Biology Notes for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 - FREE PDF Download


FAQs on Ecosystem Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the core concepts to prioritise when revising the Class 12 Biology Ecosystem chapter?
The main concepts to focus on during quick revision include ecosystem structure and types, energy flow (including the 10% law), functions of producers, consumers, and decomposers, ecological pyramids (number, biomass, energy), key nutrient cycles (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus), and essential processes in decomposition. Covering these areas ensures you are well-prepared for commonly tested exam questions as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. What is an effective order to revise topics in the Ecosystem Class 12 Notes for maximum retention?
The suggested revision sequence for Ecosystem Class 12 Notes is:
- Start with definitions and types of ecosystems.
- Review structure and components (biotic and abiotic).
- Cover functional aspects like productivity and decomposition.
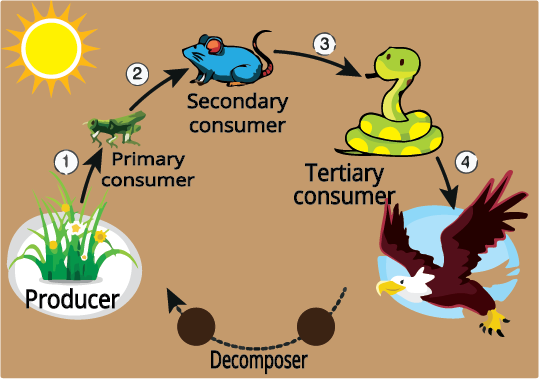
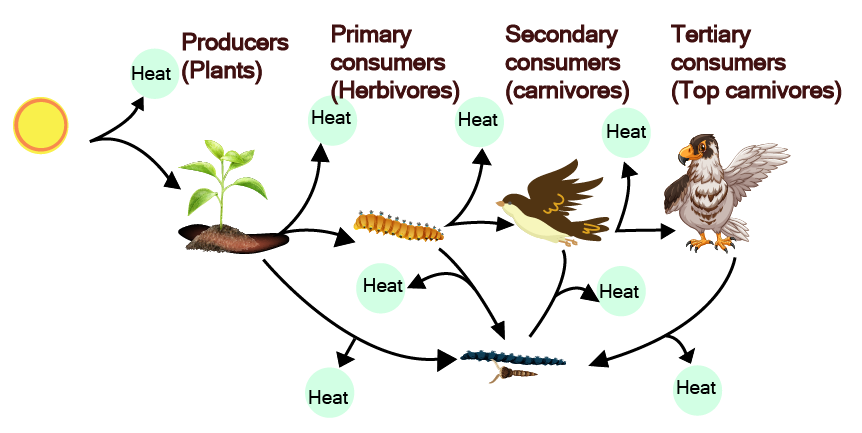
- Understand energy flow and food chains/webs.
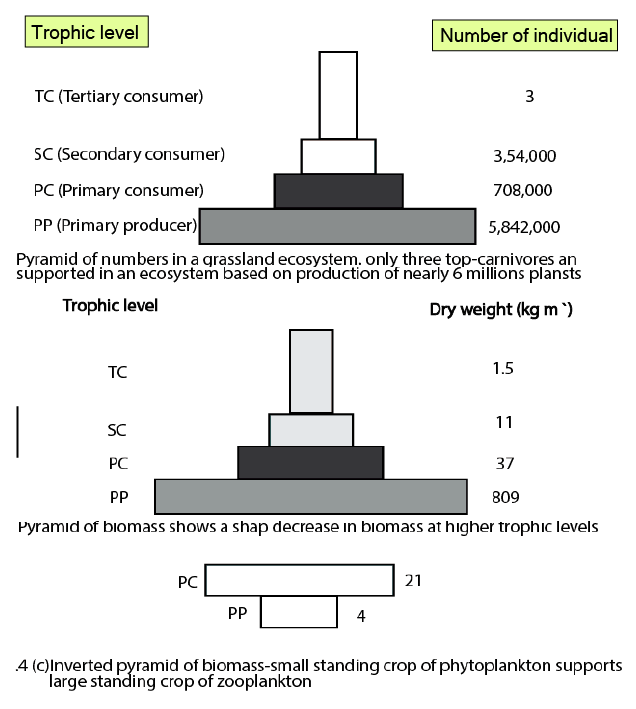
- Study trophic levels and ecological pyramids.
