angle PCA=\angle QCB[\text{Common}] $
$ \therefore \vartriangle PAC\sim\Delta QBC $
$ \dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\text{ i}\text{.e}\text{. }\dfrac{y}{x}=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\ldots \ldots .(i) $
$ \text{ Similarly, }\dfrac{z}{y}=\dfrac{AC}{AB}\text{ i}\text{.e}\text{. }\dfrac{y}{z}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\ldots \ldots .(ii) $
$ \text{Adding (i) and (ii), we get } $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{BC+AB}{AC}=\dfrac{y}{x}+\dfrac{y}{z}=y\left( \dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{z} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AC}{AC}=y\left( \dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{z} \right)\Rightarrow 1=\left( \dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{z} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{z} $
3. In the given figure, $ \text{DE}||\text{BC} $ and AD:DB \[=\mathbf{5}:\text{ }\mathbf{4},\]find $ \dfrac{\text{ area }(\Delta DFE)}{\text{ area }(\Delta CFB)} $ .
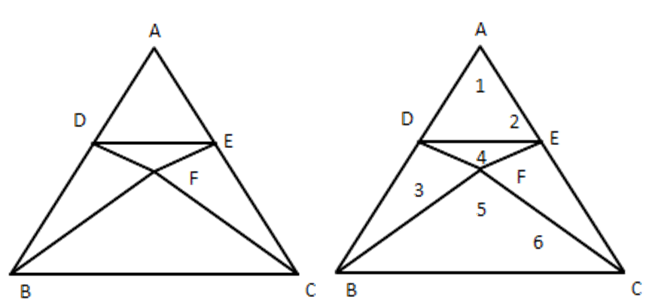
Ans: In $ \vartriangle ADE $ and $ \vartriangle ABC, $ $ \angle 1=\angle 1 $ (Common)
$ \angle 2=\angle ACB $ [Corresponding angles]
$ \therefore \vartriangle ADE\sim\vartriangle ABC $ [By A.A Rule]
$ \therefore \dfrac{DE}{BC}=\dfrac{AD}{AB}\ldots \ldots ..i) $
Again in $ \vartriangle DEF $ and $ \vartriangle CFB, $
$ \angle 3=\angle 6\,\,[Alternate\,\,\,angles] $
$ \angle 4=\angle 5 $ [Vertically oppositeangles]
$ \therefore \Delta DFE\sim\vartriangle CFB $ [By A.A Rule]
$ \therefore \dfrac{\text{ Area }(\Delta DFE)}{\text{ area }(\Delta CFB)}=\dfrac{D{{E}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}}={{\left( \dfrac{AD}{AB} \right)}^{2}} $ [From (i)]
$ ={{\left( \dfrac{5}{9} \right)}^{2}}\left[ \because \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{5}{4}\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{AD+DB}=\dfrac{5}{5+4}\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{5}{9} \right] $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{area}(\Delta DFE)}{\operatorname{area}(\Delta CFB)}=\dfrac{25}{81} $
3. Determine the length of an altitude of an equilateral triangle of side ‘2a’ cm.
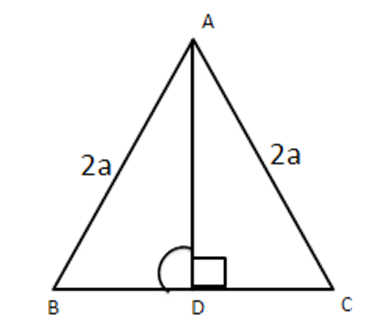
Ans: In right triangles $ \vartriangle ADB $ and $ \vartriangle ADC, $
\[A\text{ }B=A\text{ }C\]
\[A\text{ }D=A\text{ }D\]
$ \therefore \angle ADB=\angle ADC\left( {} \right.Each\left. ={{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right) $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ADB\cong \vartriangle ADC(RHS) $
$ \therefore BD=DC(CPCT) $
$ \therefore BD=DC=a[\because BC=2a] $
In right $ \vartriangle ADB,A{{D}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}} $ (By Pythagoras Theorem)
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{(2a)}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=4{{a}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow AD=\sqrt{3}a~\text{cm} $
4. In the given figure, if $ \angle 1=\angle 2 $ and $ \vartriangle NSQ\cong \vartriangle MTR. $ Then prove that $ \Delta PTS\sim\Delta PRO $
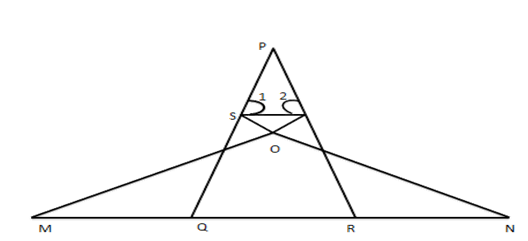
Ans: $ \Rightarrow \angle Q=\angle R(\text{ in }\Delta PQR) $
$ ={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-\dfrac{1}{2}\angle P $
$ \text{Again }\angle 1=\angle 2[\text{given}\,\,\,\text{in}\,\,\vartriangle \text{PST}] $
$ \therefore \angle 1=\angle 2=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{180}^{{}^\circ }}-\angle P \right) $
$ ={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-\dfrac{1}{2}\angle P $
Thus, in $ \Delta PTS $ and $ \vartriangle PRQ $
$ \angle 1=\angle Q\left[ \text{ Each }={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-\dfrac{1}{2}\angle P \right] $
$ \angle 2=\angle R,\angle P=\angle P(\text{ Common }) $
$ \Delta PTS\sim\Delta PRQ $
5. In the given figure the line segment XY||AC and XY divides triangular region ABC into two points equal in area, Determine $ \dfrac{AX}{AB} $ .
