
A convex mirror and a concave mirror of radius \[10cm\] each are placed \[15cm\] apart facing each other. An object is kept midway between them. If the reflection first takes place in the concave mirror and then occurs in convex mirror, the position of the final image will be,
A. on the pole of the convex mirror.
B. on the pole of the concave mirror.
C. at a distance of \[10cm\]from the convex mirror.
D. at a distance of \[5cm\] from the convex mirror.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: First of all draw the diagram as per the conditions mentioned in the question. Then find out the image position when the light initially passes through the concave mirror. This will be taken as the object distance for the convex mirror. Calculate the final image distance from the convex mirror using the mirror equation. This will help you to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us draw the ray diagram.
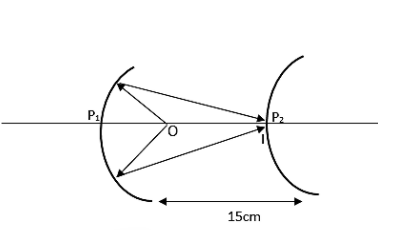
The values of the terms as per mentioned in the question are,
The radius of curvature of the convex and concave mirror is given as,
\[R=10cm\]
Therefore the focal length will be the half of the radius of curvature.
\[f=\dfrac{R}{2}=5cm\]
Distance between the mirrors is,
\[d=15cm\]
First of all light is falling on the convex mirror. So let us calculate the image distance from this,
As the object is placed midway between the mirrors we can write that the object distance to the concave mirror will be,
\[u=-7.5cm\](As per sign convention)
And the focal length will be,
\[f=-5cm\]
Using mirror equation, we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Substituting the values in it,
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{7.5}=\dfrac{1}{-5}\]
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{2}{15}+\dfrac{1}{-5}=\dfrac{5}{-75} \\
& v=-15cm \\
\end{align}\]
Which means the image of the concave mirror will be falling on the pole of the convex mirror.
Therefore the object distance for the convex mirror will be,
\[u=0cm\]
And the focal length will be,
\[f=+5cm\]
Substituting these in the mirror equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{0}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& v=0cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the final image will be on the pole of the convex mirror. Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: Sign convention is an important point to be noted when we solve this type of problem. A quantity is taken as positive if the direction of the position of the quantity is in the same direction of incident ray. In the same way, a quantity is given a negative sign when it is in the opposite direction of the incident ray.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us draw the ray diagram.

The values of the terms as per mentioned in the question are,
The radius of curvature of the convex and concave mirror is given as,
\[R=10cm\]
Therefore the focal length will be the half of the radius of curvature.
\[f=\dfrac{R}{2}=5cm\]
Distance between the mirrors is,
\[d=15cm\]
First of all light is falling on the convex mirror. So let us calculate the image distance from this,
As the object is placed midway between the mirrors we can write that the object distance to the concave mirror will be,
\[u=-7.5cm\](As per sign convention)
And the focal length will be,
\[f=-5cm\]
Using mirror equation, we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Substituting the values in it,
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{7.5}=\dfrac{1}{-5}\]
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{2}{15}+\dfrac{1}{-5}=\dfrac{5}{-75} \\
& v=-15cm \\
\end{align}\]
Which means the image of the concave mirror will be falling on the pole of the convex mirror.
Therefore the object distance for the convex mirror will be,
\[u=0cm\]
And the focal length will be,
\[f=+5cm\]
Substituting these in the mirror equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{0}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& v=0cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the final image will be on the pole of the convex mirror. Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: Sign convention is an important point to be noted when we solve this type of problem. A quantity is taken as positive if the direction of the position of the quantity is in the same direction of incident ray. In the same way, a quantity is given a negative sign when it is in the opposite direction of the incident ray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




