Science Notes for Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World Class 6 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Science Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the main concept of 'diversity in the living world' for a Class 6 student's revision?
The main concept for revision is understanding that our planet has a vast variety of plants and animals. These organisms live in different natural surroundings, or habitats, and possess special features, known as adaptations, which are crucial for their survival in those specific environments.
2. How can you quickly summarise the main types of plants based on their size and stem for easy recall?
For a quick revision, remember plants in three main groups:
- Herbs: These are small plants that have soft, green, and tender stems. Examples include coriander and mint.
- Shrubs: These are medium-sized, bushy plants. They have hard, woody stems that typically branch out near the ground. Examples include rose and lemon plants.
- Trees: These are tall, large plants distinguished by a very thick, hard, and woody main stem called a trunk. Examples include mango and banyan trees.
3. What is the core difference between a habitat and an adaptation?
A habitat is simply the natural home or address where an organism lives, such as a pond, desert, or forest. An adaptation is a specific physical feature or behaviour that helps an organism to survive successfully within that habitat, like a polar bear's thick fur for surviving in the cold.
4. What are the key characteristics that all living things share?
All living organisms share several key characteristics that are important to remember for this chapter. They all need food for energy, they respire (breathe), they excrete (remove waste), they respond to stimuli (react to their surroundings), they reproduce, they show movement, and they grow.
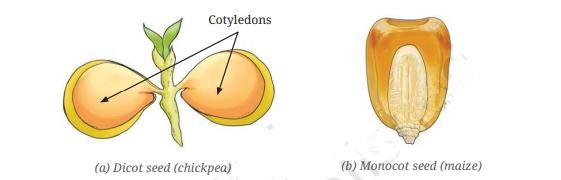
5. How can you remember the difference between taproots and fibrous roots for revision?
A simple memory trick is that a taproot system features one main, thick root that 'taps' down into the soil, with smaller roots growing from it, like a carrot. In contrast, a fibrous root system looks like a cluster of fibres, with many thin, similar-sized roots spreading out from the base of the stem, as seen in grass or wheat.
6. Is there a connection between a plant's root type and the pattern of veins in its leaves?
Yes, there is a very helpful pattern to remember for exams. Plants that have a taproot system usually have leaves with reticulate venation, where the veins form a net-like pattern. Conversely, plants with a fibrous root system typically have leaves with parallel venation, where the veins run parallel to one another.
7. Why is a fish's adaptation for breathing different from a whale's, even though both live in water?
This highlights a key concept in adaptation. A fish is adapted to breathe underwater using gills, which extract dissolved oxygen directly from the water. A whale, however, is a mammal and has lungs. It is adapted to hold its breath for long periods but must surface to breathe air. This shows how different types of animals develop unique adaptations for the same habitat.
8. How does the concept of 'adaptation' explain the vast diversity of life in places like deserts and mountains?
Adaptation is the key reason for this diversity. Organisms in a desert developed features to conserve water and withstand heat, like a cactus having spines instead of leaves. In mountains, animals developed adaptations for cold and steep terrains, like a yak's thick fur and a mountain goat's strong hooves. These specialised adaptations allow different forms of life to thrive in different environments, leading to the rich diversity we see on Earth.
9. If a car moves and uses fuel, why is it not considered a living thing according to this chapter's summary?
A car is non-living because it only mimics some characteristics of life but lacks others. While it moves and uses fuel (like food), it cannot grow, reproduce on its own, respire, or excrete waste. An organism must exhibit all the essential characteristics of life to be classified as living.