




What is the Floral Formula of Solanaceae?
The Solanaceae family, commonly referred to as the "potato family," is a diverse group of angiosperms found across tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions globally. This family encompasses a variety of plants, including important crops, medicinal plants, and spices. Well-known vegetables such as potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers, and eggplants belong to the Solanaceae family.
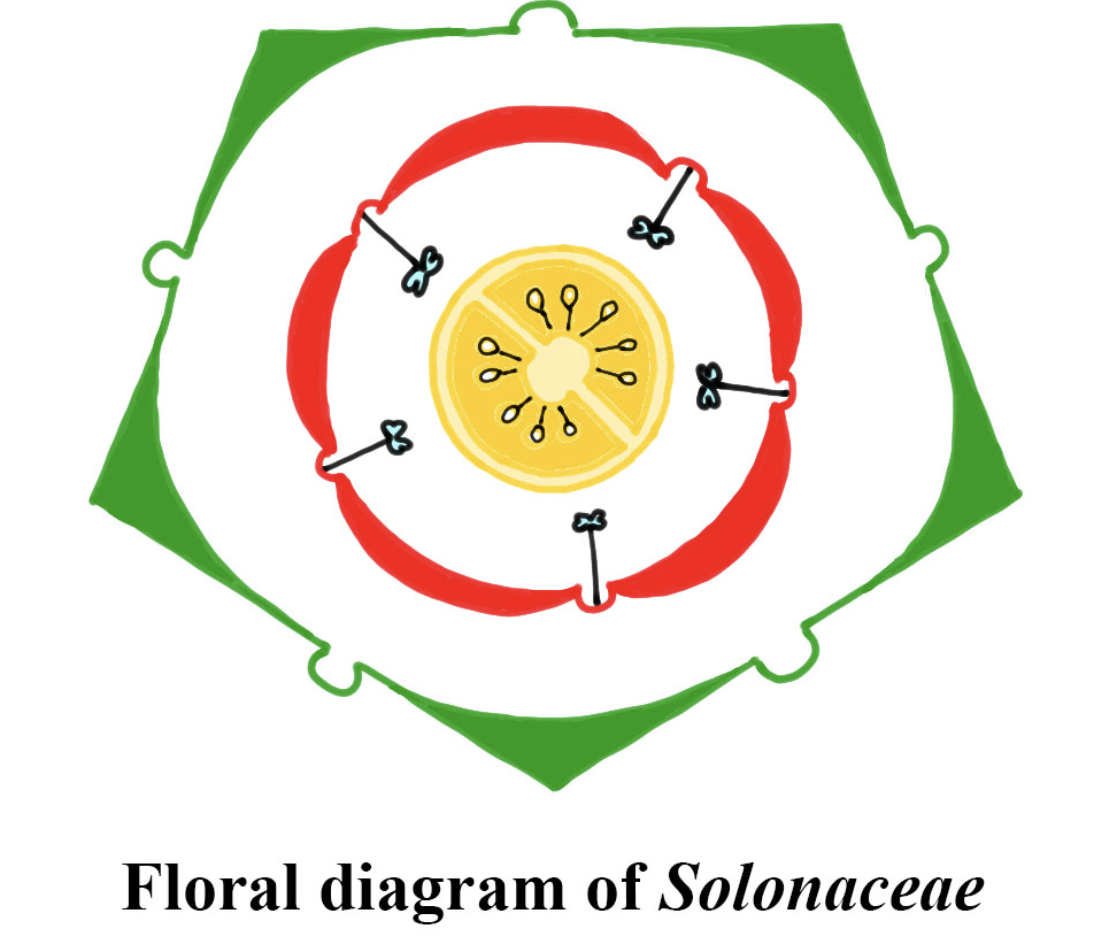
Floral Formula
The general floral formula for the Solanaceae family (which includes plants like tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and peppers) is as follows-
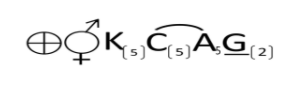
K(5)- 5 sepals, fused (calyx)
C(5)- 5 petals, fused (corolla)
A(5)- 5 stamens, fused (androdium)
G(2)- 2 carpels, fused (gynoecium)
⚥- Bisexual
⊕- Actinomorphic (radial symmetry)
This formula represents a typical flower structure in the Solanaceae family, with five sepals and petals, five fused stamens, and a gynoecium with two fused carpels. The numbers indicate the parts of the flower, and the parentheses around the numbers denote that the parts are fused or united.
Systematic Position of Solanaceae Family
Kingdom- Plantae
Subkingdom- Tracheobionta
Super Division- Spermatophyta
Division- Magnoliophyta
Class- Magnoliopsida
Subclass- Asteridae
Order- Solanales
Family- Solanaceae
Key Features of the Solanaceae Family
The Solanaceae family is a large and diverse group of flowering plants with about 102 genera and around 2500 species. Some common plants in this family include-
Family Description
Habit- Includes herbs, shrubs, and some small trees.
Root- Usually a tap root system with branching.