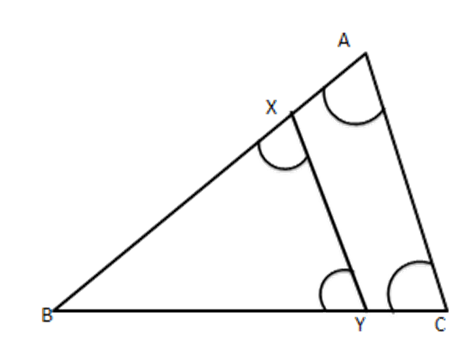
Ans: Since $ XY\|AC $
$ \therefore \angle BXY=\angle BAC $
$ \angle BYX=\angle BCA $ [Corresponding angles]
$ \therefore \Delta BXY\sim\vartriangle BAC $ [A.A. similarity]
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta BXY)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta BAC)}=\dfrac{B{{X}^{2}}}{B{{A}^{2}}} $
But $ \operatorname{ar}(\Delta BXY)=\operatorname{ar}(XYCA) $
$ \therefore 2(\Delta BXY)=\operatorname{ar}(\Delta BXY)+\operatorname{ar}(XYCA) $
$ =\operatorname{ar}(\Delta BAC) $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta BXY)}{ar(\Delta BAC)}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{B{{X}^{2}}}{B{{A}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{BX}{BA}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{BA-BX}{BA}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AX}{AB}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{2}}{2} $
6. BL and CM are medians of $ \vartriangle ABC $ right angled at A. Prove that $ 4\left( \text{B}{{\text{L}}^{2}}+\text{C}{{\text{M}}^{2}} \right)=5\text{B}{{\text{C}}^{2}} $
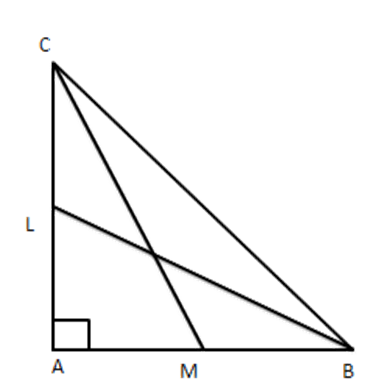
Ans: BL and CM are medians of a $ \vartriangle ABC $ in which $ \angle A={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
From $ \Delta ABC,B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}} $
From right angled $ \vartriangle ABL, $
$ B{{L}^{2}}=A{{L}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}} $
$ i.e.,B{{L}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 4B{{L}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+4A{{B}^{2}} $
(ii)
From right-angled $ \vartriangle CMA $
$ C{{M}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+A{{M}^{2}} $
i.e. $ C{{M}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{AB}{2} \right)}^{2}} $ [ mid-point]
$ \Rightarrow C{{M}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow 4C{{M}^{2}}=4A{{C}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}} $
Adding (ii) and (iii), we get
i.e. $ 4\left( B{{L}^{2}}+C{{M}^{2}} \right)=5B{{C}^{2}} $ [From (i)]
7. $ \text{ABC} $ is a right triangle right angled at $ \text{C}. $ Let $ \text{BC}=\text{a},\text{CA}=\mathbf{b},\text{AB}=\text{c} $ and let $ \text{p} $ be the length of perpendicular from C on AB, prove that
(i) $ \mathbf{cp}=\mathbf{ab} $
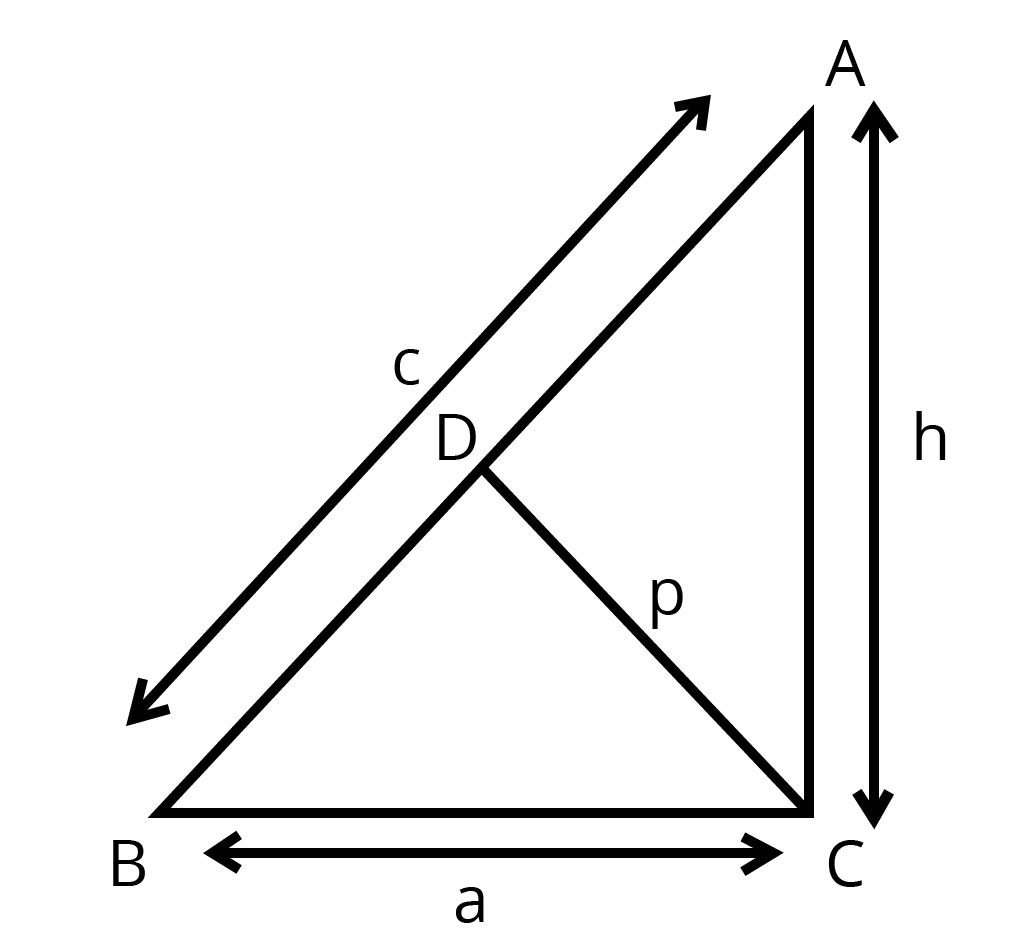
Ans: Draw $ CD\bot AB $
Then, $ CD=p $
Now area of $ \vartriangle ABC=\dfrac{1}{2}(BC\times CA) $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2} a b $
Also area of $ \Delta ABC=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\times CD $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}cp $ Then, $ \dfrac{1}{2}ab=\dfrac{1}{2}cp $
$ \Rightarrow cp=ab $
(ii) $ \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}} $
Ans: Since $ \vartriangle ABC $ is a right-angled triangle with $ \angle C={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ \therefore A{{B}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{ab}{p} \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} $
$ \therefore cp=ab $
$ \Rightarrow c=\dfrac{ab}{p} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}} $
Thus $ \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}} $
8. In figure, a triangle $ \text{ABC} $ is right-angled at B. side BC is trisected at points $ \text{D} $ and $ \text{E}, $ prove that $ 8A{{E}^{2}}=3A{{C}^{2}}+5A{{D}^{2}} $ .
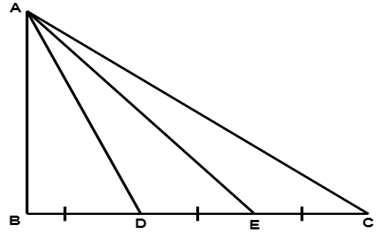
Ans: Given: $ \vartriangle ABC $ is right-angled at \[B.\]Side BC is trisected at D and E.
To Prove: $ 8A{{E}^{2}}=3A{{C}^{2}}+5A{{D}^{2}} $
Proof: D and E are the paints of trisection of BC
$ BD=\dfrac{1}{3}BC\text{ and }BE=\dfrac{2}{3}BC $
In right-angled triangle $ \text{ABD} $
$ A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}}\ldots \ldots \ldots .(ii) $ [Using Pythagoras theorem]
In $ \vartriangle ABE $
$ A{{E}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{E}^{2}}\ldots \left( iii \right) $
In $ \vartriangle ABC $
$ A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}\ldots \left( iv \right) $
From (ii) and (iii), we have
$ A{{D}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}=B{{D}^{2}}-B{{E}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{3}BC \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{2}{3}BC \right)}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{9}B{{C}^{2}}-\dfrac{4}{9}B{{C}^{2}}=\dfrac{-3}{9}B{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{E}^{2}}-A{{D}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}B{{C}^{2}}\ldots \ldots .(v) $
From (iii) and (iv), we have
$ A{{C}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}-B{{E}^{2}} $
$ =B{{C}^{2}}-\dfrac{4}{9}B{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{9}B{{C}^{2}} $
From (v) and (vi), we get
$ A{{C}^{2}}-A{{E}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{3}\left( A{{E}^{2}}-A{{D}^{2}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow 3A{{C}^{2}}-3A{{E}^{2}}=5A{{E}^{2}}-5A{{D}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 8A{{E}^{2}}=5A{{D}^{2}}+3A{{C}^{2}} $
9. In figure, DEFG is a square and $ \angle BAC={{90}^{{}^\circ }}, $ show that $ D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC $ .
