




Comprehensive Guide to Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers for NEET Preparation
Alcohols, phenols, and ethers are fundamental organic compounds that play an important role in NEET Examinations. Understanding their structure, properties, preparation methods, classification, and chemical reactions is crucial for mastering these topics. Let’s get into a detailed overview of each compound.
Alcohols- Introduction, Classification, Structure, Properties, and Reactions
Introduction to Alcohols
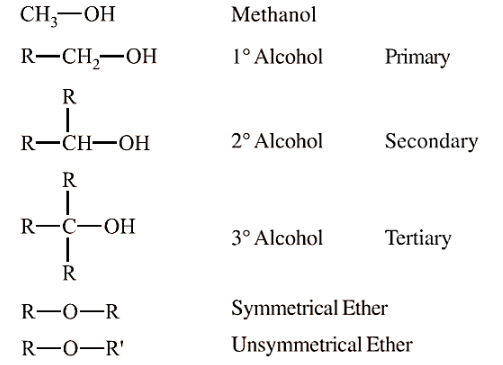
Alcohols are organic compounds in which a hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols are classified based on the number of hydroxyl groups present in the molecule and the type of carbon to which the -OH group is attached. Alcohols are widely used in industry, medicine, and as solvents.
Classification of Alcohols
Based on the Number of Hydroxyl Groups
Monohydric Alcohols-Contain one hydroxyl group (e.g., methanol, ethanol).
Dihydric Alcohols- Contain two hydroxyl groups (e.g., ethylene glycol).
Trihydric Alcohols- Contain three hydroxyl groups (e.g., glycerol).
Polyhydric Alcohols- Contain more than three hydroxyl groups (e.g., sorbitol).
Based on the Type of Carbon Bonded to Hydroxyl Group-
Primary Alcohols (1°)- The hydroxyl group is attached to a primary carbon (e.g., ethanol, methanol).
Secondary Alcohols (2°)- The hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon (e.g., isopropyl alcohol).
Tertiary Alcohols (3°)- The hydroxyl group is attached to a tertiary carbon (e.g., tert-butyl alcohol).
Allylic Alcohols- The hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon adjacent to a double bond (e.g., 3-hydroxypropene).
Benzylic Alcohols- The hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon adjacent to an aromatic ring (e.g., benzyl alcohol).
Structure of Alcohols
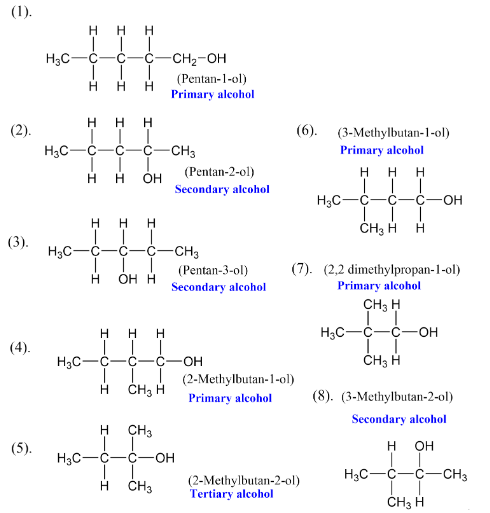
C-O Bond- The carbon and oxygen in the hydroxyl group are bonded through sp3 hybridized orbitals. The bond angle between the C-O-H is 108.9°, which is slightly less than the typical tetrahedral angle (109.5°) due to electron pair repulsion.
Bond Length- In methanol, the bond length of the C-O bond is 142 pm.
Properties of Alcohols
Boiling Point- Alcohols have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons due to hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups. The boiling point increases with the size of the molecule.
Solubility- Alcohols are soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding. Solubility decreases as the carbon chain length increases.
Acidity- Alcohols are weak Bronsted acids. The acidity decreases with increasing electron-donating alkyl groups. The order of acidity is- 1° > 2° > 3°.
Reactions of Alcohols
Nucleophilic Substitution-
Alcohols can react with HX (hydrogen halides) to form alkyl halides.
Reaction with metal to form alkoxides.
Oxidation-
Primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes, which can further be oxidized to carboxylic acids.
Secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones.
Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation.
