
How many ATP molecules are produced from the complete oxidation of a molecule of active acetate or acetyl CoA?
(a)38 ATP
(b)15 ATP
(c)12 ATP
(d)4 ATP
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: TCA cycle or Kreb cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria. It is a long and steps by step process which ends up in a loop. The end products give 6 NADH, 2 ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$, and 2 ATP.
Complete answer:
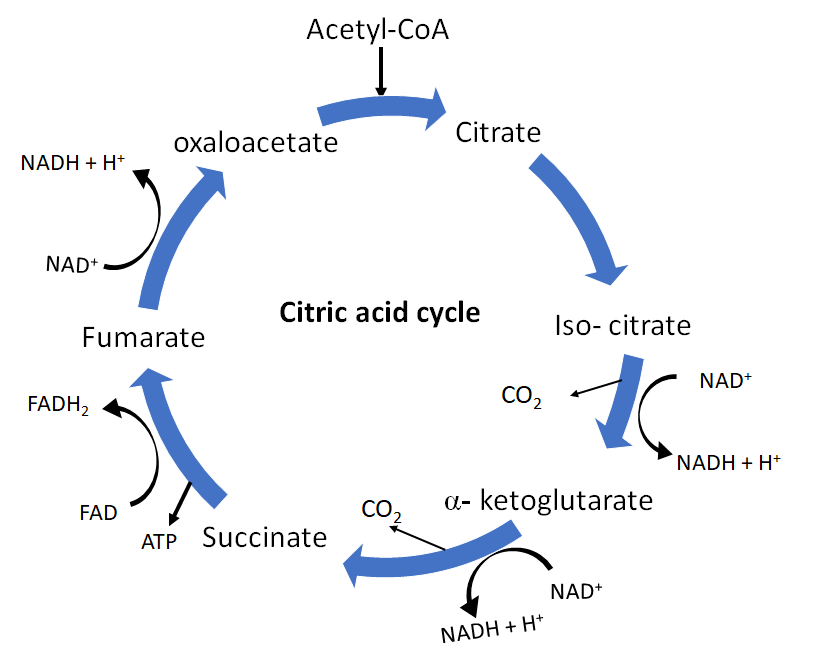
2 molecules of pyruvates are formed during glycolysis of glucose. These 2 pyruvates again convert into 2 molecules of acetyl CoA which enters the Krebs cycle.
In the Krebs cycle,
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of isocitrate to oxalosuccinate.
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA.
1 GTP is produced in the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid.
1 ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ is produced in the conversion of succinic acid into fumaric acid.
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate.
Adding all the ATP produced, the total ATP will be
1 NADH + 1 NADH + 1GTP+ 1 ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$+ 1 NADH
= 3+ 3+ 1+ 2+ 3
= 12
Additional Information: This question is related to the citric acid cycle that occurs in the matrix of mitochondria in the aerobic organisms in order to release energy through the oxidation of acetyl CoA. This is also known as the Krebs cycle. This pathway occurs between NADH and FADH2. It is a close loop as the last pathway of this process leads to the regeneration of the first molecule.
Here are the steps of the TCA cycle:
1.Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate which is a 4-carbon compound to release the CoA group and make citrate.
2.This citrate converts into isocitrate by losing a water molecule and again gaining one to form the later.
3.Orocess of oxidation of isocitrate catalyzed by the isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme.
4.Oxidation of à-ketoglutarate to reduce ${ NAD }^{ + }$ to NADH and release a CO2 molecule. At the same time, the remaining 4 carbon molecules pick up CoA to form succinyl CoA.
5.CoA of succinyl CoA replaced with a phosphate group and transferred to ADP to produce ATP and succinate.
6.Oxidation of succinate to fumarate, FAD produces ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$.
7.Water is added to the fumarate and converts it to malate.
8.Oxidation of malate and regeneration of oxaloacetate through it. Another molecule of ${ NAD }^{ + }$ also gets reduced to NADH.
Therefore, in the end, the products we get are
-6 NADH
-2ATP
-2${ FADH }_{ 2 }$
So, the correct answer is 12 ATP. Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note: All aerobic organisms perform the citric acid cycle or Kreb cycle as the second part of respiration in order to release the stored energy by oxidation of acetyl CoA. In addition to that, it provides precursors of amino acids and NADH. The animals that lack mitochondria such as prokaryotic bacteria, the citric acid cycles occur in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production across the plasma membrane.
Complete answer:
2 molecules of pyruvates are formed during glycolysis of glucose. These 2 pyruvates again convert into 2 molecules of acetyl CoA which enters the Krebs cycle.
In the Krebs cycle,
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of isocitrate to oxalosuccinate.
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA.
1 GTP is produced in the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid.
1 ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ is produced in the conversion of succinic acid into fumaric acid.
1 NADH is formed in the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate.
Adding all the ATP produced, the total ATP will be
1 NADH + 1 NADH + 1GTP+ 1 ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$+ 1 NADH
= 3+ 3+ 1+ 2+ 3
= 12
Additional Information: This question is related to the citric acid cycle that occurs in the matrix of mitochondria in the aerobic organisms in order to release energy through the oxidation of acetyl CoA. This is also known as the Krebs cycle. This pathway occurs between NADH and FADH2. It is a close loop as the last pathway of this process leads to the regeneration of the first molecule.
Here are the steps of the TCA cycle:
1.Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate which is a 4-carbon compound to release the CoA group and make citrate.
2.This citrate converts into isocitrate by losing a water molecule and again gaining one to form the later.
3.Orocess of oxidation of isocitrate catalyzed by the isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme.
4.Oxidation of à-ketoglutarate to reduce ${ NAD }^{ + }$ to NADH and release a CO2 molecule. At the same time, the remaining 4 carbon molecules pick up CoA to form succinyl CoA.
5.CoA of succinyl CoA replaced with a phosphate group and transferred to ADP to produce ATP and succinate.
6.Oxidation of succinate to fumarate, FAD produces ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$.
7.Water is added to the fumarate and converts it to malate.
8.Oxidation of malate and regeneration of oxaloacetate through it. Another molecule of ${ NAD }^{ + }$ also gets reduced to NADH.
Therefore, in the end, the products we get are
-6 NADH
-2ATP
-2${ FADH }_{ 2 }$
So, the correct answer is 12 ATP. Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note: All aerobic organisms perform the citric acid cycle or Kreb cycle as the second part of respiration in order to release the stored energy by oxidation of acetyl CoA. In addition to that, it provides precursors of amino acids and NADH. The animals that lack mitochondria such as prokaryotic bacteria, the citric acid cycles occur in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production across the plasma membrane.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