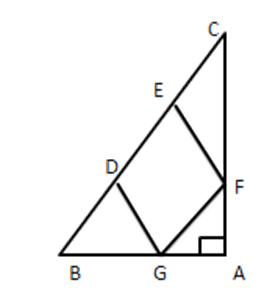
Ans: Given: $ \vartriangle ABC $ is right-angled at A and DEFG is a square To Prove: $ D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC $
Proof: Let $ \angle C=x\ldots \ldots ..(i) $
Then, $ \angle ABC={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-x[\because \Delta ABC $ is right angled ]
Also $ \Delta BDG $ is right-angled at D.
$ \angle BGD={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-\left( {{90}^{{}^\circ }}-x \right)=x\ldots \ldots .(ii) $
From (i) and (ii), we get
$ \angle BGD=\angle C\ldots \ldots ..(iii) $
Consider $ \Delta BDG\,\,and\,\,\Delta CEF $
$ \angle CEF=\angle BDG=90[\because DEFG $ is square ]
$ \angle BGD=\angle C $ [From (iii) ]
$ \therefore \vartriangle BDG\sim\vartriangle FEC\,\,[ByAAsimilarity] $
$ \therefore \dfrac{BD}{EF}=\dfrac{DG}{EC} $
$ \Rightarrow EF\times DG=BD\times EC $
But $ EF=DG=DE[\because $ side of a square]
$ \Rightarrow DE\times DE=BD\times EC $
$ \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=BD\times EC $
10.In a quadrilateral $ \text{ABCD},\text{P},\text{Q},\text{R},\text{S} $ are the mid-points of the sides $ \text{AB},\text{BC},\text{CD} $ and DA respectively. Prove that PQRS is a parallelogram.
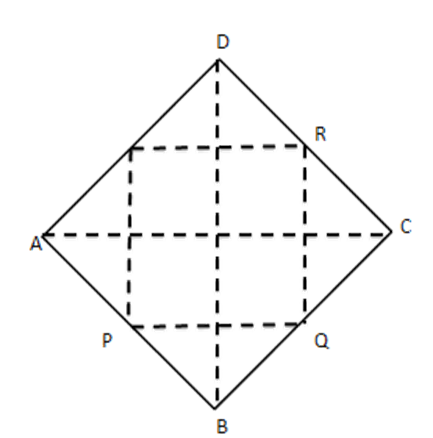
Ans: To Prove: PQRS is a parallelogram
Construction: Join AC
Proof: In $ \vartriangle DAC, $
$ \dfrac{DS}{SA}=\dfrac{DR}{RC}=1[\because \text{S} $ and R are mid-points of AD and DC ]
$ \Rightarrow SR\|AC $ ....... (i) [by converse of B.P.T]
In $ \Delta BAC,\dfrac{PB}{AP}=\dfrac{BQ}{QC}=1[\because \text{P} $ and $ \text{Q} $ are mid points of $ \text{AB} $ and BC]
$ \Rightarrow PQ\|AC $ .......(ii) [By converse of B.P.T]
From (i) and (ii), we get
$ SR\|PQ\ldots \ldots .(iii) $
Similarly, join B to D and PS| |QR
$ \Rightarrow \therefore PQRS $ is a parallelogram.
11. Triangle $ \text{ABC} $ is right-angled at $ \text{C} $ and $ \text{CD} $ is perpendicular to $ \text{AB}, $ prove that $ B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}\times BD $
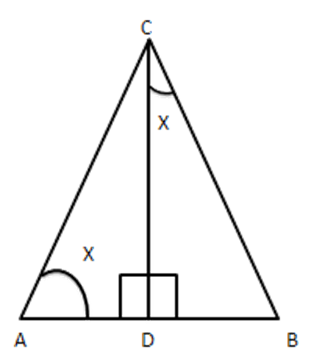
Ans: Given: A $ \vartriangle ABC $ right angled at $ \text{C} $ and $ CD\bot AB $
To Prove: $ B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}\times BD $
Proof: Consider $ \vartriangle ACD\,\,\,and\,\,\Delta DCB $
Let $ \angle A=x $
Then $ \angle B={{90}^{{}^\circ }}-x[\because \Delta ACB $ is right angled]
$ \Rightarrow \angle DCB=x[\because \Delta CDB $ is right angled ]
In $ \vartriangle ADC $ and $ \vartriangle CDB, $
$ \angle ADC=\angle CDB\left[ {{90}^{{}^\circ }}\text{ each } \right] $
$ \angle A=\angle DCB=x $
$ \vartriangle ACD\sim\vartriangle CBD $ [By AA similarity ]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}\Delta ACD}{\operatorname{ar}\Delta CBD}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}AD\times CD}{\dfrac{1}{2}BD\times CD}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}\times BD $
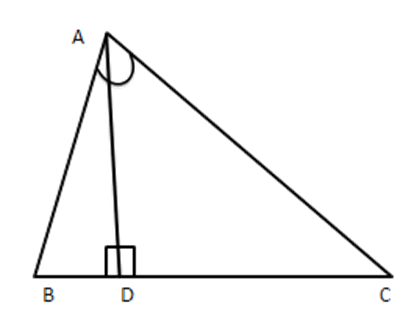
12. Triangle $ \text{ABC} $ is right angled at $ \text{C} $ and $ \text{CD} $ is perpendicular to $ \text{AB}. $ Prove that $ B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}\times BD $
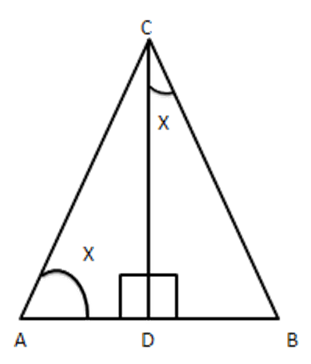
Ans: Given: \[\vartriangle ABC\]right-angled at C and $ CD\bot AB $
To prove: $ B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}\times BD $
Proof: Consider $ \vartriangle ACD $ and $ \vartriangle DCB $
Let $ \angle A=x $
Then $ \angle B=90-x[\because \Delta ACB $ is right angled ]
$ \Rightarrow \angle DCB=x[\because \Delta CDB $ is right angled ]
In $ \vartriangle ADC $ and $ \Delta CDB $
$ \angle ADC=\angle CDB\left[ {{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right. $ each ]
$ \angle A=\angle DCB=x[ $ from above ]
$ \therefore \vartriangle ACD\sim\Delta CBD[ $ AA similarity]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ACD)}{ar(\Delta VBD)}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}\times AD\times CD}{\dfrac{1}{2}\times BD\times CD}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}\times AD=A{{C}^{2}}BD $
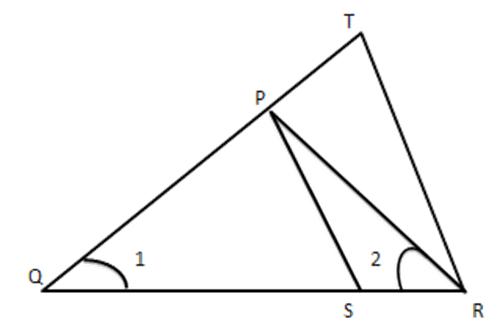
13. In figure, $ \text{ABC} $ and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. If AD intersect EC at 0, prove that $ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{ar(\Delta DBC)}=\dfrac{AO}{DO} $
Ans: Given: ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC but on the opposite sides of BC, AD intersects BC at O.
