
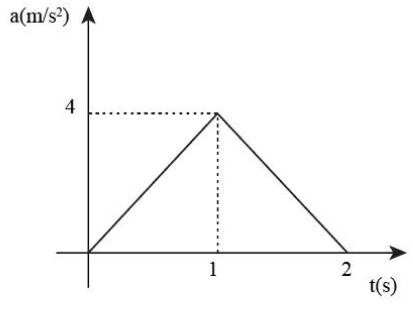
The acceleration time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. The velocity of the particle at time \[t = 0\] is \[2\;{\rm{m/s}}\]. The velocity after \[2\;{\rm{s}}\] will be
A. \[6\;{\rm{m/s}}\]
B. \[4\;{\rm{m/s}}\]
C. \[2\;{\rm{m/s}}\]
D. \[8\;{\rm{m/s}}\]

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:The above problem is resolved by using the kinematic equation of motion. Moreover, the first kinematic equation of motion is used to resolve the problem. In the first kinematic equation of motion, the variables like the magnitude of initial velocity, the time interval, and the magnitude of acceleration can be identified by analysing the velocity-time graph. And by analysing this graph, the values are obtained. After obtaining the values, the substitution is made for the values to the mathematical equation of motion, and then the final answer is obtained.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The velocity at \[t = 0\] is, \[u = 2\;{\rm{m/s}}\].
The time interval is, \[t = 2\;{\rm{s}}\].
In order to find the velocity after 2 seconds, We need to find the area of the graph.
As, base represents the time and height represents the magnitude of acceleration \[a = 4\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
Then the area of the acceleration time graph is,
\[
v = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2} \times t \times a} \right)\\
\Rightarrow v = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2\;{\rm{s}} \times 4\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}} \right)\\
\therefore v = 8\;{\rm{m/s}}
\]
Therefore, the velocity after 2 seconds is \[8\;{\rm{m/s}}\] and option (D) is correct.
Note: To resolve the given problem, the concepts and applications of the kinematic equations of motion need to be taken under consideration and the various practical applications of the equations. While applying the kinematic equations of motion, one must always remember the increase or decrease of the variables' values. This is important because the sign conventions are decided by the increment and decrement of these variables' magnitude.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The velocity at \[t = 0\] is, \[u = 2\;{\rm{m/s}}\].
The time interval is, \[t = 2\;{\rm{s}}\].
In order to find the velocity after 2 seconds, We need to find the area of the graph.
As, base represents the time and height represents the magnitude of acceleration \[a = 4\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
Then the area of the acceleration time graph is,
\[
v = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2} \times t \times a} \right)\\
\Rightarrow v = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2\;{\rm{s}} \times 4\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}} \right)\\
\therefore v = 8\;{\rm{m/s}}
\]
Therefore, the velocity after 2 seconds is \[8\;{\rm{m/s}}\] and option (D) is correct.
Note: To resolve the given problem, the concepts and applications of the kinematic equations of motion need to be taken under consideration and the various practical applications of the equations. While applying the kinematic equations of motion, one must always remember the increase or decrease of the variables' values. This is important because the sign conventions are decided by the increment and decrement of these variables' magnitude.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




