




Cornea Structure, Function, and Difference from Lens for NEET Exam
The concept of function of cornea in human eye is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively.
Understanding Function of Cornea in Human Eye
The function of cornea in human eye refers to the main roles played by the transparent, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye that covers the pupil and iris. This concept is important in areas like refraction of light, structure of human eye, and vision focusing power. In NEET and other biology exams, understanding the cornea’s function helps students differentiate between its role and those of the lens, iris, and pupil.
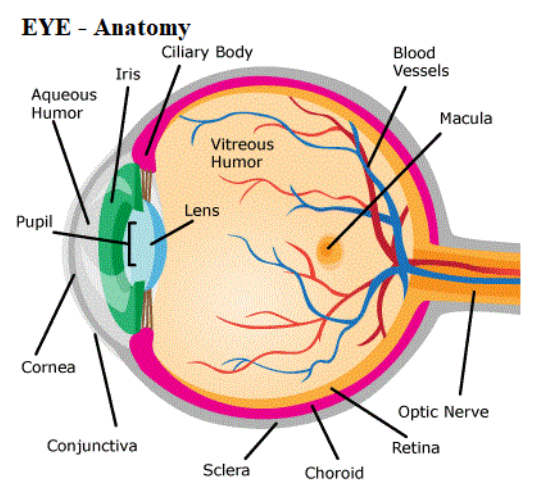
Core Functions of the Cornea
The main functions of the cornea in the human eye are:
- Refraction of light: The cornea bends (refracts) most of the incoming light rays, contributing about 65–75% of the eye’s total focusing power.
- Focusing images: By bending light, the cornea directs rays towards the lens and ultimately helps to form a sharp image on the retina.
- Protection: It acts as a barrier, protecting inner eye structures (like pupil, lens, and iris) from dust, germs, and injury.
- Transparency: The cornea is transparent and allows light to enter the eye without scattering.
- Sensory role (corneal reflex): Contains many nerve endings that trigger blinking when touched, keeping the eye safe.
Structure & Anatomy of the Cornea
The cornea is the anterior part of the eye and is composed of five distinct layers:
- Corneal epithelium: Multilayered, regenerates quickly, spreads tears, and keeps the surface moist.
- Bowman’s layer: Mainly collagen fibers that strengthen and protect the corneal stroma.
- Corneal stroma: Thick, transparent layer with collagen and keratocytes, giving cornea its shape and clarity.
- Descemet’s membrane: Acts as a basement membrane for the inner layer.
- Corneal endothelium: Maintains fluid balance, does not regenerate, essential for transparency.
Unlike most tissues, the cornea has no blood vessels – it gets nutrients from aqueous humour and tears. Sensory nerves in the cornea are responsible for ‘corneal reflex’ (quick blinking on touch).
Comparison: Cornea vs Other Eye Parts
It is common to get confused between cornea, lens, iris, and pupil in exams like NEET. Here's a quick difference:
| Part | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Cornea | Major refraction, protection | Front outer layer |
| Lens | Fine focusing, accommodation | Behind iris, after cornea |
| Iris | Controls pupil size, regulates light entering | Colored ring, behind cornea |
| Pupil | Opening for light entry | Center of iris |
Quick Revision Summary: Cornea’s Focusing Power
Cornea contributes about 65–75% of the eye's total focusing power. The lens performs 'fine-tuning' for focus (especially for near or far vision).
Worked Example – NEET MCQ Practice
Q: What is the primary function of the cornea in the human eye?
- Accommodation
- Refraction of light
- Production of aqueous humour
- Color vision
Correct Answer: 2. Refraction of light
Explanation: Cornea's main function is bending light to focus it onto the retina.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing function of cornea with lens (which is mainly for accommodation and fine focus).
- Forgetting that the cornea has no blood vessels.
- Labeling errors in eye diagrams – always mark cornea in the outermost front layer.
Real-World Applications
The concept of function of cornea in human eye is used in fields like medicine (e.g., vision correction, LASIK surgeries), optometry, and research on eye diseases. Corneal damage can cause blurred vision or blindness, highlighting why its function is crucial. Vedantu helps students connect these topics to real-life eye care and common vision problems.
In this article, we explored function of cornea in human eye, its key processes, anatomy, real-life importance, and how to answer NEET-style questions. To master such concepts and improve exam performance, keep practicing and learning with Vedantu resources.