Construction: Draw $ AL\bot BC $ and $ DM\bot BC $
To prove: $ \dfrac{ar(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DBC)}=\dfrac{AO}{EO} $
Proof: In $ \vartriangle ALO\,\,\,and\,\,\,\vartriangle DMO $
$ \angle ALO=\angle DMO\left[ each \right. $ $ \left. {{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right] $
$ \angle AOL=\angle DOM[Vertically\,\,\,opposite\,\,angles] $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ALO\sim\Delta DMO[ $ By AA similarily]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AL}{DM}=\dfrac{AO}{DO} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{ar(\Delta DBC)}=\dfrac{AO}{DO} $
14. In figure, ABC is a right triangle right-angled at B. Medians AD and CE are of respective lengths 5 cm and $ 2\sqrt{5}cm $ , find length of AC.
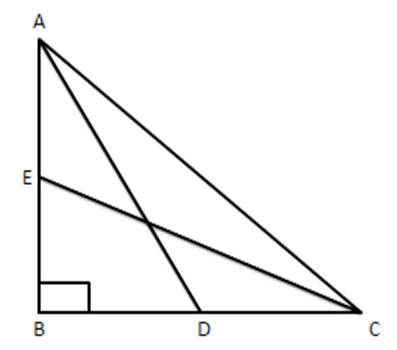
Ans: Given: $ \vartriangle ABC $ with $ \angle B={{90}^{{}^\circ }},\text{AD} $ and $ \text{CE} $ are medians
To find: Length of AC
Proof: In $ \vartriangle ABD $ right-angled at B,
$ A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}}[By\text{ pythagoras theorem }] $
$ =A{{B}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}BC \right)}^{2}}\left[ \because BD=\dfrac{1}{2}BC \right] $
$ =A{{B}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{4}B{{C}^{2}} $
$ 4A{{D}^{2}}=4A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}\ldots \ldots ..(i) $
In $ \Delta BCE $ right-angled at B
$ C{{E}^{2}}=B{{E}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow C{{E}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}AB \right)}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow C{{E}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{4}A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 4C{{E}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+4B{{C}^{2}}\ldots \ldots .(ii) $
$ \Rightarrow 4A{{D}^{2}}+4C{{E}^{2}}=5A{{B}^{2}}+5B{{C}^{2}}=5\left( A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow 4A{{D}^{2}}+4C{{E}^{2}}=5A{{C}^{2}} $
Given that $ \text{AD}=5 $ and $ CE=2\sqrt{5} $
$ 4{{(5)}^{2}}+4{{(2\sqrt{5})}^{2}}=5A{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 100+80=5A{{C}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=\dfrac{180}{5} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=36\Rightarrow AC=6~\text{cm} $
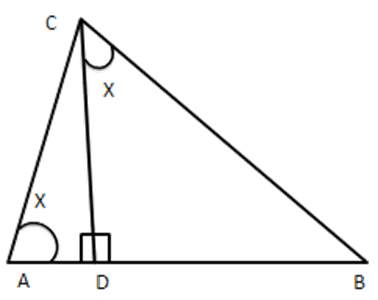
15. In the given figure, $ \dfrac{QR}{OS}=\dfrac{QT}{PR} $ and $ \angle 1=\angle 2, $ show that $ \vartriangle PQS\sim\Delta TQR. $
Ans: Given: $ \dfrac{QR}{QS}=\dfrac{QT}{PR} $ and $ \angle 1=\angle 2 $
Proof: As $ \angle 1=\angle 2 $
$ PQ=PR\ldots ..(i)[ $ side opposite to equal angles are equal]
Also $ \dfrac{QR}{QS}=\dfrac{QT}{PR}( $ given) $ \ldots \ldots .(ii) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{QR}{QS}=\dfrac{QT}{PQ} $ From (i) and (ii)
In $ \vartriangle PQS $ and TQR, we have
$ \dfrac{QR}{QS}=\dfrac{QT}{QP}=\dfrac{QS}{QT}\Rightarrow \dfrac{QR}{QP}[ $ From (ii)]
16. Given a triangle ABC. 0 is any point inside the triangle $ \text{ABC},\text{X},\text{Y},\text{Z} $ are points on $ \text{OA}, $ OB and OC, such that $ \text{XY}||\text{AB}\,\,\,and\,\,\,\text{XZ}||\text{AC}, $ show that $ \text{YZ}\|AC. $
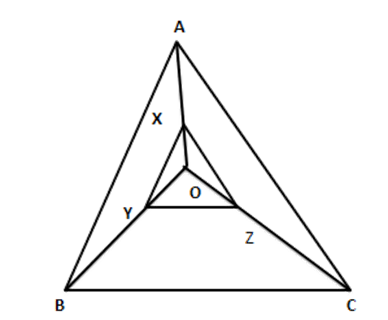
Ans: Given: A $ \vartriangle ABC,O $ is a point inside $ \vartriangle ABC,X,Y $ and $ Z $ are points on $ OA,OB $ and OC respectively such that $ \text{XY}||\text{AB} $ and $ \text{XZ}\|\text{AB} $ and $ \text{XZ}||\text{AC} $
To show: YZ| | BC
Proof: In $ \vartriangle OAB,XY\|AB $
$ \dfrac{OX}{AX}=\dfrac{OY}{BY}\ldots \ldots .(i)[By\text{B}.\text{P}.\text{T}] $
In $ \Delta OAC,XZ\|AC $
$ \therefore \dfrac{OX}{AX}=\dfrac{OZ}{CZ}\ldots \ldots ..(ii)[By\text{B}.\text{P}.\text{T}] $
From (i) and (ii), we get $ \dfrac{OY}{BY}=\dfrac{OZ}{CZ}\ldots \ldots \ldots . $ (iii)
Now in $ \vartriangle OBC\dfrac{OY}{BY}=\dfrac{OZ}{CZ}(from(iii)) $
$ \Rightarrow YZ\|BC $ [Converse of B.P.T]
17. PQR is a right triangle right angled at Q. If QS = SR, show that $ P{{R}^{2}}=4P{{S}^{2}}-3P{{Q}^{2}} $

Ans: Given: PQR is a right Triangle, right-angled at Q Also $ QS=SR $
To prove: $ P{{R}^{2}}=4P{{S}^{2}}-3P{{Q}^{2}} $
Proof: In right-angled triangle PQR right angled at Q.
$ P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}} $ [By Pythagoras theorem]
Also $ QS=\dfrac{1}{2}QR[\because QS=QR] $
In right-angled triangle PQS, right angled at Q.
$ P{{S}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{S}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow P{{S}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}QR \right)}^{2}}[\text{ From }(ii)] $
$ \Rightarrow 4P{{S}^{2}}=4P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}\ldots \ldots .(iii) $
From (i) and (iii), we get
$ P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+4P{{S}^{2}}-4P{{Q}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow P{{R}^{2}}=4P{{S}^{2}}-3P{{Q}^{2}} $
18. A ladder reaches a window which is 12 m above the ground on one side of the street. Keeping its foot at the same point, the ladder is turned to the other side of the street to reach a window 9 m high. Find the width of the street if the length of the ladder is 15 m.
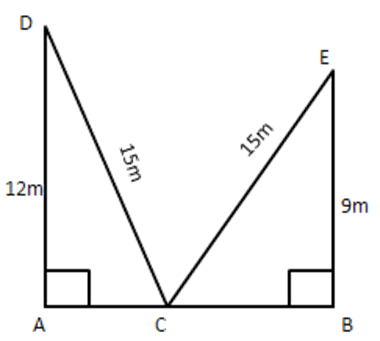
Ans: Let AB be the width of the street and C be the foot of ladder.
