Biology Notes for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Notes are prepared to simplify the complex processes of the nervous system for students. These notes cover important topics such as the structure and function of neurons, the central and peripheral nervous systems, the mechanism of nerve impulse transmission, and the role of neurotransmitters. With detailed explanations, diagrams, and summaries, students can easily understand the important concepts. Class 11 Biology Notes help students improve their understanding and perform well in their CBSE exams by offering clear and concise content along with practical examples.
Download the FREE PDF of Neural Control And Coordination Notes from Vedantu, updated according to the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Syllabus, to enhance your learning and exam preparation.
Access Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination
Section–A (1 Mark Questions)
1. How many pairs of cranial nerves are present in man?
Ans. 12 pairs of cranial nerves are present in man.
2. Name the band of nerve fibres that joins the two cerebral hemispheres in mammals.
Ans. Corpus callosum is the band of nerve fibres that join the two cerebral hemispheres in mammals.
3. Rearrange the following in the correct order of involvement in electrical impulse movement- Synaptic knob, dendrites, cell body, Axon terminal, Axon.
Ans. Synaptic knob → Dendrites → Cell body → Axon → Axon terminal.
4. What is the function ascribed to Eustachian tube?
Ans. Eustachian tube carries extra sound in tympanic cavity to the pharynx. It is done to maintain optimum pressure around ear drum.
5. Name the fluid that surrounds and protects the brain.
Ans. Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds and protects the brain.
Section–B (2 Mark Questions)
6. Define neurotransmitter.
Ans. Neurotransmitter is a chemical substance that acts as a signalling molecule which is released at the end of nerve fibre. It diffuses across the synapse and transmits the impulse to the next neuron, muscle or other structure.
7. The flowchart given here shows functional organization of the human neural system.
Identify A to E.
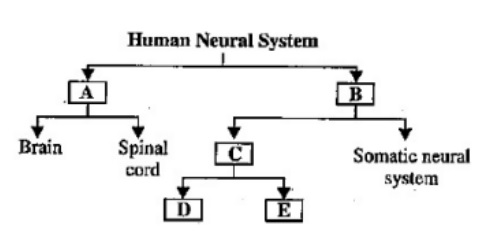
Ans.
8. Complete the following paragraph by selecting the option that gives the correct sequence of words.
When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane, the membrane at that site becomes freely permeable to __(i)__ ions. It causes rapid influx of __(ii)__ ions leading __(iii)__ of the membrane.
Ans. (i) Sodium ions.
(ii) Sodium ions
(iii) Depolarization
9. Answer the following:
(a) Which part of the human brain is the most developed?
(b) Which part of our central neural system acts as a master clock?
Ans. (a) Forebrain is the largest and the most developed part of the human brain.
(b) Hypothalamus acts as a master clock in the human body.
10. What happens when the membrane of a nerve cell carries out a sodium pump?
Ans. When the membrane of a nerve cell carries out a sodium pump, it transports 3 Na+ ions outwards and 2 K+ ions into the cell. As a result, the outer surface of the axonal membrane becomes a positively charge while its inner surface is negatively charged. It restores its resting membrane potential.
11. Name the meninges that surround the brain from outside to inside.
Ans. Dura mater
Arachnoid Layer
Pia mater


PDF Summary - Class 11 Biology Neural Control and Coordination Notes (Chapter 18)
Neural Control and Coordination
The interaction of two or more organs among each other and to complement each other’s function is known as coordination.
Neural System
The structural and functional units of the neural system are known as neurons. They can detect, receive, and transmit stimuli.
