
Permanent magnet has properties retentivity and coercivity respectively as:
A. high-high
B. low-low
C. low-high
D. high-low
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: A good permanent magnet should produce a high magnetic field with a low mass and should be stable against the influences which would demagnetize it. The desirable properties of such magnets are typically stated in terms of the retentivity (remanence) and coercivity of the magnet materials.
Complete step by step solution:
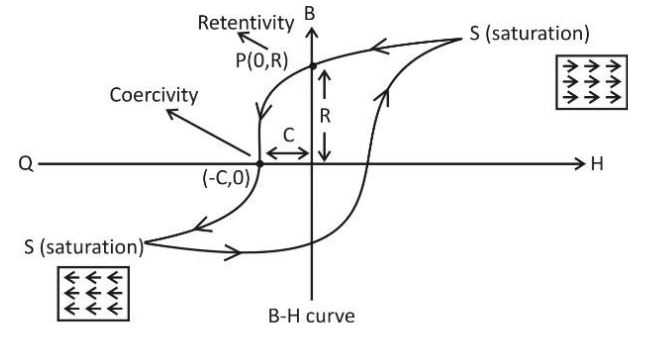
Retentivity$\left( R \right)$: It is a measure of the remaining magnetization when the driving field$\left( H \right)$is dropped to zero.
Coercivity$\left( C \right)$: It is a measure of the reverse field needed to drive the magnetization into zero after being saturated.
The materials suitable for permanent magnets must have high retentive, high coercivity and high permeability.
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note: The material used for permanent magnet must be high retentively so that magnet be strong and that of high coercively so that the magnetism does not unify out on applying strong magnetic field through it.
Complete step by step solution:

Retentivity$\left( R \right)$: It is a measure of the remaining magnetization when the driving field$\left( H \right)$is dropped to zero.
Coercivity$\left( C \right)$: It is a measure of the reverse field needed to drive the magnetization into zero after being saturated.
The materials suitable for permanent magnets must have high retentive, high coercivity and high permeability.
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note: The material used for permanent magnet must be high retentively so that magnet be strong and that of high coercively so that the magnetism does not unify out on applying strong magnetic field through it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