Let D and E be the windows at heights $ 12~\text{m} $ and $ 9~\text{m} $ respectively from the ground.
In $ \Delta CAD, $ right angled at A, we have
$ C{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+A{{D}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {{15}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=225-144=81 $
$ \Rightarrow AC=9~\text{m} $
In $ \Delta CBE, $ right angled at B, we have
$ C{{E}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+B{{E}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {{15}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+{{9}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=225-81 $
$ \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=144 $
$ \Rightarrow BC=12m $
Hence, width of the street $ \text{AB}=\text{AC}+\text{BC}=9+12=21~\text{m} $
19. In figure, $ \dfrac{XP}{PY}=\dfrac{XQ}{QZ}=3 $ , if the area of\[\vartriangle XYZ\] is $ 32c{{m}^{2}} $ then find the area of the quadrilateral PYZQ.
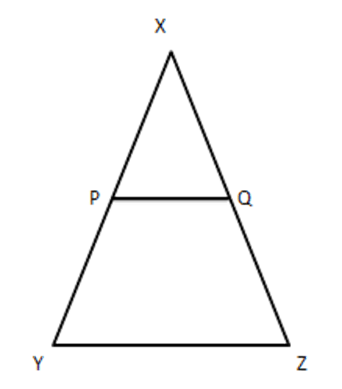
Ans: Given $ \dfrac{XP}{PY}=\dfrac{XQ}{QZ} $ (given)
$ \Rightarrow PQ\|YZ..... $ (i) (By converse of B.P.T)
In $ \vartriangle XPQ $ and $ \vartriangle XYZ $ , we have
($ \angle XPQ=\angle Y $) (From (i) corresponding angles)
$ \angle X=\angle Y[\text{common}] $
$ \therefore \Delta XPQ\sim\Delta XYZ $ (By AA similarity)
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta XYZ)}{ar(\Delta XPQ)}=\dfrac{X{{Y}^{2}}}{X{{P}^{2}}} $
We have $ \dfrac{PY}{XP}=\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow \dfrac{PY}{XP}+1=\dfrac{1}{3+1}\Rightarrow \dfrac{PY+XP}{XP}=\dfrac{4}{3} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{XY}{XP}=\dfrac{4}{3} $
Substituting in (i), we get
$ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta XYZ)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta XPQ)}={{\left( \dfrac{4}{3} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{16}{9} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{32}{\operatorname{ar}(XPQ)}=\dfrac{16}{9} $
$ \operatorname{ar}(XPQ)=\dfrac{32\times 9}{16}=18~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
Area of quadrilateral $ PYZQ=32-18=14~\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
4 Marks Questions
1. Prove that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in district points, ten other two sides are divided in the same ratio. By using this theorem, prove that in\[\vartriangle ABC\] if $ DE\left\| BC \right. $ then, $ \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AE}{AC} $
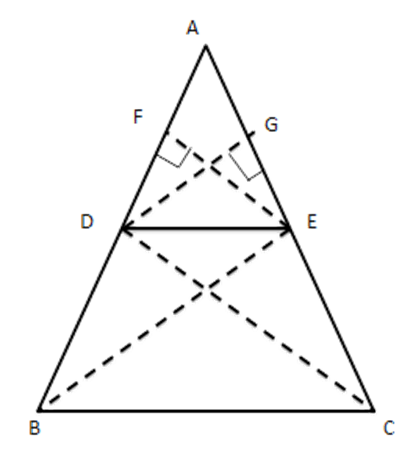
Ans: Given: In $ \vartriangle ABC\,\,\,\,DE\|BC $ intersect AB at D and AC at E. To Prove: $ \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{AE}{EC} $
Construction: Draw $ EF\bot AB $ and $ DG\bot AC $ and join DC and $ \text{BE}. $
Proof: $ \operatorname{ar}\vartriangle ADE=\dfrac{1}{2}AD\times EF $
$ \operatorname{ar}\Delta DBE=\dfrac{1}{2}DB\times EF $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}\vartriangle ADE}{\operatorname{ar}\Delta DBE}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}AD\times EF}{\dfrac{1}{2}DB\times EF}=\dfrac{AD}{DB}\ldots \ldots .(i) $
Similarly, $ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}\Delta ADE}{\operatorname{ar}\Delta DEC}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}AE\times DG}{\dfrac{1}{2}EC\times DG}=\dfrac{AE}{EC}\ldots \ldots ..(ii) $
Since $ \vartriangle DBE $ and $ \vartriangle DEC $ are on the same base and between the same parallels
$ \therefore \operatorname{ar}(\Delta DBE)=\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEC) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DBE)}=\dfrac{1}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEC)} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}\Delta ADE}{\operatorname{ar}\Delta DBF}=\dfrac{\operatorname{ar}\Delta ADE}{ar\Delta DFC} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{AB}{EC} $
$ \because DE\|BC $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{AD+DB}=\dfrac{AE}{AE+EC}\left[ \because \dfrac{p}{q}=\dfrac{r}{s}\Rightarrow \dfrac{p}{p+q}=\dfrac{r}{r+s} \right] $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{AE}{AC} $
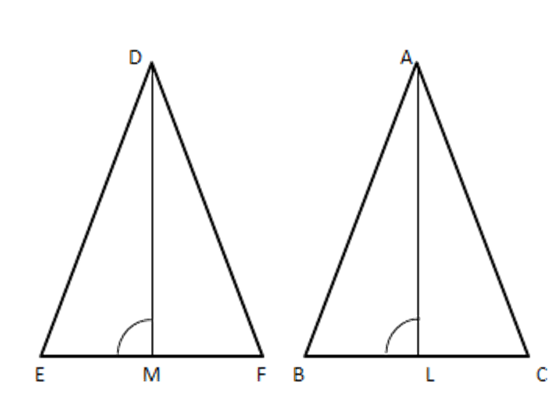
2. Prove that the ratio of areas of two similar triangles are in the ratio of the squares of the corresponding sides. By using the above theorem solve in two similar triangles PQR and LMN, QR = 15cm and MN = 10 cm. Find the ratio of areas of two triangles.
Ans: Given: Two triangles ABC and DEF
Such that $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle DEF $
To Prove: $ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{D{{E}^{2}}}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{D{{F}^{2}}} $
Construction: Draw $ AL\bot BC\,\,\,and\,\,\,DM\bot EF $
$ \text{Proof: }\dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}(BC)(AL)}{\dfrac{1}{2}(EF)(DM)} $
$ \left[ \because ar\text{ of }\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}b\times h \right] $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{Area(\Delta ABC)}{Area(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}\times \dfrac{AL}{DM}\ldots \ldots ..\left( i \right) $
Again, in $ \vartriangle ALB $ and $ \vartriangle DME $ we have
$ \angle ALB=\angle DME\left[ \text{ Each }={{90}^{{}^\circ }} \right] $
$ \angle ABL=\angle DEM\left[ \begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \because \vartriangle ABC\sim\vartriangle DEF \\ \therefore \angle B=\angle E \\ \end{array} \right] $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ALB-\vartriangle DME $ [By AA rule]
$ \therefore \dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{AL}{DM}[\because $ Corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional] Further, $ \vartriangle ABC\sim\Delta DEF $
$ \therefore \dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{AC}{DF} $
From (ii) and (iii),
$ \dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{AL}{DM} $
Putting in (i), we get
$ \dfrac{\text{ Area }(\Delta ABC)}{\text{ Area }(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{Al}{DM}\times \dfrac{AL}{DM} $
$ =\dfrac{A{{L}^{2}}}{D{{M}^{2}}}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{D{{E}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{D{{F}^{2}}} $
$ \text{Hence, }\dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{ar(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{D{{E}^{2}}}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{D{{F}^{2}}} $
Since $ \vartriangle PQR\sim\vartriangle LMN $
$ \therefore \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta PQR)}{ar(\Delta LMN)}=\dfrac{Q{{R}^{2}}}{M{{N}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{(15)}^{2}}}{{{(10)}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{225}{100}=\dfrac{9}{4} $
Hence, required ratio is 9: 4.