Human Nervous System
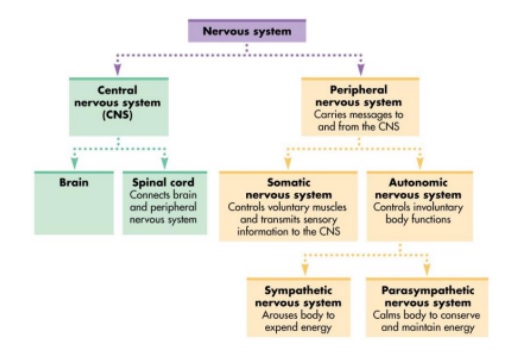
The classification of the nervous system is done into two types-
(i) central nervous system (CNS)
(ii) peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The brain and Spinal cord are the 2 parts of the Central nervous system whereas the peripheral nervous system is composed of all the nerves present in the brain and the spinal cord. The two types of nerve fibers present in PNS are-
(a) afferent nerve fibers or sensory nerve fiber
(b) efferent nerve fibers or motor nerve fiber
Impulses are carried from organs/tissues to the CNS in Afferent nerve fibers whereas, in efferent nerve fibers, impulses are transmitted from CNS to the target tissue/organ.
PNS Is Classified Into Two Types-
(i) somatic nervous system
(ii) autonomic nervous system.
Impulses are transmitted from the CNS to skeletal muscles in the somatic nervous system while the autonomic nervous system innervates cardiac and smooth muscles of the glands which transmit the impulses from the CNS to the involuntary part of the body. The classification of the autonomic nervous system is done into two types-
(i) sympathetic nervous system
(ii) parasympathetic nervous system
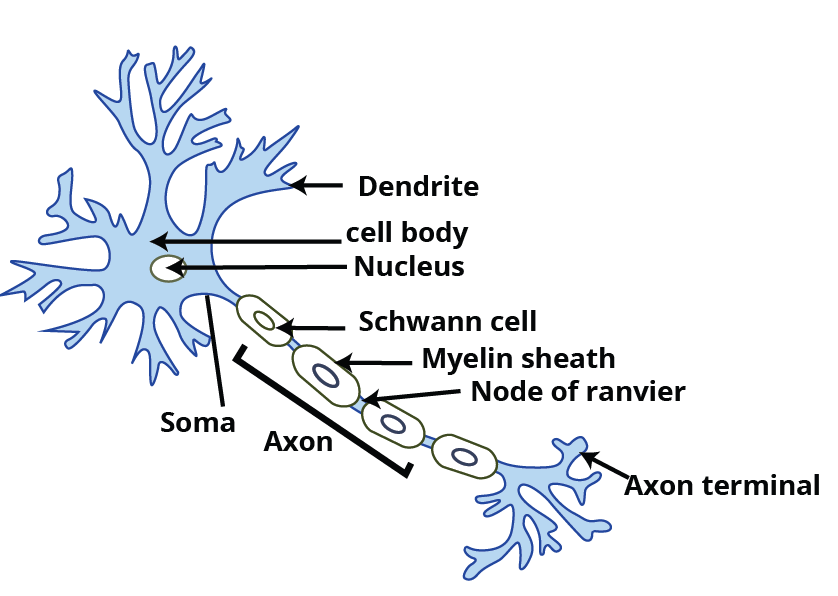
Structure and the Function of the Neuron
A neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It comprises 3 parts-
(i) cell body
(ii) dendrites
(iii) axon.
The cell body is made up of cytoplasm that contains granular bodies called Nissl’s granules. Short, several, finger-like projections that arise from the cell body are called dendrites. Dendrites carry nerve impulses towards or into the cell body. Axon is a long, single structure whose distal end is branched. Each of the axons ends into a bulb-like structure known as the synaptic knob, which contains neurotransmitters. The cells of the axon which produce and cover the myelin sheath are known as Schwann cells. The interruption between the two-adjacent myelin sheath is known as Nodes of Ranvier.
