
Following represents the Maxwell distribution curve for an ideal gas at two temperatures ${{T}_{1}}$ and ${{T}_{2}}$. Which of the following option(s) are true?
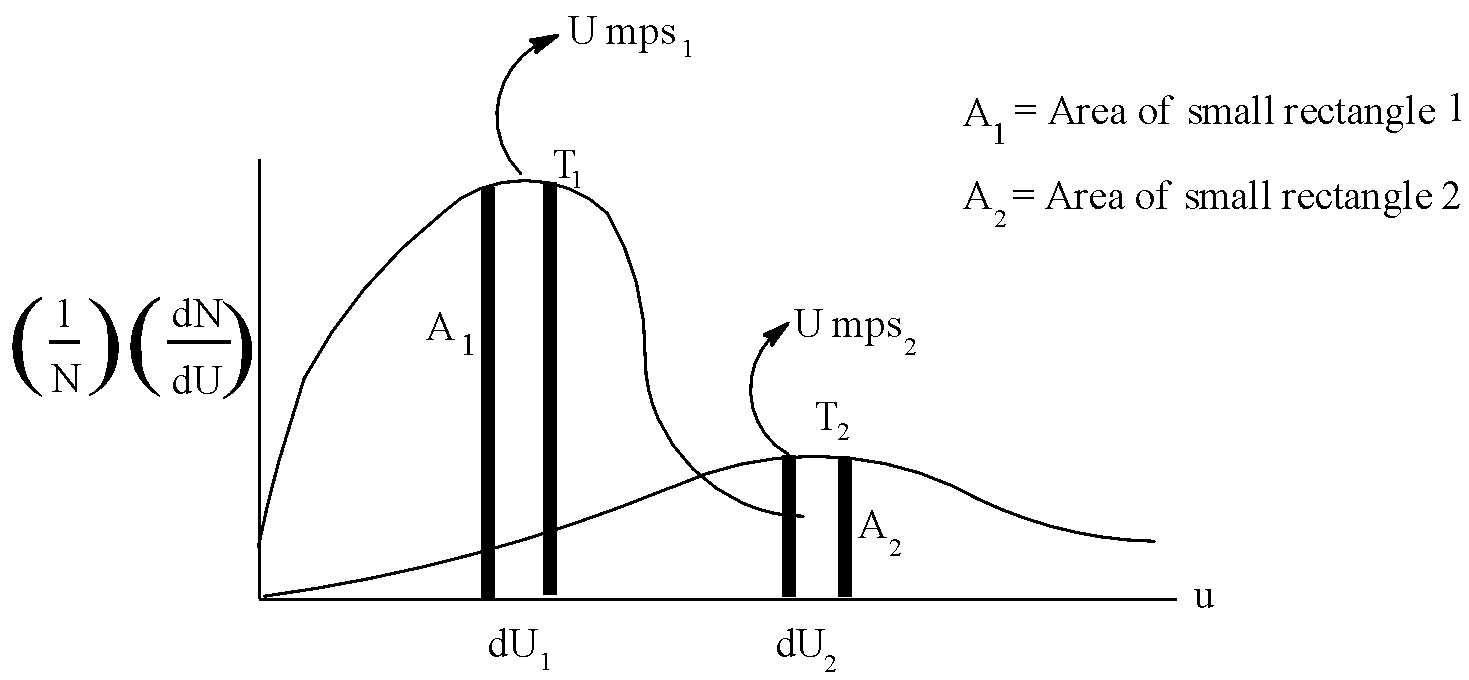
A.Total area under the two curves is independent of moles of gas.
B. If $d{{U}_{1}}=f\,\,Ump{{s}_{1}}\,\And \,d{{U}_{2}}=f\,Ump{{s}_{2}}$ then ${{A}_{1}}={{A}_{2}}$
C.${{T}_{1}} > {{T}_{2}}$ and hence higher the temperature, sharper the curve.
D. The fraction of molecules having speed = $Umps$ decreases as temperature increases.

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The concept of Maxwell’s Distribution of speeds is to be used while solving this question. The graph gives us an idea about the behaviour of the fraction of molecules and their speeds/energy as the temperature is changed.
Complete answer:
In order to answer this question, we need to have an idea about the Maxwell Distribution of Speeds graph. In the graph, we see the effect of temperature. In a given sample of gas, at a given temperature, all the molecules of the reacting species do not have the same kinetic energy. Since it is difficult to predict the behaviour of individual molecules with precision, Ludwig Boltzmann and James Clerk Maxwell used statistics to predict the behaviour of large numbers of molecules. The peak of the curve can be used to determine the most probable kinetic energy i.e., kinetic energy which the maximum fraction of molecules possesses.
Only those collisions result in the formation of products which have energy more than the certain minimum energy or the threshold. Collisions of the molecules which are less than the threshold cannot form products. In between the products and the reactants an energy barrier exists and this needs to be crossed before the reactants get converted into products. The energy required for crossing this energy barrier is called activation energy. When the temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules increases ($K.E\,\alpha \,T$) therefore, the maximum of the energy distribution curve gets flattened and shifts towards higher energy value i.e., shifts to right as there is now greater proportion of molecules with much higher energies.
Now, let us come to the solution. We know that area under the curve represents the fraction of molecules, and that the total area is constant. So, option A is correct. Moreover, as both the areas are equal, the condition in option B is also satisfied. As explained above, temperature will increase, speed of fraction of molecules will increase with increase in energy. But, ${{T}_{1}} < {{T}_{2}}$.
So, we obtain the correct answer as options A, B and D.
Note:
It is to be noted that for every ${{10}^{0}}$ rise in the temperature, the rate of reaction almost gets doubled. A catalyst speeds up the reaction by providing an alternative pathway of lower activation energy.
Complete answer:
In order to answer this question, we need to have an idea about the Maxwell Distribution of Speeds graph. In the graph, we see the effect of temperature. In a given sample of gas, at a given temperature, all the molecules of the reacting species do not have the same kinetic energy. Since it is difficult to predict the behaviour of individual molecules with precision, Ludwig Boltzmann and James Clerk Maxwell used statistics to predict the behaviour of large numbers of molecules. The peak of the curve can be used to determine the most probable kinetic energy i.e., kinetic energy which the maximum fraction of molecules possesses.
Only those collisions result in the formation of products which have energy more than the certain minimum energy or the threshold. Collisions of the molecules which are less than the threshold cannot form products. In between the products and the reactants an energy barrier exists and this needs to be crossed before the reactants get converted into products. The energy required for crossing this energy barrier is called activation energy. When the temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules increases ($K.E\,\alpha \,T$) therefore, the maximum of the energy distribution curve gets flattened and shifts towards higher energy value i.e., shifts to right as there is now greater proportion of molecules with much higher energies.
Now, let us come to the solution. We know that area under the curve represents the fraction of molecules, and that the total area is constant. So, option A is correct. Moreover, as both the areas are equal, the condition in option B is also satisfied. As explained above, temperature will increase, speed of fraction of molecules will increase with increase in energy. But, ${{T}_{1}} < {{T}_{2}}$.
So, we obtain the correct answer as options A, B and D.
Note:
It is to be noted that for every ${{10}^{0}}$ rise in the temperature, the rate of reaction almost gets doubled. A catalyst speeds up the reaction by providing an alternative pathway of lower activation energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




