Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds - 2025-26



FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds - 2025-26
1. What are the two essential properties of carbon that lead to the formation of a vast number of compounds, a topic frequently asked for 2 marks?
For the CBSE Class 10 board exam, the two key properties of carbon you must explain are:
- Catenation: This is the unique ability of carbon to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms, creating long chains, branched chains, and rings.
- Tetravalency: Carbon has a valency of four, meaning it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms (like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.). This allows for a huge diversity in the structure of compounds.
2. What types of 1-mark objective questions can be expected from IUPAC nomenclature and functional groups in the 2025-26 board exam?
In Chapter 4, you can expect 1-mark questions that test your ability to:
- Identify the functional group (e.g., -OH for alcohol, -CHO for aldehyde, -COOH for carboxylic acid, >C=O for ketone) in a given compound structure.
- Provide the correct IUPAC name for a simple hydrocarbon or a compound with one functional group (e.g., Propanone, Ethanoic acid).
- Identify the correct structure for a given IUPAC name.
- Count the number of covalent bonds in a simple alkane like ethane or propane.
3. Explain the complete mechanism of the cleaning action of soap. Why is this a common 3 or 5-mark question?
The cleaning action of soap is a crucial application-based concept. The mechanism involves the formation of micelles:
- A soap molecule has two parts: a long hydrocarbon tail which is hydrophobic (water-repelling) and an ionic head which is hydrophilic (water-attracting).
- When soap is added to water, the molecules arrange themselves into spherical clusters called micelles. The hydrophobic tails point inwards towards any oil or grease particle, while the hydrophilic heads face outwards, remaining in contact with the water.
- This structure traps the oily dirt at the centre of the micelle, which can then be washed away with water. Agitation helps break the grease into smaller droplets and allows more soap molecules to surround it.
This question is frequently asked because it tests understanding of molecular structure and its real-world application.
4. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated based on chemical tests? Provide balanced equations for this important 3-mark question.
To differentiate between ethanol and ethanoic acid, you can use the following tests:
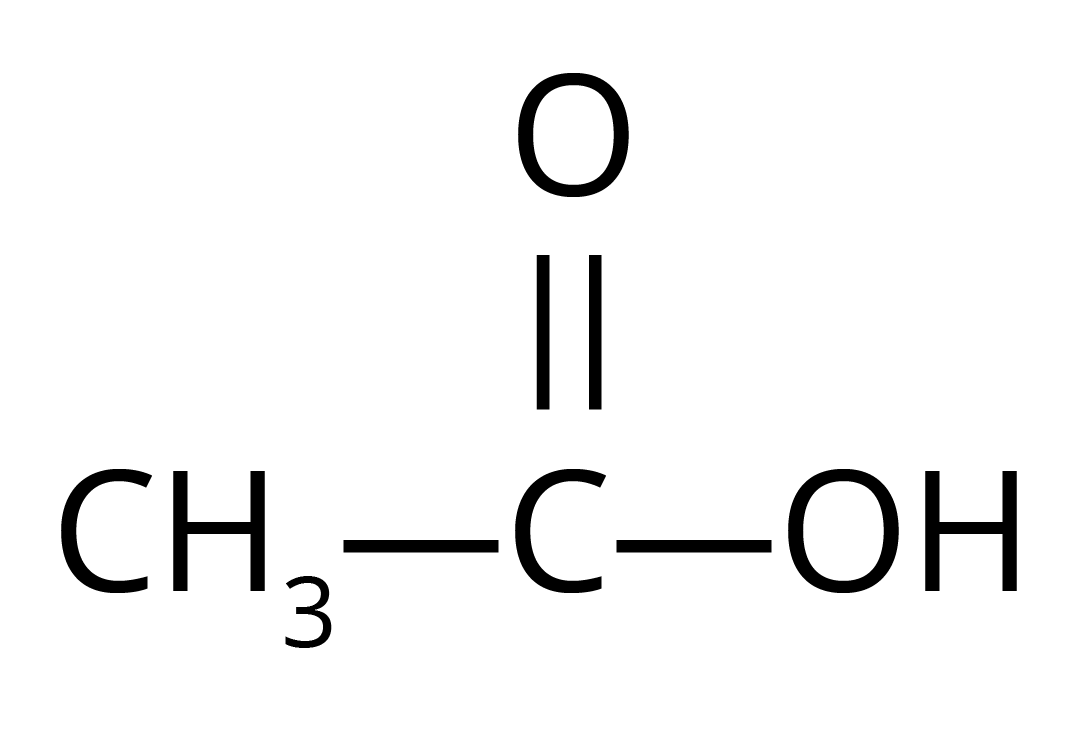
- Sodium Bicarbonate Test: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) to produce brisk effervescence due to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. Ethanol does not react.
Reaction: CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃ → CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂ - Alkaline KMnO₄ Test: When a few drops of alkaline potassium permanganate are added to warm ethanol, its purple colour disappears as ethanol is oxidised to ethanoic acid. Ethanoic acid does not cause this colour change.
Reaction: CH₃CH₂OH + 2[O] (from alkaline KMnO₄) → CH₃COOH + H₂O
5. What is a homologous series? List any two of its characteristics as per the CBSE syllabus.
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds that have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. Key characteristics for exams are:
- All members of the series can be represented by the same general formula (e.g., Alkanes: CₙH₂ₙ₊₂).
- Any two successive members in the series differ by a –CH₂ group and have a mass difference of 14 atomic mass units (amu).
- Members show a gradual change in physical properties like boiling point and melting point as the molecular mass increases.