- Revise key nutrient cycles.
- Conclude with the human impact and ecosystem conservation.
3. How do concept maps help in summarising and revising Ecosystem Class 12 topics efficiently?
A well-organised concept map visually links major themes such as structure, function, and interconnections within an ecosystem. It consolidates key points for productivity, decomposition, energy flow, and nutrient cycles, making last-minute and high-yield revision before the Class 12 Biology exam faster and more effective.
4. What are some common misconceptions to avoid when preparing revision notes for the Ecosystem chapter?
Students should be cautious of these misconceptions:
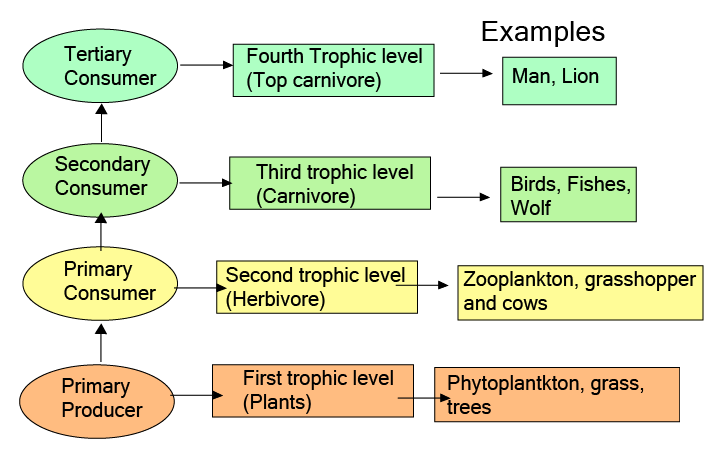
- Assuming all ecological pyramids are always upright (only the energy pyramid is always upright; number and biomass pyramids can be inverted).
- Believing decomposition occurs at the same rate everywhere (it varies due to temperature, moisture, and chemical makeup).
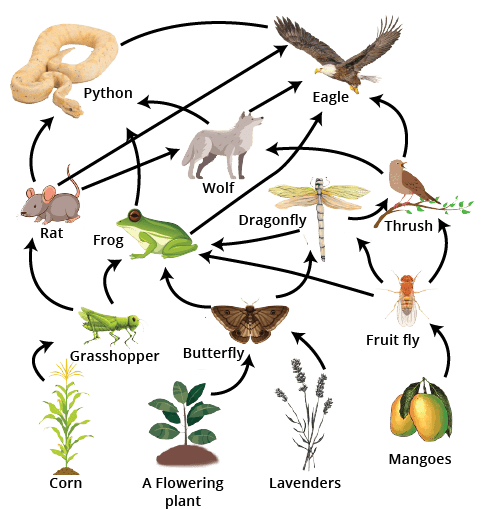
- Thinking food chains never overlap (real ecosystems are networks of interconnected food webs).
- Assuming unlimited trophic levels in food chains (in reality, energy loss restricts them to usually 4–5 levels).