Dehydrogenation- Alcohols undergo dehydrogenation when heated with copper at 573K, resulting in the formation of aldehydes or ketones.
Reaction with Carboxylic Acids- Alcohols react with carboxylic acids to form esters in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid.
Phenols- Introduction, Classification, Structure, Properties, and Reactions
Introduction to Phenols
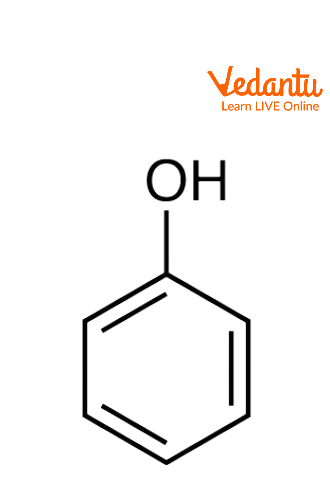
Phenols are organic compounds where the hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to an aromatic ring. Phenols are weaker acids than carboxylic acids, but they are stronger acids than alcohols. They are commonly used in antiseptics, industrial chemicals, and resins.
Classification of Phenols
Based on the Number of Hydroxyl Groups
Monohydric Phenols- Contain one hydroxyl group (e.g., phenol).
Dihydric Phenols- Contain two hydroxyl groups (e.g., catechol).
Polyhydric Phenols- Contain more than two hydroxyl groups (e.g., resorcinol).
Structure of Phenols
Phenols consist of a C-O bond where the carbon is part of an aromatic ring (sp2 hybridized). The bond angle between C-O-H is 109°, and the bond length of C-O is 136 pm.
The hydroxyl group in phenols can participate in resonance, stabilising the structure and making the molecule slightly acidic.
Properties of Phenols
Boiling Point- Phenols have higher boiling points than alcohols and ethers due to hydrogen bonding.
Solubility- Phenol is soluble in water, but solubility decreases as the hydrophobic part of the molecule increases.
Acidity- Phenols are more acidic than alcohols because the negative charge on the oxygen after deprotonation is stabilized by the delocalization of electrons in the aromatic ring. The acidity order is Nitrophenol > Phenol > Cresol > Ethanol.
Reactions of Phenols
Electrophilic Substitution-
Phenols undergo electrophilic substitution reactions such as nitration, halogenation, and sulfonation.
Reaction with NaOH- Phenols react with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide.
Oxidation- Phenols can undergo oxidation to form quinones.
Reaction with Carboxylic Acids- Phenols react with carboxylic acids to form esters.
Ethers- Introduction, Classification, Structure, Properties, and Reactions
Introduction to Ethers
Ethers are organic compounds where an oxygen atom is bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. They are known for their low reactivity and are widely used as solvents. Ethers are generally less reactive than alcohols and phenols.
Classification of Ethers
Symmetrical Ethers- Both alkyl groups attached to oxygen are the same (e.g., dimethyl ether).
Unsymmetrical Ethers- The alkyl or aryl groups attached to oxygen are different (e.g., ethyl methyl ether).
Structure of Ethers
Ethers consist of an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. The C-O-C bond angle is approximately 111.7°, which is slightly larger than the tetrahedral angle due to repulsion between bulky alkyl groups. The C-O bond length is around 141 pm, similar to alcohols.
Properties of Ethers
Boiling Point- Ethers have lower boiling points than alcohols because they do not form hydrogen bonds.
Solubility- Ethers are soluble in water and many organic solvents.
Acidity- Ethers are less acidic than alcohols and phenols. They are weak acids but are more acidic than hydrocarbons.
Reactions of Ethers
Electrophilic Substitution-
Ethers undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Friedel-Crafts Reaction- Ethers can participate in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions.
Cleavage of C-O Bond- Ethers undergo cleavage of the C-O bond under acidic conditions, forming alcohols or alkyl halides.
Classification of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers

 Share
ShareFAQs on Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
1. What are alcohols, phenols, and ethers?
Alcohols: Organic compounds containing a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a saturated carbon atom.
Phenols: Compounds where a hydroxyl group is attached directly to an aromatic benzene ring.