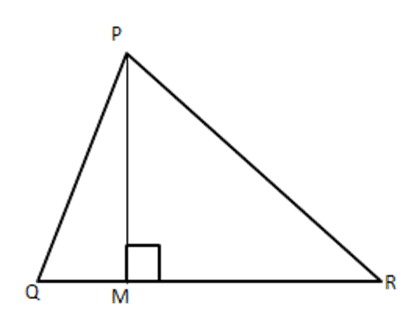
3. Prove that in a right-angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum 45 of the squares of the other two sides. Use the above theorem in the given figure to prove that
$ P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}-2QM.QR $
Ans: Given: $ \vartriangle ABC $ right-angled at A
To Prove: $ B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}} $
Construction: Draw $ AD\bot BC $ from A to BC
Proof: In $ \vartriangle BAD $ and $ \vartriangle ABC $ ,
$ \angle B=\angle B $ [Common] $ \angle BAC=\angle BDA={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ \therefore \vartriangle BAD\sim\vartriangle BCA[ $ By AA similarity ]
$ \therefore \dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{BD}{AB} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=BC\times AD\quad \ldots \ldots .(i) $
Similarly, in $ \vartriangle ADC $ and $ \vartriangle BAC $
$ \angle ADC=\angle BAC\left[ {{90}^{{}^\circ }}\text{ each } \right] $
$ \angle C=\angle C[\text{Common}] $
$ \therefore \vartriangle ADC\sim\vartriangle BAC[\text{ByAAsimilarity}] $
$ \therefore \dfrac{DC}{AC}=\dfrac{AC}{BC} $
$ \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=DC\times BC\ldots \ldots .(ii) $
$ (i)+(ii) $
$ A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=BC\times BD+DC\times BC $
$ \quad =BC[BD+DC] $
$ =BC\times BC $
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}} $
To Prove: $ P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+QR2-2QM\cdot QR $
Proof: In $ \vartriangle PMR $
$ P{{R}^{2}}=P{{M}^{2}}+M{{R}^{2}}[ $ Using above theorem]
$ =P{{M}^{2}}+{{(QR-QM)}^{2}} $
$ =P{{M}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}+Q{{M}^{2}}-2QM\cdot QM $
$ =\left( P{{M}^{2}}+Q{{M}^{2}} \right)+Q{{R}^{2}}-2QM\cdot QR $
$ =P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}-2QM\cdot QR\left[ \because P{{Q}^{2}}=Q{{M}^{2}}+P{{M}^{2}} \right] $
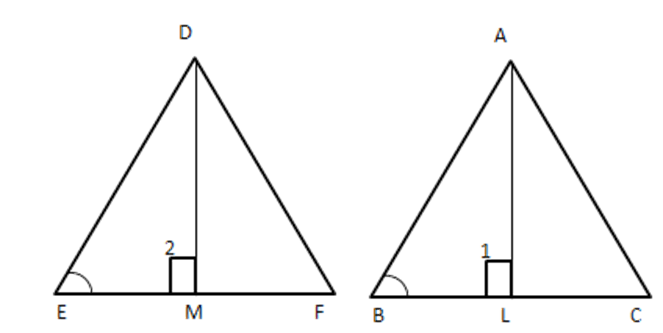
4. Prove that the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of their corresponding sides. Using the above theorem do the following the area of two similar triangles are $ 81c{{m}^{2}} $ and $ 144c{{m}^{2}} $ , if the largest side of the smaller triangle is 27 cm, then find the largest side of the largest triangle.
Ans: Given: Two triangles ABC and DEF such that $ \vartriangle ABC\sim \vartriangle DEF $
To prove: $ \dfrac{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{ar}(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{D{{E}^{2}}}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{D{{F}^{2}}} $
Construction: Draw $ AL\bot BC $ and $ DM\bot EF $
Proof: Since similar triangles are equiangular and their corresponding sides are proportional
$ \therefore \vartriangle ABC\sim\Delta DEF $
$ \Rightarrow \angle A=\angle D,\angle B=\angle E,\angle C=\angle F $
And $ \dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{AC}{DF}\ldots \ldots .(i) $
In $ \vartriangle ALB $ and $ \vartriangle DMB $ ,
$ \angle 1=\angle 2\text{ and }\angle B=\angle E $
$ \Rightarrow \vartriangle ALB-\vartriangle DME[\text{ByAAsimilarity}] $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{AL}{DM}=\dfrac{AB}{DE}\cdots \ldots ...(ii) $
From (i) and (ii), we get
$ \dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{AC}{DF}=\dfrac{AL}{DM} $
Now $ \dfrac{\text{ area }(\Delta ABC)}{\operatorname{area}(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}(BC\times AL)}{\dfrac{1}{2}(BF\times DM)} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{ Area }(\Delta ABC)}{\text{ Area }(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}\times \dfrac{AL}{DM} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{ Area }(\Delta ABC)}{\text{ Area }(\Delta DEF)}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}\times \dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}} $
Hence, $ \dfrac{\text{ Area }\vartriangle ABC}{\text{Area}\vartriangle DEF}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}}{D{{E}^{2}}}=\dfrac{B{{C}^{2}}}{E{{F}^{2}}}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}}{D{{F}^{2}}} $
Let the largest side of the largest triangle be $ x~\text{cm} $
Using above theorem,
$ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{27}^{2}}}=\dfrac{144}{81}\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{27}=\dfrac{12}{9} $
$ \Rightarrow x=36~\text{cm} $
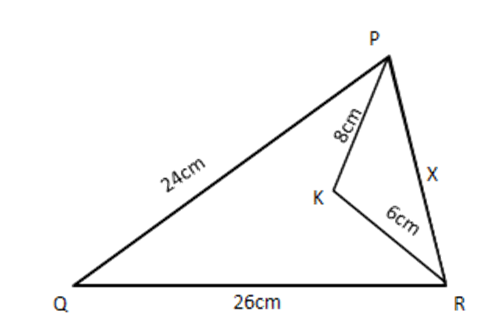
5. In a triangle if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides. Prove that the angle apposite to the first side is a right angle. Use the above theorem to find the measure $ \angle PKR $ of in figure given below.
Ans: Given: A $ \vartriangle ABC $ such that
$ A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} $
To prove: Triangle ABC is right angled at B
Construction: Construct a triangle DEF such that
$ DE=AB,EF=BC\text{ and D}E={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
Proof: $ \because \Delta DEF $ is a right angled triangle right angled at E[construction]
$ \therefore $ By Pythagoras theorem, we have
$ D{{F}^{2}}=D{{E}^{2}}+E{{F}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow D{{F}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}[\because DE=AB\text{ and }EF=BC] $
$ \Rightarrow D{{F}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}\left[ \because A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} \right] $
$ \Rightarrow D{{F}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}\left[ \because A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} \right] $
$ \Rightarrow DF=AC $
Thus, in $ \vartriangle ABC $ and $ \vartriangle DEF $ , we have
$ AB=DE,BC=EF\,\,and\,\,\,AC=DF $ [By Construction and (i)]
$ \therefore \vartriangle ABC\cong \vartriangle DEF $
$ \Rightarrow \angle B=\angle E={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
Hence, $ \vartriangle ABC $ is a right triangle.
