Class 4 Maths Chapter 2 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Long and Short Class 4 Maths Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the main concepts to summarise in the Class 4 chapter 'Long and Short'?
For a quick revision of Chapter 2, 'Long and Short', focus on these key concepts:
- Understanding Length: Identifying which objects are long and which are short.
- Standard Units: Learning the basic standard units of length, which are centimetres (cm), metres (m), and kilometres (km).
- Measurement: Using a ruler or scale to measure the length of objects accurately.
- Conversion: Understanding the simple relationship between metres and centimetres (1 m = 100 cm).
- Estimation: Making a sensible guess about the length of an object before measuring it.
2. What is the simple rule for converting metres (m) to centimetres (cm) for a quick revision?
The key rule to remember for revision is: 1 metre is equal to 100 centimetres. To convert metres to centimetres, you multiply the number of metres by 100. For example, 3 metres is 3 x 100 = 300 centimetres. To convert centimetres to metres, you can think of grouping them in hundreds; for instance, 500 cm is equal to 5 m.
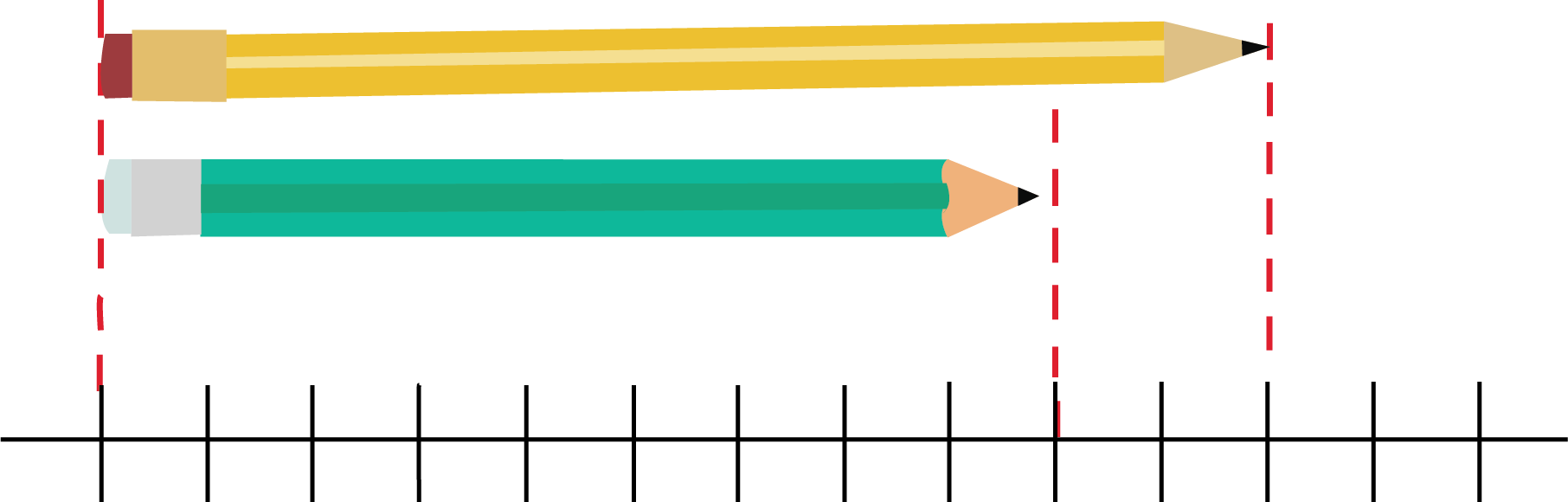
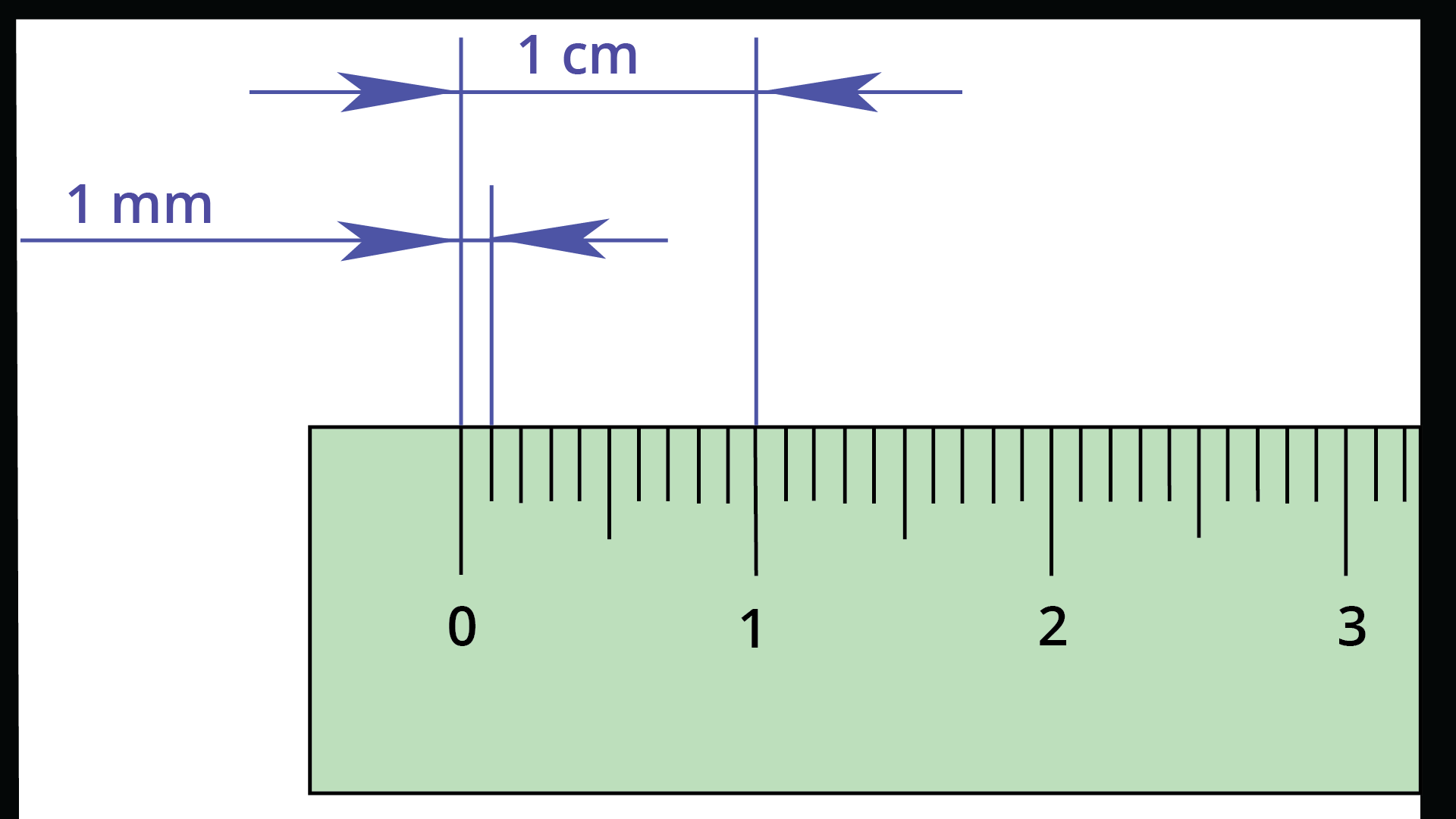
3. What is the key summary of how to measure length correctly using a scale or ruler?
To correctly measure length with a ruler, follow this summary:
- Place the '0' mark of the ruler exactly at the starting point of the object you want to measure.
- Keep the ruler straight along the edge of the object.
- Read the number on the ruler that aligns with the object's ending point.
- This number tells you the length of the object in centimetres (cm).
4. Why is it better to use a standard unit like a centimetre instead of non-standard units like a handspan for measuring things?
