
Compensation point is
A. Where there is neither photosynthesis or respiration
B. When rate of photosynthesis is equal to rate of respiration
C. When there is enough water just to meet the requirements of plant
D. When the entire food synthesized in photosynthesis remains unutilized
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Compensation point is the point at which the photosynthesis and respiration are in balance. At the compensation point, the uptake of oxygen by respiration becomes equal to the photosynthetic release of oxygen.
Complete answer
The amount of oxygen produced by photosynthesis will be equal to the amount which is used by the respiration. The carbon dioxide assimilation is zero and at this point NO oxygen bubbles are present in the leaf disc. There is no bubble of carbon dioxide as it is more soluble in water.
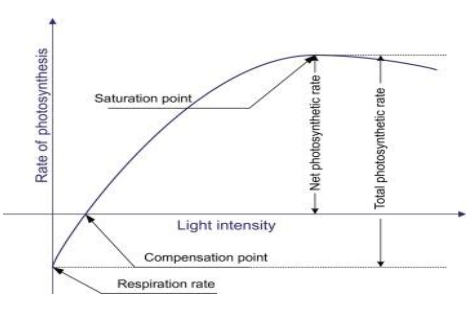
The figure shows:
On the light curve, the compensation point is defined as a point where the rate of cellular respiration is equal to the rate of photosynthesis.
As the light intensity increases, the compensation point is reached. If it is reached beyond the compensation point, the rate of photosynthesis increases until the point of saturation is reached.
Photosynthesis depends on the intensity of sunlight whereas respiration is constant.
AT COMPENSATION POINT:
The plants neither consume nor build biomass because at this point the rate of photosynthesis is balanced to the rate of respiration.
This point occurs in early mornings and late evenings.
The net gaseous exchange is also zero
Photosynthesis depends on the intensity of sunlight whereas respiration is constant.
The correct answer is when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
Note: At the compensation point, the net productivity is zero. No growth can occur at this point. It is a useful estimate of the lowest irradiance at which algae can maintain an autotrophic existence.
Complete answer
The amount of oxygen produced by photosynthesis will be equal to the amount which is used by the respiration. The carbon dioxide assimilation is zero and at this point NO oxygen bubbles are present in the leaf disc. There is no bubble of carbon dioxide as it is more soluble in water.

The figure shows:
On the light curve, the compensation point is defined as a point where the rate of cellular respiration is equal to the rate of photosynthesis.
As the light intensity increases, the compensation point is reached. If it is reached beyond the compensation point, the rate of photosynthesis increases until the point of saturation is reached.
Photosynthesis depends on the intensity of sunlight whereas respiration is constant.
AT COMPENSATION POINT:
The plants neither consume nor build biomass because at this point the rate of photosynthesis is balanced to the rate of respiration.
This point occurs in early mornings and late evenings.
The net gaseous exchange is also zero
Photosynthesis depends on the intensity of sunlight whereas respiration is constant.
The correct answer is when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
Note: At the compensation point, the net productivity is zero. No growth can occur at this point. It is a useful estimate of the lowest irradiance at which algae can maintain an autotrophic existence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