Hence, $ \vartriangle ABC $ is a right triangle.
$ \text{ In }\Delta QPR,\angle QPR={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ \Rightarrow {{24}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}={{26}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow x=10\Rightarrow PR=10~\text{cm} $
Now in $ \Delta PKR,P{{R}^{2}}=P{{K}^{2}}+K{{R}^{2}}\left[ {} \right. $ as $ \left. {{10}^{2}}={{8}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}} \right] $
$ \therefore \Delta PKR $ is right angled at $ \text{K} $
$ \Rightarrow \angle PKR={{90}^{{}^\circ }} $
Maths Class 10 Chapter 6 Triangles Important Points and Theorems
Introduction
The triangles class 10 notes chapter 6 provided here is a crucial study resource for the students studying in class 10. These CBSE class 10 maths triangles important questions are brief, and it also covers all the theories from this lesson. Questions from these theories are likely to be asked in the board exam. You will also learn about theorems that are based on comparable concepts. In your preceding year's classes, you must have studied the basics of triangles, for example, the perimeter of a triangle and its area, etc.
Triangle
A triangle can be characterized as a polygon that has three points and three sides. The inside points of a triangle total up to 180 degrees, and the outside points total up to 360 degrees. Based on the length and its angle, it can be classified into the following kinds-
Scalene Triangle – Each side of the triangle is of different measure.
Isosceles Triangle – Any two different sides of the triangle are of equivalent length.
Symmetrical Triangle – All the three sides of a triangle are equivalent, and each angle is 60 degrees.
Acute Angled Triangle – All the angles are not more than 90 degrees.
Right Angle Triangle – Any of the three angles is equivalent to 90 degrees.
Obtuse-Angled Triangle – One out of the three angles is more than 90 degrees.
Similar Figures
Two forms having an identical shape, but not necessarily identical, are referred to as similar figures.
All congruent forms are similar, but not all similar forms are congruent.
Example- any two squares since their sides are proportional.
Triangles Similarity Criteria
To determine if the two triangles are similar or not, you need to check the following four criteria:
Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarity Criterion – When the relating sides of any two triangles are in a similar proportion, at that point, their comparing angles will be equivalent, and the triangle will be considered as similar triangles.
Point Angle (AAA) Similarity Criterion – When the relating angles of any two triangles are equivalent, at that point, their comparing side will be in similar proportion, and the triangles are viewed as similar.
Point Angle (AA) Similarity Criterion – When two angles of one triangle are separately equivalent to the two angles of the other triangle, at that point, the two triangles are considered as similar.
Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Similarity Criterion – When one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides incorporating these angles are in a similar proportion (relative), at that point, the triangles are supposed to be similar.
Thales Theorem
Statement: A-line that is drawn parallel to any side of a triangle will intercross the other two remaining sides in separate points. The other two remaining sides are then declared to be divided in an equivalent ratio."
Proof:
In ∆ABC, DE || BC.
To prove: ADDB=AEEC
Construction: Draw EM perpendicular AD and DN perpendicular AE. Join point B to point E and point C to point D.
Proof: In ∆ADE and ∆BDE,
ar(ΔADE)ar(ΔBDE)=12×AD×EM12×DB×EM=ADDB (i) [Area of ∆ = 12 x base x corresponding altitude
In ∆ADE and ∆CDE,
ar(ΔADE)ar(ΔCDE)=12×AE×DN12×EC×DN=AEEC
∵ DE || BC …[Given
∴ ar(∆BDE) = ar(∆CDE)
From (i), (ii) and (iii),
ADDB=AEEC
Example - If point D is the center/radius of the circle and BC is 4 cm, and AC is 3 cm, What is the diameter of the circle?
Solution
According to Thales theorem, triangle ABC is considered as a right triangle where ∠ACB = 90°.
To determine the diameter of the given circle, one should apply the Pythagorean theorem.
BC2 + AC2 =AB2
4*4 + 3*3 = AB2
16 + 9 = AB2
25 = AB2
AB = 5 cm
Hence, the diameter of the circle is 5 cm
Area of Triangles
Statement- "The ratios of the areas of any two comparable triangles is equivalent to the square of the ratio of their similar sides."
Proof
Given: ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
To prove: ar(ΔABC)ar(ΔDEF) = AB2 DE2 = BC2 EF2 = AC2 DF2
Construction: Draw AM perpendicular BC and DN perpendicular EF.
Proof: In ∆ABC and ∆DEF
ar(ΔABC)ar(ΔDEF)=12×BC×AM12×EF×DN=BCEF.AMDN …(i)
[Area of ∆ = 12 x base x corresponding altitude]
∵ ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
∴ ABDE=BCEF …..(ii) …[Sides are proportional]
∠B = ∠E ……..[∵ ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF]
∠M = ∠N …..[each 90°]
∴ ∆ABM ~ ∆DEN ……[AA similarity]
∴ ABDE=AMDN …..(iii) …[Sides are proportional]
From (ii) and (iii), we can deduce- BCEF=AMDN …(iv)
From (i) and (iv), we can deduce- ar(ΔABC)ar(ΔDEF)=BCEF.BCEF=BC2 EF2
Similarly, it can be proven that
ar(ΔABC)ar(ΔDEF)=AB2 DE2 = AC2 DF2
∴ar(ΔABC)ar(ΔDEF)=AB2 DE2=BC2 EF2=AC2 DF2
Example -In ΔABC andΔAPQ, the length of the sides are given as AP = 4 cm , PB = 8 cm and BC = 6 cm. Determine the ratio of the areas of triangle ABC and triangle APQ.
In triangle ABC and triangle APQ, ∠PAQ is common
and
∠APQ = ∠BAC (corresponding angles)
ΔABC ~ ΔAPQ (AA criterion for similar triangles)
Since the two triangles are comparable, we can use the theorem based on the areas of similar triangles,
area of ΔABC / area of ΔAPQ = (AB/AP)2 = (12/6)2 = 4
Pythagoras’ Theorem
Statement: In a right-angled triangle, the total of the squares of the remaining two sides of the triangle is equivalent to the square of the hypotenuse.
Proof
Given: ABC is a right triangle that is right-angled at point B.
To prove: AB² + BC² = AC²
Construction: Draw BD ⊥ AC
Proof: In ∆s ABC and ADB
∠A = ∠A (common)
∠ABC = ∠ADB (each angle 90°)
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆ADB (AA Similarity rule)
∴ ABAD=ACAB (sides are proportional)
⇒ AB² = AC.AD
Now in ∆ABC and ∆BDC
∠C = ∠C (common)
∠ABC = ∠BDC (each 90°)
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆BDC (AA similarity)
∴ BCDC=ACBC (sides are proportional)
BC² = AC.DC (ii)
On adding (i) and (ii), we get
AB² + BC² = ACAD + AC.DC
⇒ AB² + BC² = AC.(AD + DC)
AB² + BC² = AC.AC
∴AB² + BC² = AC²
Example:
The height of the triangle is 4 and the breadth is 3, find the hypotenuse.
Solution
EG and GF are the two given sides of the right-angled Triangle.