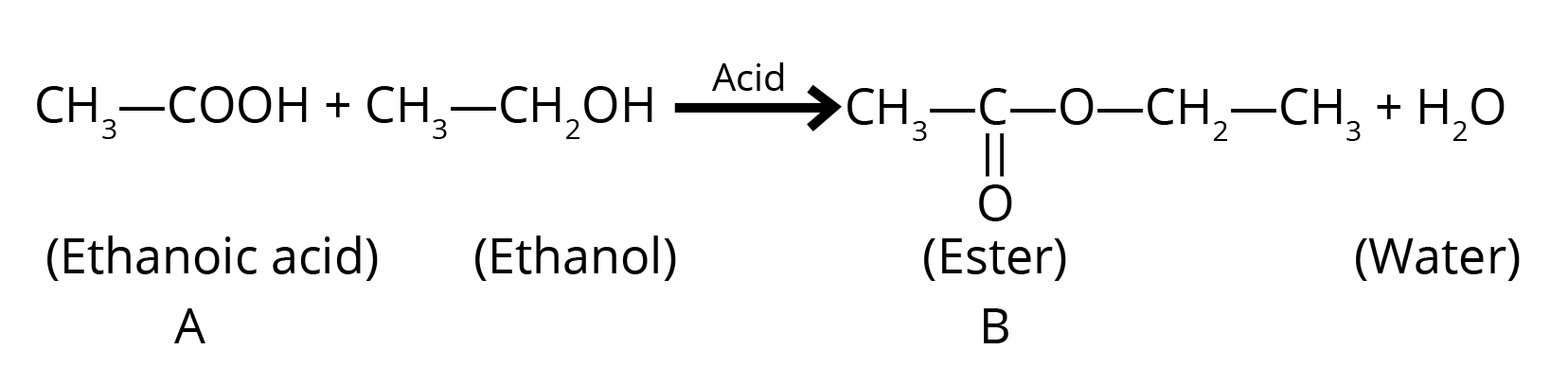
6. Explain the process of esterification with a chemical equation. What is the specific role of concentrated sulphuric acid in this reaction?
Esterification is the chemical reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a sweet-smelling compound called an ester.
Reaction: When ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated H₂SO₄, ethyl ethanoate is formed.
CH₃COOH (Ethanoic Acid) + CH₃CH₂OH (Ethanol) ⇌ CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ (Ethyl Ethanoate) + H₂O
The role of concentrated sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄) is twofold: it acts as a catalyst to speed up the reaction and as a dehydrating agent to remove the water produced, which prevents the reaction from reversing and thus increases the yield of the ester.
7. What are structural isomers? Draw the possible structures for pentane (C₅H₁₂), a question often asked for 3 marks.
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms. For the molecular formula C₅H₁₂, there are three possible structural isomers:
- n-pentane: A straight chain of five carbon atoms.
CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃ - Isopentane (2-methylbutane): A branched chain with four carbon atoms in the main chain and one methyl group on the second carbon.
CH₃–CH(CH₃)–CH₂–CH₃ - Neopentane (2,2-dimethylpropane): A branched chain with three carbon atoms in the main chain and two methyl groups on the central carbon.
C(CH₃)₄
8. Why are unsaturated hydrocarbons like ethene generally more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons like ethane?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons due to the presence of double (C=C) or triple (C≡C) bonds. These bonds contain weakly held pi (π) electrons, which are easily available for chemical attack. This allows unsaturated compounds to undergo addition reactions, where atoms are added across the double or triple bond to form a more stable single-bonded compound. Saturated hydrocarbons only have strong sigma (σ) single bonds, making them less reactive and only able to undergo substitution reactions, which require more energy.
9. A student observes that the bottom of a cooking vessel is turning black. What does this indicate about the combustion of the fuel, and what type of hydrocarbon is likely being used?
A blackened vessel bottom indicates incomplete combustion of the fuel. This happens when there is an insufficient supply of oxygen. During incomplete combustion, unburnt carbon is released in the form of soot, which deposits on the vessel.
This is characteristic of unsaturated hydrocarbons (like alkenes and alkynes), which have a higher carbon-to-hydrogen ratio and tend to burn with a yellow, sooty flame. Saturated hydrocarbons generally undergo complete combustion to produce a clean, blue flame.
10. While both detergents and soaps are cleansing agents, why are detergents considered more effective, especially in hard water?
Detergents are more effective than soaps in hard water for a key chemical reason. Hard water contains calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions.
- Soaps react with these ions to form an insoluble, curdy precipitate called scum. This scum reduces the cleaning efficiency of the soap and sticks to the clothes.
- Detergents are typically ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. When they react with the calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, they form soluble salts that do not precipitate. This ensures the detergent remains active and effective as a cleansing agent, producing lather even in hard water.
11. Based on previous board exam trends, what are some of the most frequently asked 5-mark questions from Carbon and Its Compounds?
Based on trends, high-value 5-mark questions from this chapter often combine multiple concepts. Important areas to focus on for the 2025-26 exam include:
- Soaps and Detergents: A question combining the mechanism of micelle formation, the reason soaps don't work in hard water, and the advantage of using detergents.
- Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid: A problem-based question involving the preparation, properties (like oxidation of ethanol or esterification), and chemical tests to distinguish between them.
- Isomerism and Nomenclature: Drawing all possible isomers for a given hydrocarbon (like hexane), providing their IUPAC names, and explaining what isomers are.
- Carbon's Unique Nature: Explaining catenation and tetravalency in detail, followed by drawing electron-dot structures for compounds like ethene, ethyne, or cyclopentane.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video