It is better to use a standard unit like a centimetre (cm) because everyone in the world agrees on its exact length. A handspan is a non-standard unit because everyone's hand is a different size. If you and your friend measure the same table with your handspans, you might get different answers. Using a standard unit like a centimetre ensures that the measurement is always the same, no matter who measures it.
5. How do you decide which unit of length—centimetres, metres, or kilometres—is best for describing different objects or distances?
You can decide which unit to use by thinking about the size of what you are measuring. Here is a simple guide:
- Use centimetres (cm) for small objects, like the length of a pencil, an eraser, or a book.
- Use metres (m) for longer things, like the length of a room, the height of a door, or a saree.
- Use kilometres (km) for very long distances, like the distance between two cities or the length of a river.
6. Beyond just measuring, what is the importance of 'estimating' length in our daily lives?
Estimating length is important because it helps us make quick, smart guesses without needing a tool. For example, by estimating, you can quickly figure out if a new table will fit in your room, if a thread is long enough to tie a box, or roughly how far away your school is. It's a useful mental math skill that helps in planning and problem-solving every day.
7. How does understanding conversion between units help in solving word problems about distance?
Understanding conversion is crucial for solving word problems because sometimes the information is given in different units. For example, a problem might mention a distance in metres and ask for the answer in kilometres, or vice-versa. To solve it correctly, you must first convert all measurements to the same unit. This ensures your addition or subtraction is accurate, helping you find the correct total distance or difference in length.