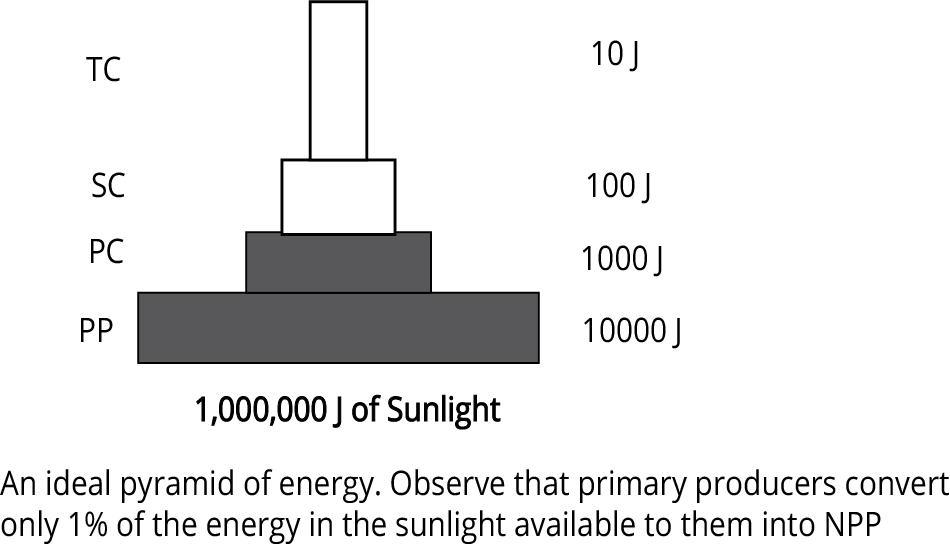
5. How does understanding the 10% law enhance revision of energy flow in ecosystems?
The 10% law states that only about 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, with the remainder lost as heat. This principle clarifies why there are a limited number of trophic levels and why energy pyramids are always upright. Mastery of this concept is crucial for reasoning and HOTS questions in board exams.
6. What strategies can be used for rapid recall of key nutrient cycles during revision?
To quickly remember nutrient cycles such as the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles:
- Use flowcharts and simplified diagrams for each cycle.
- Memorise main steps and transformations (e.g., fixation, assimilation, release).
- Practice narrating the process as a story.
- Note main reservoirs and movement paths in the ecosystem.
7. How can concept-based revision help tackle unfamiliar questions in the Ecosystem chapter?
Concept-based revision focuses on core principles rather than memorising facts. This allows students to apply knowledge to new or unfamiliar questions, construct logical explanations, and adapt to HOTS or reasoning-based problems effectively during board exams as per current CBSE guidelines.
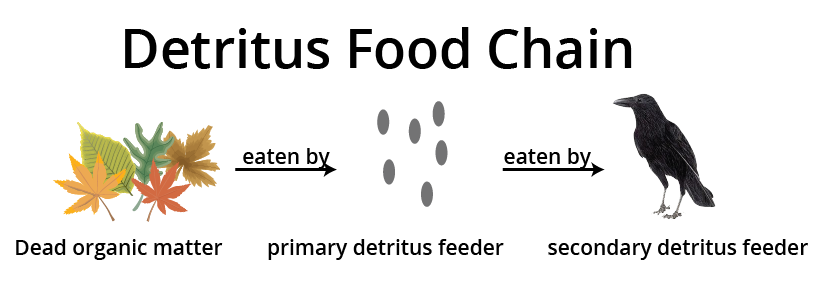
8. What summary points about decomposition are vital for Ecosystem Class 12 revision?
Key points on decomposition include:
- It breaks complex organic matter into simpler inorganic substances.
- Main steps are fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification, and mineralisation.
- Decomposition is affected by temperature, moisture, and the chemical nature of detritus.
- It is fundamental for nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
9. Why is the pyramid of energy always upright in ecosystem diagrams?
The pyramid of energy is always upright because energy decreases at each successive trophic level due to losses, mainly as heat. Unlike number or biomass pyramids, this decay in available energy means higher levels cannot be sustained with more energy than lower ones, visually reinforcing the 10% law in revision diagrams.
10. What is the benefit of linking revision concepts in Ecosystem Class 12 Notes with real-world examples?
Connecting concepts from Ecosystem Class 12 Notes with examples from forests, ponds, oceans, or aquariums reinforces understanding, aids memory retention, and helps students tackle application-based exam questions, as required by CBSE’s current focus on conceptual clarity and critical thinking.