EG = 5 cm and GF = 12 cm
From Pythagoras Theorem, we have:
EF2 = EG2 + GF2
= (5)2 + (12)2
= 25 + 144
So, EF2 = 169
EF = 13 cm
Converse of Pythagoras’ Theorem
Statement: In a triangle, if the sum of the squares of the other two remaining sides of the triangle is equivalent to the square of one side of the triangle then the angle opposite the primary side is definitely a right angle."
Proof
To prove: ∠ABC = 90°
Construction: Draw a right-angled ∆DEF in which DE = AB and EF = BC
Proof: In ∆ABC,
AB² + BC² = AC² …(i) (given)
In rt. ∆DEF
DE² + EF² = DF² …(By pythagoras theorem)
AB² + BC² = DF² …..(ii) …(DE = AB, EF = BC)
From (i) and (ii), we get
AC² = DF²
⇒ AC = DF
Now, DE = AB …(by cont)
EF = BC …(by cont)
DF = AC …….(proved above)
∴ ∆DEF ≅ ∆ABC ……(sss congruence)
∴ ∠DEF = ∠ABC …..(CPCT)
∠DEF = 90° …(by cont)
∴ ∠ABC = 90°
Benefits of Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 - Triangles
These questions serve as a strategic tool to aid students in their exam preparation by offering a focused and efficient way to revise crucial concepts and theorems related to triangles.
By concentrating on key topics, they help students identify the most relevant material for their exams, saving time and ensuring a comprehensive understanding.
Moreover, these important questions often mimic the examination format and challenge levels, enabling students to gauge their preparedness and build confidence.
Triangles class 10 important questions are available in a compiled PDF form to download on any device and can be used to prepare for their exams.
The PDF will also ask as a model question paper and help students get an insight into what to expect in their actual board exam.
Triangles class 10 extra questions with solutions will focus on more theoretical-based questions.
They will act as revision notes to help you to revise the entire triangles chapter in a short span right before the maths exam.
Conclusion
Vedantu's Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 - Triangles offer a valuable resource for students seeking to excel in their mathematics studies. With a comprehensive selection of essential questions and in-depth explanations, Vedantu equips learners with the necessary tools to master the concept of triangles. By practising these questions, students can strengthen their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in tackling various triangle-related problems. Furthermore, Vedantu's user-friendly platform and expert faculty ensure a seamless learning experience. Whether preparing for exams or aiming for a deeper understanding of the subject, Vedantu's Important Questions provide an effective and convenient learning aid, empowering students to achieve academic success in mathematics.
Important Study Materials for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles
S. No | CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles Other Study Materials |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. |
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-wise Important Questions
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-wise Important Questions and Answers include topics from all chapters. They help students prepare well by focusing on important areas, making revision easier.
S. No | Chapter-wise Important Questions for Class 10 Maths |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Important Questions |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Important Questions |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 |
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Maths
S. No | CBSE Class 10 Maths Study Materials |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 |
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics in Class 10 Maths Chapter 6, Triangles, for the CBSE 2025-26 board exam?
For the CBSE 2025-26 board exam, the most crucial topics in the Triangles chapter that are frequently tested include:
- Basic Proportionality Theorem (BPT) and its Converse: Expect direct proofs or numerical problems.
- Similarity Criteria (AA, SAS, SSS): Focus on applying these to prove triangles are similar and then finding unknown sides or angles.
- Pythagoras Theorem: Be prepared for its proof using similarity and application-based problems.
- Area of Similar Triangles Theorem: This is a common source for MCQs and short-answer questions linking side ratios to area ratios.
2. Which similarity criterion is most important for the board exam, and how should I apply it for full marks?
The Angle-Angle (AA) similarity criterion is the most frequently used and therefore highly important. To score full marks when applying it:
- Step 1: Clearly identify and name the two triangles being compared.
- Step 2: Prove two corresponding angles are equal, stating a valid geometric reason for each (e.g., common angle, alternate interior angles, etc.).
- Step 3: Write the concluding statement clearly, for instance, 'Therefore, ΔABC ~ ΔPQR (By AA similarity criterion)'.
- Step 4: If needed for the solution, correctly state that corresponding sides are proportional (e.g., AB/PQ = BC/QR = AC/PR).
3. What types of questions are expected from the Triangles chapter in the 2025-26 board exams based on marks?
You should prepare for a mix of question types from the Triangles chapter, categorised by marks:
- 1-Mark Questions (MCQ): Often test direct results from the Area of Similar Triangles theorem or BPT.
- 2 or 3-Mark Questions: Typically involve proving a smaller result using similarity or applying theorems to find missing lengths.
- 4 or 5-Mark Questions (Case-Study/HOTS): These are usually proof-based (like proving Pythagoras Theorem) or complex application problems requiring multiple steps.
4. Why is it so important to practise questions from Triangles instead of just memorising the theorems?
Practising a variety of important questions is crucial because Triangles is a chapter focused on application and logical reasoning, not just memory. Solving problems helps you master the ability to:
- Correctly identify which theorem or criterion to apply in a specific problem scenario.
- Develop the skill of writing a structured, logical proof, which is essential for scoring in geometry.
- Recognise common problem patterns and solve complex, multi-step questions efficiently under exam pressure.
5. What is a common mistake students make in Triangles proofs that leads to losing marks?
A very common and critical mistake is writing the incorrect correspondence of vertices when declaring two triangles similar. For example, writing ΔABC ~ ΔPQR when the correct correspondence is actually ΔABC ~ ΔQPR. This single error makes all subsequent steps involving proportional sides (CPST) incorrect, leading to a significant loss of marks. Always match vertices based on their corresponding equal angles.
6. How are questions based on the Basic Proportionality Theorem (BPT) typically framed in the board exam?
In the CBSE board exam, questions on BPT and its converse go beyond simple definitions. Expect to see them in these formats:
- Direct Application: You will be given a triangle with a line drawn parallel to one side and asked to calculate the length of a missing segment.
- Component in a Larger Proof: You may need to use BPT to establish a relationship that is a necessary step to prove a more complex result in a 3 or 5-mark question.
- Converse Application: Using the converse to first prove that two lines are parallel and then using that fact to prove another property, like a quadrilateral being a trapezium.
7. What kind of Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) questions can be expected from Chapter 6, Triangles?
HOTS questions from the Triangles chapter test your ability to synthesise concepts. For the 2025-26 exam, be prepared for questions that require you to:
- Combine two or more theorems in one proof, such as using BPT to find a ratio and then applying the Pythagoras Theorem.
- Work with proofs involving the properties of medians, altitudes, or angle bisectors in relation to triangle similarity.
- Solve problems where the required similar triangles are overlapping or not immediately obvious, requiring you to redraw or visualise them separately.
8. How is the Pythagoras Theorem in Class 10 different from what we learned in earlier classes?
In Class 10, the focus shifts from just using the Pythagoras theorem for calculations to understanding its geometric origin. A key important question is the formal proof of the theorem using the concept of similar triangles formed by dropping a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse. You are also expected to solve problems based on its converse and combine it with other similarity concepts.
9. What are some typical word problems from the Triangles chapter that are important for exams?
The board exam often features practical word problems based on the principle of indirect measurement using similarity. Important types include:
- Calculating the height of a tall structure (like a tower or tree) by comparing its shadow with the shadow of a smaller object of a known height (like a pole or person).
- Problems involving a light source (like a lamp post) and finding the length of a shadow cast by a person walking away from it.
- Finding distances or lengths in geometric figures or diagrams that model real-world scenarios.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video

















