Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Summary Notes PDF Download


FAQs on Directing Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the core concept of 'Directing' in management for a quick summary?
Directing is a key managerial function that involves instructing, guiding, and motivating employees to work efficiently towards achieving organisational goals. It is the action-oriented function that initiates work in the organisation and transforms plans into performance.
2. What are the four main elements of Directing to remember for revision?
The four essential elements of directing are fundamental for revision. They are:
- Supervision: Overseeing employees at work to ensure work is done as per plans.
- Motivation: Stimulating and inspiring employees to perform to their best abilities.
- Leadership: Influencing the behaviour of others to work willingly towards common goals.
- Communication: The process of exchanging ideas and information to create a shared understanding.
3. How are the four elements of directing—Supervision, Motivation, Leadership, and Communication—interrelated?
These four elements are deeply interconnected and work together. A leader uses effective communication to motivate their team. This motivation is reinforced through proper day-to-day supervision. Without clear communication, leadership is ineffective, and without proper motivation, supervision can feel like mere policing. Their synergy is essential for the directing function to be successful.
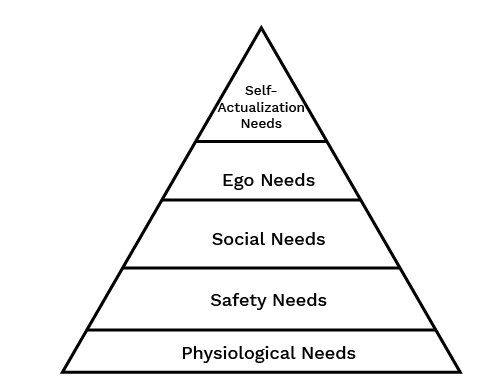
4. Can you summarise Maslow's Need Hierarchy Theory for a quick revision?
Maslow's theory suggests that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, and an individual is motivated to satisfy the next level of need only after the current level is substantially met. The five levels to remember are:
- Basic Physiological Needs: Essential survival needs like food, shelter, and sleep.
- Safety/Security Needs: The need for job security, and physical and emotional safety.
- Social/Belonging Needs: The need for affection, friendship, and a sense of belonging.
- Esteem Needs: The need for recognition, status, and self-respect.
- Self-Actualisation Needs: The highest level, representing the drive to become what one is capable of becoming.
5. What is the key difference to recall between financial and non-financial incentives?
The key difference lies in the form of the reward. Financial incentives are monetary or can be measured directly in money, such as salary, bonus, and profit sharing. In contrast, non-financial incentives focus on satisfying psychological and emotional needs, such as status, job enrichment, employee recognition, and career advancement opportunities.
6. Why is 'Harmony of Objectives' a crucial principle of directing?
The 'Harmony of Objectives' principle is crucial because it aligns the personal goals of employees with the overall organisational goals. When employees feel that achieving company objectives also helps them fulfil their personal ambitions (like career growth or higher pay), they become more motivated and committed. This prevents conflicts and ensures all efforts are channelled in the same productive direction.
7. How can a manager use Maslow's theory to design a motivation strategy for their team?
A manager can use Maslow's theory by identifying which need level an employee is on. For an employee seeking safety needs, offering job security is motivating. For someone at the social needs level, fostering teamwork is effective. For an employee at the esteem needs level, a promotion or public recognition (like 'employee of the month') would be a powerful motivator. The strategy must be tailored to the individual's current needs.
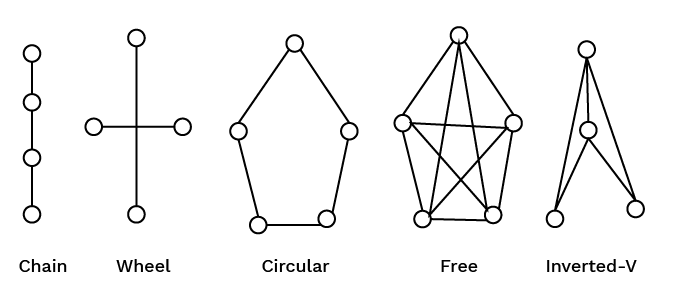
8. What are the different types of formal communication networks to revise for the exam?
The main types of formal communication networks as per the 2025-26 CBSE syllabus are:
- Single Chain: Communication flows from a superior to an immediate subordinate.
- Wheel: All communication passes through one central person or hub.
- Circular: Each person communicates with their two adjoining persons.
- Free Flow: Everyone is free to communicate with everyone else.
- Inverted V: A subordinate can communicate with their immediate superior as well as their superior's superior.
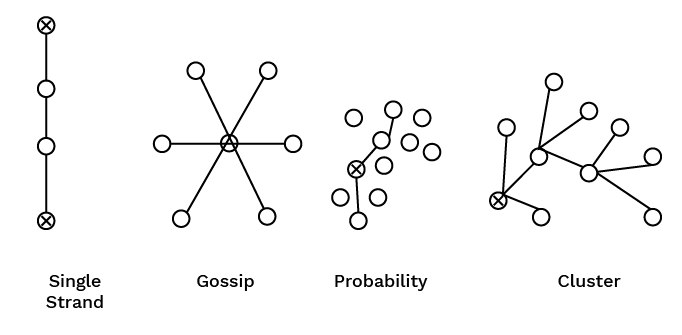
9. Why is informal communication, or the 'grapevine', often considered a double-edged sword in an organisation?
The grapevine is a double-edged sword because it has both benefits and drawbacks. On one hand, it can transmit information very fast and serve as an outlet for employee anxieties. On the other hand, it often spreads rumours and distorted information, which can harm morale and productivity. A manager cannot eliminate the grapevine but must manage it carefully.