
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structure.
Answer
535.1k+ views
Hint: Nephron is the functional and structural unit of the kidneys that consists of glomerulus and its associated tubules to which the glomerular filtrate passes before it emerges in urine. There are about millions of nephrons present in the kidney.
Complete Answer:
1) Nephrons are the structural units that are composed of a renal corpuscle and renal tubule. It is a tube-like structure and 30-55mm long in length.
2) Renal tubule is a long, convoluted structure that emerges from glomerulus and further divided into 3 parts: proximal convoluted tubule (PCT); Henle’s loop; distal convoluted tubule.
3) PCT stays in the renal cortex due to its proximity to the glomerulus. The second part is Henle’s loop is also called a nephritic loop because it forms a loop that goes through renal medulla. Distal convoluted tubule which is the third part of renal tubule is also restricted to the renal cortex.
4) A cup-like structure called Bowman's capsule in which capillaries of glomerulus are enclosed. Then Bowman’s capsule extends to highly coiled tubules called proximal convoluted tubules (PCT).
5) PCT continues to form a Henle’s loop that ascends to DCT and which in turn opens into the collecting duct. Collecting duct is straight, long where potassium and hydrogen ions are secreted to maintain the electrolytic balance of blood.
6) Renal corpuscle consists of glomerulus that is surrounded by Bowman’s capsule. Glomerulus arises from afferent arteriole and empty in efferent arteriole.
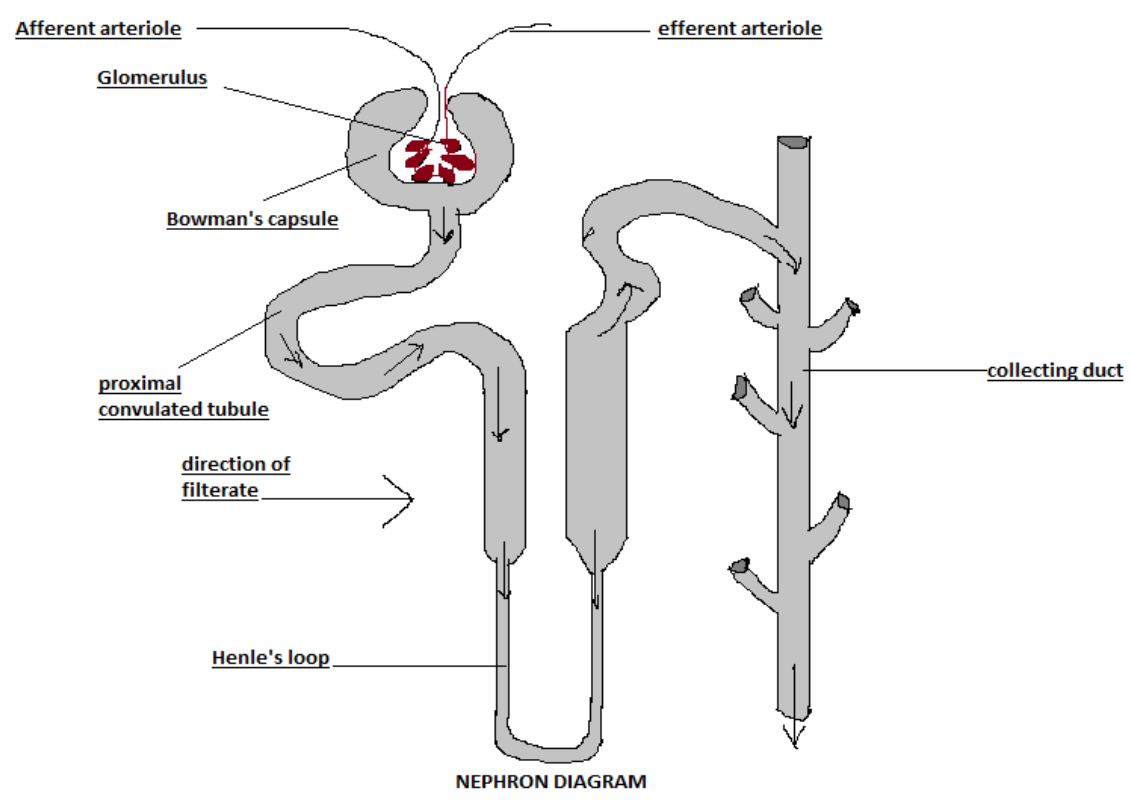
Note: In collecting duct, maximum reabsorption of water takes place which produces concentrated urine. Efferent arterioles have smaller diameters because it helps in maintaining the high blood pressure in glomerulus.
Complete Answer:
1) Nephrons are the structural units that are composed of a renal corpuscle and renal tubule. It is a tube-like structure and 30-55mm long in length.
2) Renal tubule is a long, convoluted structure that emerges from glomerulus and further divided into 3 parts: proximal convoluted tubule (PCT); Henle’s loop; distal convoluted tubule.
3) PCT stays in the renal cortex due to its proximity to the glomerulus. The second part is Henle’s loop is also called a nephritic loop because it forms a loop that goes through renal medulla. Distal convoluted tubule which is the third part of renal tubule is also restricted to the renal cortex.
4) A cup-like structure called Bowman's capsule in which capillaries of glomerulus are enclosed. Then Bowman’s capsule extends to highly coiled tubules called proximal convoluted tubules (PCT).
5) PCT continues to form a Henle’s loop that ascends to DCT and which in turn opens into the collecting duct. Collecting duct is straight, long where potassium and hydrogen ions are secreted to maintain the electrolytic balance of blood.
6) Renal corpuscle consists of glomerulus that is surrounded by Bowman’s capsule. Glomerulus arises from afferent arteriole and empty in efferent arteriole.

Note: In collecting duct, maximum reabsorption of water takes place which produces concentrated urine. Efferent arterioles have smaller diameters because it helps in maintaining the high blood pressure in glomerulus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