Related Topics and Further Study
- Structure of Eye: Understand overall human eye anatomy for diagram-based questions.
- Retina: Learn how the cornea and retina work together for clear vision.
- Pupil Eye: Clarify the roles of pupil, iris, and cornea in NEET MCQs.
- Iris: Compare iris and cornea functions—common exam confusion.
- Cornea (In-depth): For multi-layered, advanced concepts.
- Sclera: See how sclera and cornea differ in structure and exam diagrams.
- Human Eye and the Colorful World: Broader vision and refraction for NEET content linkage.
- Eye Diseases: Application-based MCQs relating to corneal function and health.
- Diagram of Eye: Practice for accurate eye structure labelling.
FAQs on What Is the Function of Cornea in the Human Eye?
1. What is the main function of the cornea in the human eye in NEET?
The main function of the cornea is to act as the transparent, dome-shaped outer layer that refracts (bends) incoming light, helping to focus it on the retina. It contributes about 60-75% of the eye's total focusing power, making it essential for clear vision, as per the NEET syllabus.
2. How do I remember the difference between cornea and lens for NEET 2025?
To differentiate cornea and lens:
• Cornea is the transparent outermost layer and provides most of the eye’s focusing power, but it is fixed.
• Lens is located behind the pupil and changes shape (accommodation) to focus on near or distant objects.
Remember the cornea as the "front window" and the lens as the "adjustable focusing glass" in the eye.
3. Can you see without a cornea?
No, vision is severely impaired without a functional cornea. Since the cornea provides the majority of the eye's focusing power and protects internal eye structures, its absence or damage causes blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and increased risk of infection, making it critical for sight.
4. What is the function of corneal reflex?
The corneal reflex is a protective, involuntary blinking response triggered when the cornea is touched or exposed to irritants. This reflex helps prevent foreign particles from damaging the eye, ensuring safety and maintaining eye health as emphasized in the NEET curriculum.
5. What is the function of cornea and iris?
The cornea primarily refracts incoming light and protects the eye, while the iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the pupil size. Together, they regulate and focus light to create clear images on the retina, fundamental for vision in human eyes.
6. How does the cornea contribute to eye focusing power?
The cornea refracts light entering the eye due to its curved surface and transparency. This bending of light rays contributes roughly 70% of the eye’s total focusing ability, helping to form a clear image on the retina before further focusing by the lens.
7. Why is the cornea’s function often confused with the lens in MCQs?
Confusion arises because both the cornea and lens focus light on the retina. However, the cornea provides fixed, majority refractive power, whereas the lens fine-tunes focus by changing its shape during accommodation. NEET questions often highlight this distinction to test conceptual clarity.
8. What silly mistakes do students make when drawing the cornea in diagrams?
Common errors include:
• Labeling the cornea as the entire front part of the eye instead of only the transparent portion.
• Confusing cornea with sclera, which is opaque and white.
• Omitting the curvature of the cornea, which is vital to its refractive function.
Accurate labelling as per NCERT and NEET guidelines is essential.
9. Is cornea function ever tested as a “match the following” in NEET?
Yes, the function of cornea is frequently tested in formats like "match the following" or MCQs, pairing parts of the eye with their respective functions. Being familiar with its role in light refraction, protection, and corneal reflex helps in scoring well in these questions.
10. How can I avoid mixing up cornea and sclera under exam pressure?
To avoid confusion:
• Remember that the cornea is the transparent, curved front window of the eye.
• The sclera is the white, opaque outer layer surrounding most of the eyeball.
• Visualize the cornea as the clear, focusing surface and the sclera as the protective white covering.
Mnemonics or labelled diagrams aid quick recall.
11. What’s a good mnemonic for cornea’s role in light refraction?
A useful mnemonic is:
• Clear Outer Refraction Network Essential for Accuracy — CORNEA.
This reminds you that the cornea is the transparent outer layer responsible for the main refraction of light, essential for precise vision.
12. Will NEET ask percent contribution of cornea vs lens in vision?
Yes, NEET often expects students to know the approximate percentage contribution of the cornea (about 70%) and the lens (about 30%) to the eye's total refractive power. This understanding assists in answering conceptual and diagram-based questions accurately.