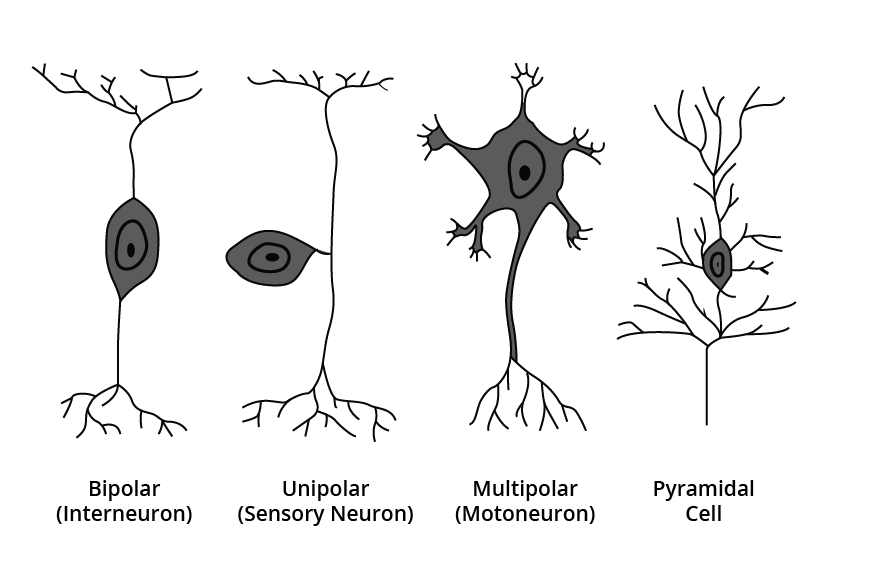
Types of Neurons
Multipolar Neurons- Several processes arise in them, having one axon and many dendrites. For example, in the cerebral cortex.
Bipolar Neurons- They are the ones with one axon and one dendrite. For example, retina.
Unipolar Neurons- Unipolar neurons have only two fibers arising close together, i.e., one axon, no dendrite. For example, embryonic stage.
Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulses
The cells which can be stimulated and electrically excited are called neurons. The membrane of the neurons is in a polarized state. The membrane contains selectively permeable ion channels with varying permeability to different ions. The membrane becomes more permeable to potassium ions and impermeable to sodium ions when no nerve impulse is being transmitted. This is the resting membrane potential. Therefore, there is a high concentration of potassium ions present in the membrane as compared to sodium ions. But, the case becomes opposite outside, high concentration of potassium in comparison to sodium. A concentration gradient gets developed due to the difference in the concentration of these ions. Sodium potassium pump helps in maintaining this gradient by actively transporting 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside the neuronal membrane. Thus, the outer surface of the axonal membrane possesses a positive charge and its inner surface becomes negatively charged. This is the reason behind the depolarization of the membrane. The membrane becomes freely permeable to sodium ions when a stimulus reaches a neuronal membrane. Thus, it will cause an influx of sodium ions inside the neuronal membrane. The inner side of the membrane becomes positively charged whereas outside the membrane is negatively charged due to this polarity. An electrical potential difference gets created called action potential.
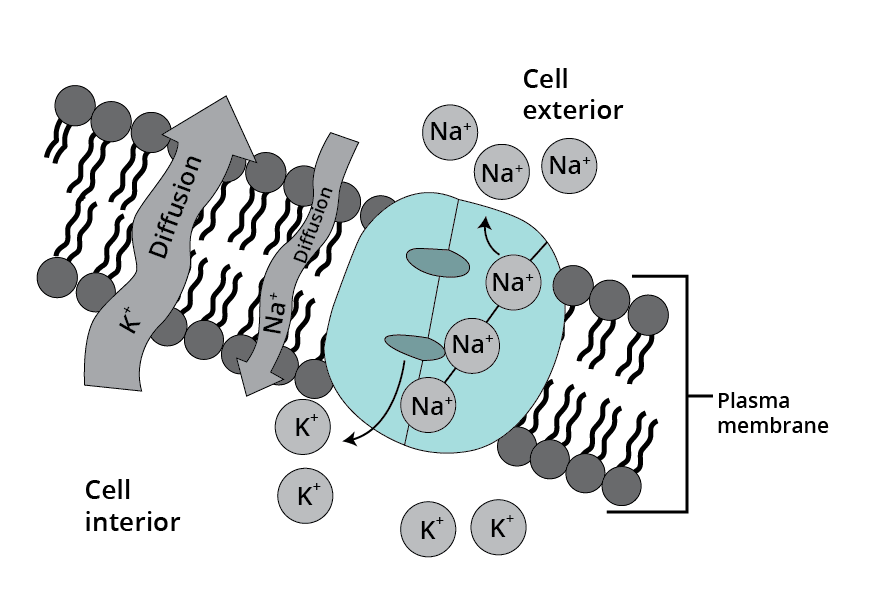
The permeability of sodium ions decreases, and the permeability of potassium ions increases with time. In the axonal membrane, there is an efflux of sodium ions polarization which occurs from inside to outside. Again, the polarity is reversed. This sequence of events is repeated along the complete axon which helps in the conduction of the nerve impulse.