Stem- Aerial, branched, erect, and mostly herbaceous. Some, like potato, have underground stems.
Leaf- Simple, alternate, and sometimes pinnately compound. Venation is reticulate. Some leaves are exstipulate, sessile, or modified into spines.
Inflorescence- Flowers can be solitary or grouped, with axillary or cymose arrangements.
Flower Characteristics-
Bracteate or Ebracteate- The flowers may or may not have bracts.
Symmetry- Actinomorphic (radial symmetry) and generally hermaphroditic.
Structure- Pentamerous and hypogynous (ovary positioned below the other flower parts).
Calyx- Typically 5 sepals, which are gamosepalous (united), persistent, with valvate aestivation (sepals do not overlap).
Corolla- Composed of 5 fused petals (gamopetalous), with either valvate or imbricate aestivation.
Androecium- Five polyandrous (free) stamens, epipetalous (attached to petals).
Gynoecium- Bicarpellary, syncarpous (fused carpels), with a superior ovary and axile placentation. It has one style and either a simple or bilobate stigma.
Fruit- Can be a berry (e.g., tomatoes) or a capsule (as seen in Datura).
Seeds- Numerous, with a round, flat shape and endospermic (containing stored food). Chromosome count is typically 2n = 24, but polyploidy can occur.
Pollination- Predominantly entomophilous (insect-pollinated).
Economic Significance of Solanaceae
The Solanaceae family holds considerable economic importance due to its diverse uses-
Edible Crops- Many species serve as vegetables, such as potatoes, tomatoes, eggplant, and bell peppers.
Medicinal Value- Plants like Atropa belladonna, Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), and Datura are known for their medicinal properties, including alkaloids like tropanes, nicotine, capsaicin, and hyoscyamine. However, some of these alkaloids can also be toxic.
Commercial Use- Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) is a significant commercial crop.
Ornamentals- Petunias and other ornamental plants in the family add aesthetic value to gardens and landscapes.
In summary, flowers of the Solanaceae family are complete, bisexual, actinomorphic, and hypogynous. They typically feature five sepals (united), five petals (fused), five stamens (free and attached to petals), and a bicarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium with a superior ovary. The fruit can be a berry or capsule, and the plants are often insect-pollinated.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on Floral Formula of Solanaceae Family
1. What is the Solanaceae family?
The Solanaceae family, also known as the nightshade family, is a large group of flowering plants with approximately 102 genera and around 2500 species. It includes many important agricultural and medicinal plants such as tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and tobacco.
2. What are some common plants in the Solanaceae family?
Some well-known members of the Solanaceae family include-
Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
Eggplant (Solanum melongena)
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
Bell pepper (Capsicum annuum)
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum)
Belladonna (Atropa belladonna)
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
Datura (Datura stramonium)
Petunia (Petunia hybrida)
3. What is the typical structure of a Solanaceae flower?
Flowers in the Solanaceae family are typically-
Complete (all floral parts present),
Actinomorphic (radially symmetrical),
Bisexual (having both male and female reproductive organs),
Pentamerous (with five parts in each whorl),
Hypogynous (ovary positioned below other floral parts).
4. What are the characteristics of the calyx and corolla in Solanaceae flowers?
Calyx- Consists of five sepals, which are fused (gamosepalous), persistent, and show valvate aestivation (the sepals do not overlap).
Corolla- Composed of five fused petals (gamopetalous), with either valvate or imbricate aestivation (overlapping petals).
5. How are the reproductive organs of Solanaceae flowers structured?
Androecium- The flower contains five stamens, which are free (polyandrous) and attached to the petals (epipetalous).
Gynoecium- It is bicarpellary, syncarpous (fused), with a superior ovary. The ovary has axile placentation, and the stigma is either simple or bilobate.
6. What is the floral formula of the Solanaceae family?
The general floral formula for the Solanaceae family is-
K(5) C(5) A(5) G(2)
Where-
K(5)- 5 sepals, fused (gamosepalous),
C(5)- 5 petals, fused (gamopetalous),
A(5)- 5 stamens, free (polyandrous), epipetalous,
G(2)- 2 carpels, fused (syncarpous), superior ovary.
7. What does the 'K' in the floral formula represent?
The 'K' in the floral formula stands for the calyx, which consists of 5 sepals that are typically fused (gamosepalous). The calyx is persistent and often shows valvate aestivation, where the sepals do not overlap.
8. What does the 'C' in the floral formula represent?
The 'C' represents the corolla, which is made up of 5 fused petals (gamopetalous). The petals often show either valvate or imbricate aestivation, meaning the petals may either meet edge to edge or overlap in a particular pattern.
9. What does 'A(5)' in the floral formula indicate?
The 'A(5)' in the floral formula refers to the androecium, which consists of 5 stamens. These stamens are polyandrous (free) and epipetalous (attached to the petals).
10. What does 'G(2)' in the floral formula represent?
The 'G(2)' in the floral formula stands for the gynoecium, which consists of 2 fused carpels (syncarpous). The ovary is superior and has axile placentation, where the ovules are attached to the central axis.