Ethers: Compounds consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
2. How are alcohols classified?
Alcohols are classified based on the number of hydroxyl groups and the type of carbon to which the -OH group is attached:
Based on Hydroxyl Groups:
Monohydric Alcohols: Contain one hydroxyl group.
Dihydric Alcohols: Contain two hydroxyl groups.
Trihydric Alcohols: Contain three hydroxyl groups.
Based on Carbon Attachment:
Primary (1°) Alcohols: The -OH group is attached to a primary carbon (attached to one other carbon).
Secondary (2°) Alcohols: The -OH group is attached to a secondary carbon (attached to two other carbons)
Tertiary (3°) Alcohols: The -OH group is attached to a tertiary carbon (attached to three other carbons).
3. What is the classification of phenols?
Phenols are primarily classified based on the number of hydroxyl groups attached to the benzene ring:
Monohydric Phenols: Contain one hydroxyl group
Dihydric Phenols: Contain two hydroxyl groups.
Polyhydric Phenols: Contain multiple hydroxyl groups.
They can also be categorized based on the position of the hydroxyl group on the benzene ring:
Ortho (o): Hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbons.
Meta (m): Hydroxyl groups on alternate carbons.
Para (p): Hydroxyl groups on opposite sides of the ring.
4. How are ethers classified?
Ethers are classified based on the nature of the groups attached to the oxygen atom:
Symmetrical Ethers: Both groups attached to oxygen are identical.
Unsymmetrical Ethers: The groups attached to oxygen are different.
Additionally, ethers can be categorized as:
Simple Ethers: Both groups are alkyl groups.
Mixed Ethers: One group is an alkyl group, and the other is an aryl group.
5. What are the general properties of alcohols, phenols, and ethers?
Alcohols:
Boiling Point: Generally higher than hydrocarbons due to hydrogen bonding.
Solubility: Lower alcohols are water-soluble; solubility decreases with increasing carbon chain length.
Acidity: Weak acids; acidity decreases with the presence of electron-donating groups.
Phenols:
Boiling Point: Higher than hydrocarbons but lower than alcohols.
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; solubility decreases with increasing hydrophobicity.
Acidity: More acidic than alcohols due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion.
Ethers:
Boiling Point: Lower than alcohols but higher than hydrocarbons.
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; act as solvents for many organic compounds.
Reactivity: Relatively inert but can undergo cleavage under acidic conditions.
6. What are the common reactions of alcohols, phenols, and ethers?
Alcohols:
Oxidation: Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and further to carboxylic acids; secondary alcohols to ketones.
Dehydration: Alcohols can undergo dehydration to form alkenes.
Esterification: Reaction with carboxylic acids to form esters.
Phenols:
Electrophilic Substitution: Reaction with electrophiles like halogens, nitrating agents.
Acid-Base Reactions: Phenols react with bases to form phenoxide ions and water.
Reduction: Reduction of the aromatic ring under specific conditions.
Ethers:
Cleavage: Reaction with acids to form alcohols and alkyl halides.
Formation of Peroxides: Ethers can form peroxides, which are explosive.
7. How are alcohols, phenols, and ethers named according to IUPAC nomenclature?
Alcohols:
Named by replacing the 'e' at the end of the parent alkane name with '-ol'. The position of the hydroxyl group is indicated by a number.
Phenols:
Named as derivatives of benzene with the hydroxyl group; positions are indicated by numbers (ortho, meta, para).
8. How are alcohols and phenols classified?
Alcohols and phenols are classified based on the number of hydroxyl (-OH) groups they contain. Monohydric alcohols/phenols contain one hydroxyl group, dihydric alcohols/phenols contain two hydroxyl groups, and trihydric alcohols/phenols contain three hydroxyl groups. Additionally, tertiary alcohols have three carbon atoms directly attached to the hydroxyl group.
9. What is the difference between alcohol and ether?
Alcohols and ethers are structurally similar to water. In alcohols, one hydrogen atom of the water molecule is replaced by an alkyl group, whereas in ethers, both hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
10. What are the uses of ether?
Ethers are commonly used as anesthetics in surgery, as cooling agents, and as inert solvents in reactions such as those involving Grignard reagents.
11. What is a simple ether?
A simple ether is one where the alkyl or aryl groups attached to both sides of the oxygen atom are identical.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