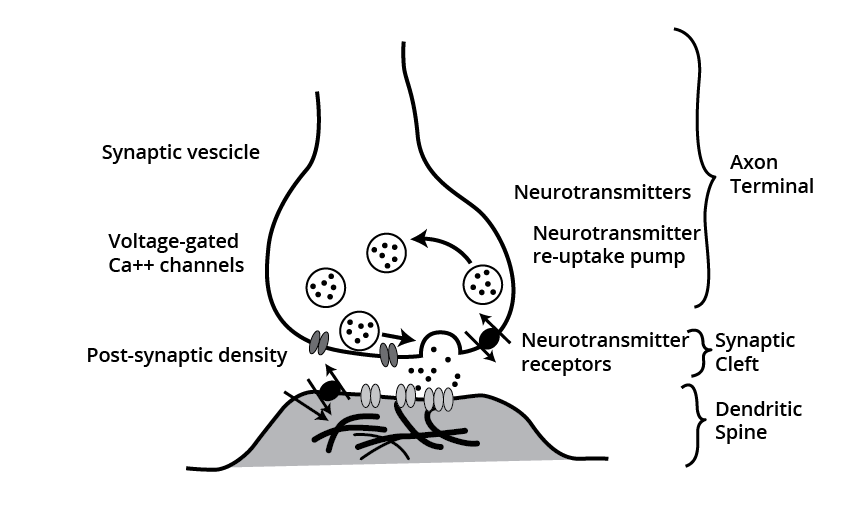
Transmission of Impulses
The transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another neuron via junctions called synapses. Synapse is a junction connecting the membrane of pre-synaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron separated by a gap known as the synaptic cleft.
Two Types of Synapses are There-
(i) Electrical synapse
(ii) Chemical synapse.
In an electrical synapse, there is proximity between pre-and post-synaptic neurons. There can be the direct flow of electric current from one neuron to another neuron. This mode of nerve impulse transmission is quicker than the chemical synapse.
In chemical synapses, pre-and post-synaptic neurons are separated by a fluid-filled space referred to as synaptic cleft. There are neurotransmitters involved in these synapses. There are axon terminals present which contain vesicles that are filled with neurotransmitters. By the time, the impulse reaches the axon terminal, synaptic vesicles start moving towards the membrane and fuse with it. This leads to the discharge of the neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft. Now, the neurotransmitters bind with the receptors which are present on the post-synaptic neuron. Thus, ion channels get opened and it results in the transmission of fuse nerve impulses.

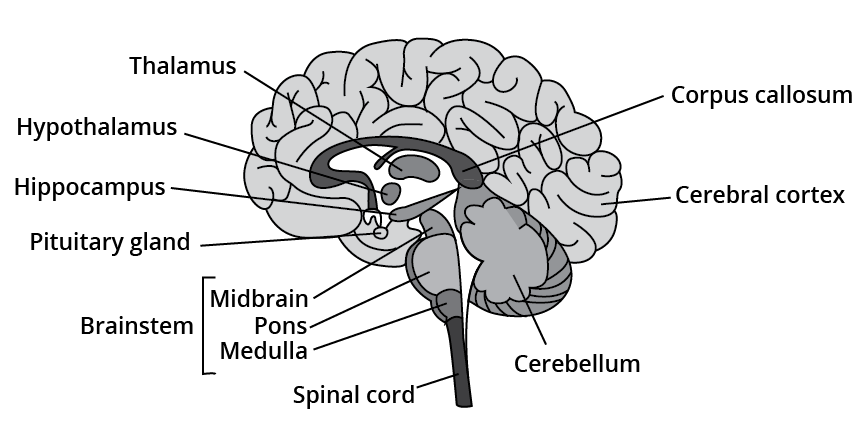
Central Nervous System
The brain controls and coordinates all the functions of the body thus, performing as a command and control system. The protection of the human brain is inside the skull. The covering of the brain is done in 3 layers known as meninges. They are-
(i) outermost dura mater,
(ii) middle arachnoid,
(iii) innermost pia mater.
