How Can Heredity And Evolution Class 10 Questions And Answers Help You Prepare For Exams Effectively
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity And Evolution (2025-26)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity And Evolution (2025-26)
1. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 help students understand the process of heredity and evolution?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 provide step-by-step explanations of key genetics concepts such as Mendel’s laws of inheritance, variations, speciation, and natural selection. The answers are structured as per CBSE 2025–26 guidelines, making them easy to follow and ensuring students build a clear and exam-ready understanding of heredity and evolution topics.
2. What is the best method to approach Mendel’s experiments using NCERT Solutions for this chapter?
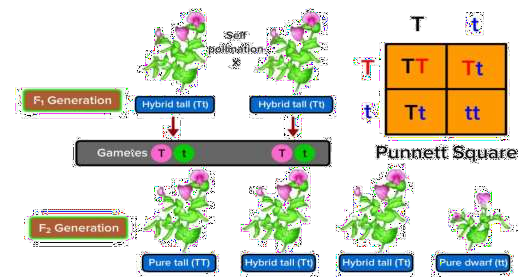
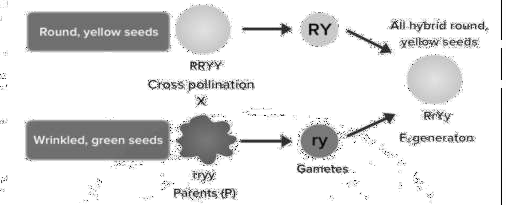
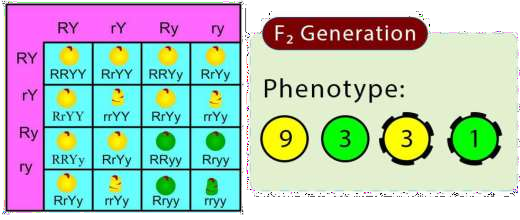
Begin by identifying the traits and parent combinations in the given problem. Next, use Punnett squares or step-by-step allele representations to trace inheritance through generations. Always conclude by comparing observed ratios to Mendel’s expected ratios, as outlined in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the determination of sex in humans for Class 10 exams?
The NCERT Solutions clarify sex determination through chromosomal contributions from both parents. Females have XX chromosomes, while males have XY chromosomes. Fusion of an ovum (X) with a sperm carrying an X gives a girl (XX); fusion with a sperm carrying a Y results in a boy (XY). This process is explained systematically to match the CBSE exam pattern.
4. Why are acquired traits not passed on to offspring as per the solution steps in this chapter?
Acquired traits occur due to environmental influences and affect only somatic (non-reproductive) cells. Since genetic information is inherited only through germ cells (sperm and egg), these acquired changes are not encoded in DNA and thus not transmitted to the next generation, as detailed in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8.
5. What stepwise approach is recommended for solving variation and speciation problems in the NCERT Solutions?
To solve variation and speciation questions:
- Identify if reproductive isolation, genetic drift, or mutation is involved.
- Check population size and reproductive method (sexual/asexual).
- Follow solution steps to see how new species can evolve through accumulated variations.
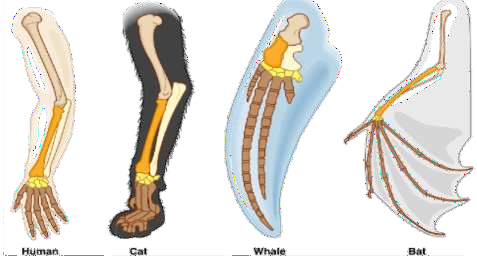
6. How can students differentiate between homologous and analogous organs when using NCERT Solutions?
Homologous organs have similar origin and structure but different functions (e.g., human arm and cat’s leg), while analogous organs perform similar functions but have different origins and structures (e.g., wings of a bird and wings of a butterfly). Using comparative diagrams and structure-function tables, as guided in NCERT Solutions, helps clarify these differences.
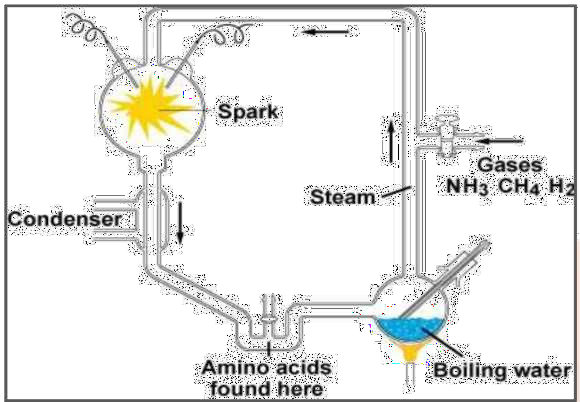
7. What role do fossils play in tracing evolutionary relationships, according to the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8?
Fossils provide direct evidence of life forms that existed in the past and depict the sequence of evolutionary changes across time. By comparing fossils at different geological layers, students can trace how complex organisms evolved from simpler forms, as described stepwise in the solutions.
8. How does the NCERT Solutions approach help overcome common misconceptions about dominant and recessive traits?
NCERT Solutions guide students through actual cross examples and genotype analysis, helping them realize that a dominant trait does not always appear in every generation if heterozygosity is involved. The detailed stepwise method avoids oversimplifying dominance, encouraging students to draw conclusions from Mendelian ratios and real genetic problems.
9. What are the main differences in stepwise solutions when dealing with inheritance by sexual versus asexual reproduction in this chapter?
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent, so NCERT Solutions involve tracing minor variations due to DNA copy errors. For sexual reproduction, solutions focus on parental allele combinations, using Punnett squares and explaining why more genetic diversity and viable variations occur, influencing evolution.
10. Why is geographical isolation not a major factor in the speciation of self-pollinating or asexual organisms, according to NCERT Solutions?
In self-pollinating and asexual species, individuals reproduce independently without requiring gene flow between populations. Therefore, geographical separation has little impact on genetic divergence or speciation, as explained clearly in the step-step methodology found in the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8.
11. How do the NCERT Solutions ensure students are prepared for CBSE board-style questions on heredity and evolution?
The solutions provide model answers with structured steps, direct application of laws, use of diagrams, and detailed reasoning aligned to CBSE 2025–26 exam expectations. They also highlight how to analyze questions, present answers, and avoid common mistakes, equipping students for board-level responses.
12. What is genetic drift, and how do NCERT Solutions approach its impact on small populations?
Genetic drift refers to random changes in gene frequency occurring by chance, especially in small populations. NCERT Solutions explain its consequences—possible loss or fixation of traits—by showing stepwise outcomes using practical examples and clear reasoning for population genetics questions.
13. In what way do the NCERT Solutions help differentiate between inherited and acquired traits with real-life examples?
Stepwise answers highlight that inherited traits are transmitted through genes (e.g., blood group, eye color), while acquired traits arise from individual experiences or environment (e.g., language learned). Real-life examples and clear distinction help avoid confusion in exam responses.
14. How does the step-by-step NCERT Solutions method aid in understanding the evidence for evolution?
By explaining fossil evidence, homologous and analogous organs, and molecular features with structured reasoning, NCERT Solutions link direct observations to broader concepts in evolution. The stepwise answers help students build logical, interconnected arguments as required by CBSE board exam marking schemes.
15. What common errors should students avoid when answering heredity and evolution questions using NCERT Solutions?
- Do not misinterpret dominant traits as always visible in every generation.
- Avoid confusing acquired with inherited traits.
- Make sure to follow each step when constructing genetic crosses or evolutionary explanations.
- Draw labeled diagrams where required, as suggested in the NCERT Solutions methodology for full marks.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video