Table Comparing Endocrine and Exocrine Glands for Quick Revision
The human body has many glands that produce important secretions. Some release hormones that help coordinate body functions, while others produce substances such as sweat, saliva or digestive enzymes. These glands can broadly be split into two main categories:
Endocrine glands: Glands without ducts that secrete hormones straight into the bloodstream.
Exocrine glands: Glands with ducts that release their secretions onto surfaces or into specific body compartments.
10 Differences Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Similarities Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Both endocrine and exocrine glands originate from glandular epithelial tissue.
They produce substances vital for bodily functions (hormones or other secretions).
Their secretions are crucial for maintaining various physiological processes.
Improper functioning of either type can lead to health issues.
Exocrine and Endocrine Glands Examples
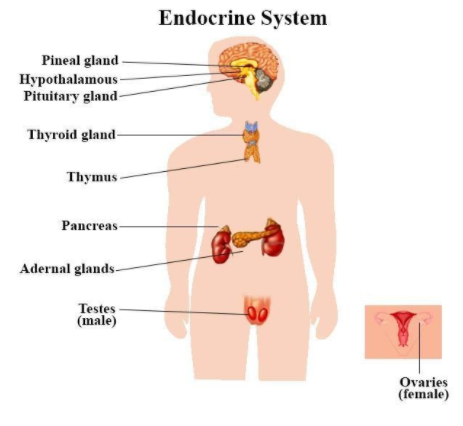
Endocrine Glands: Thyroid gland, pituitary gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, and the endocrine portion of the pancreas (producing hormones like insulin and glucagon).
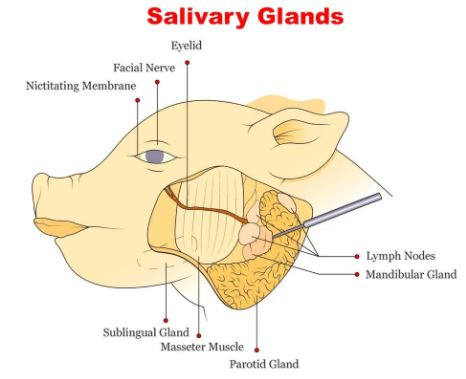
Exocrine Glands: Sweat glands, salivary glands, sebaceous glands, and the exocrine part of the pancreas (secreting digestive enzymes).
One important organ demonstrating both functions is the pancreas, known as a “mixed gland.” It secretes hormones (endocrine function) and digestive enzymes (exocrine function).
Interesting Fact
The pituitary gland is called the “master gland” because it produces hormones that regulate many other endocrine glands in the body.
Sweat glands help control body temperature and are more active when your body temperature rises or during stress.
Quick Quiz on Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Which gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions?
A. Adrenal gland
B. Pancreas
C. Thyroid gland
D. Parathyroid gland
Which of the following is an endocrine gland?
A. Sebaceous gland
B. Salivary gland
C. Pituitary gland
D. Sweat gland
Which statement best describes exocrine glands?
A. They are ductless and release hormones
B. They release secretions through ducts
C. They release hormones into the bloodstream
D. They have no role in digestion
Which of the following is NOT an exocrine secretion?
A. Sweat
B. Digestive enzymes
C. Saliva
D. Insulin
Identify a similarity between endocrine and exocrine glands.
A. Both produce hormones
B. Both are ductless
C. Both originate from epithelial tissue.
D. Both release digestive enzymes
Quiz Answers
B. Pancreas
C. Pituitary gland
B. They release secretions through ducts
D. Insulin
C. Both originate from epithelial tissue
Additional Content: Simple Activity
Try to feel your neck region carefully—just below the Adam’s apple (larynx area)—you may feel a slight swelling if you have an enlarged thyroid gland. The thyroid is one of the largest endocrine glands. Remember, only perform such checks gently, and if you suspect any abnormality, consult a healthcare professional.
Related Topics to Explore


FAQs on Endocrine vs Exocrine Glands: Differences, Functions & Examples
1. What is the main difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
The primary difference lies in their method of secretion. Exocrine glands possess ducts and release their secretions, such as enzymes or sweat, onto an external or internal body surface. In contrast, endocrine glands are ductless; they release hormones directly into the bloodstream, which then transports them to target organs throughout the body.
2. What are some common examples of exocrine glands and their secretions?
Common examples of exocrine glands found in the human body include:
- Salivary glands: Secrete saliva into the mouth to aid in digestion.
- Sweat glands: Release sweat onto the skin surface to regulate body temperature.
- Mammary glands: Produce milk for nourishing offspring.
- Lacrimal glands: Secrete tears to cleanse and lubricate the eyes.
- Gastric glands: Secrete gastric juice into the stomach to break down food.
3. What are the major endocrine glands in the human body?
The major endocrine glands, which constitute the endocrine system, are the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pineal gland, pancreas, and the gonads (ovaries in females and testes in males). Each gland produces specific hormones that regulate different physiological processes.
4. How can one organ, like the pancreas, have both endocrine and exocrine functions?
An organ with dual functions is called a heterocrine gland. The pancreas is a perfect example. Its exocrine part produces digestive enzymes and releases them through the pancreatic duct into the small intestine. Its endocrine part, known as the Islets of Langerhans, secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon directly into the bloodstream to control blood sugar levels.
5. Why is the ductless secretion of endocrine glands so important for the body?
The ductless nature of endocrine glands is crucial for systemic regulation and maintaining homeostasis. By releasing hormones into the blood, the body can send chemical signals to multiple organs and tissues simultaneously, no matter how far they are from the gland. This allows for the coordinated control of widespread, long-term processes such as growth, metabolism, mood, and reproduction, which would be inefficient to manage with ducts.
6. What is the key difference between a hormone and an enzyme?
A key difference is their point of action and transport. Hormones are produced by endocrine glands and travel through the bloodstream to act on distant target cells. In contrast, enzymes are typically produced by exocrine glands and act locally, either within the cell that made them or in a nearby cavity (like the stomach), and are not transported by blood to their site of action.
7. What happens if an endocrine or exocrine gland stops working properly?
Dysfunction in either type of gland can cause significant health issues. If an exocrine gland is blocked (e.g., a salivary duct), it can lead to localized swelling and infection. If an endocrine gland malfunctions, it can cause a hormonal imbalance affecting the entire body. For instance, insufficient insulin from the pancreas leads to diabetes mellitus, a systemic metabolic disorder.