The division of the brain is into:
(a) forebrain,
(b) midbrain,
(c) hindbrain.
The forebrain consists of 3 parts- cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The cerebrum is considered to be the largest part of the brain. The division of the cerebrum into two halves is known as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. These hemispheres are joined by a great white central canal white commissure called the corpus callosum. The covering of cerebral hemispheres by a layer of cells is known as the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is the area present at the center of the forebrain. It is involved in sensory and motor signaling. Hypothalamus lies at the base of the thalamus. The urge for eating, drink, and body temperature is all controlled and regulated by it.
The location of the midbrain is in between the forebrain and hindbrain. There are 4 lobes present known as Corpora quadrigemina.
The parts of the hindbrain are- pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. The cerebellum is considered to be the second-largest part of the brain. The medulla oblongata is placed between the spinal cord below and the pons above. The medulla controls gastric secretion, control respiration, and cardiovascular functions.
5 Important Topics of Biology Class 11 Chapter 18 You Shouldn’t Miss!
S.No. | Topic | Description |
1. | Neuron Structure and Function | Study the structure of neurons, types, and their roles in transmitting nerve impulses. |
2. | Central and Peripheral Nervous System | Understand the components and functions of the central (brain, spinal cord) and peripheral nervous systems. |
3. | Nerve Impulse Transmission | Learn the process of how nerve impulses are transmitted across neurons and synapses. |
4. | Human Brain Structure and Function | Explore the anatomy of the human brain and its role in controlling different body functions. |
5. | Synapses and Synaptic Transmission | Study the structure of synapses and how they facilitate the transmission of signals between neurons. |
Importance of Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination Notes
Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Notes break down difficult concepts like nerve impulse transmission, neuron structure, and brain functions into easy-to-understand explanations.
Visuals such as diagrams of neurons, synapses, and the brain help students visualise and retain information more effectively.
The notes are designed to cover key topics aligned with the CBSE syllabus, ensuring that students focus on the most important areas for their exams.
Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Notes are organised systematically, allowing students to quickly review and revise the core concepts of the chapter.
Understanding neural control and coordination is fundamental for studying more advanced biology topics in higher education, and Neural Control And Coordination Notes lay a strong foundation for future learning.
Tips for Learning the Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination
Understand the Basics: Start by understanding the basic structure of neurons and how nerve impulses are transmitted. This forms the foundation for the entire chapter.
Use Diagrams for Better Retention: Study the diagrams of neurons, synapses, and the human brain to visually grasp the concepts. Labelling important parts will help in better retention.
Focus on Key Terms: Pay attention to important terms like synapse, neurotransmitters, reflex actions, and nerve impulse transmission. These are frequently asked in exams.
Break Down Complex Processes: Divide complex processes, like synaptic transmission or brain functioning, into smaller steps to make them easier to learn and remember.
Revise Regularly: Regular revision is essential. Go through summaries and key points to memorise what you've learned.
Conclusion
Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Notes provide a clear and simplified understanding of how the human nervous system works. By covering important topics such as neuron structure, nerve impulse transmission, and the functions of the brain and spinal cord, these notes help students grasp the complexities of neural control. With detailed explanations and diagrams, students can easily revise key concepts and prepare well for exams. Neural Control And Coordination Notes not only strengthen the basics but also help students build a solid foundation for future studies in biology.
Related Study Materials for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination
Students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for Biology Class 11, Chapter 18–
S.No | Study Material Links for Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 |
1 | Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Important Questions |
2 | Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination NCERT Solutions |
3 | Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination NCERT Exemplar |
Chapter-wise Class 11 Biology Notes PDF Download
S. No | Chapter wise Class 11 Biology Revision Notes |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | |
14 | |
15 | |
16 | |
17 | |
18 |
Related Study Materials Links for Class 11 Biology
S. No | Related Study Materials Links for Class 11 Biology |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Papers |
6. |

























