




How to Identify 2D and 3D Shapes in Everyday Life
Kids are introduced to shapes and figures at an early age. Kids starting in Year 5 are introduced to the basic shapes and geometry. By Year 5, kids are familiarised with concepts like different shapes that they encounter every day. For example, we all have looked at and played with a ball, but have you wondered how we define its shape? The shape of a ball is a circle, similarly, a box is of a square shape. To learn more about shapes and how one can teach about shapes to Year 5 kids let us read the tips and tricks provided below.
We hope it would help you in teaching shapes to Year 5 kids, let us first discuss the concepts that can be taught to kids.
What Are the Topics Covered in Shapes in Year 5?
Before discussing the teaching methods used to teach shapes in a fun way, let us look into the topics that are covered in the introduction of shape and geometry.
The kids are taught to identify different shapes such as squares, rectangles and triangles based on their appearance.
Kids are taught about the different types of angles. Examples of angles that are introduced include acute, obtuse, right and straight angles.
Kids are also introduced to the use of protractors to measure the given angles.
The properties of individual shapes are taught to kids in Year 5. This can include the properties of a rectangle. Rectangle characteristics will be familiar to the child. For example, kids will understand that all rectangles have two sets of parellel lines, four corners, and four right angles and that the angles in all rectangles total up to 360 degrees.
How Can Parents Teach Kids Shapes in Year 5?
As we have discussed The topics that are taught under shapes in Year 5, let us now look into some of the fun cavities and methods that can help both parents and teachers in teaching shapes to kids in Year 5.
Using Mathematical Terms While Practising
One may help children learn by assisting them in describing shapes using features such as:
the total number of sides and edges
the number of vertices/corners the number of faces
lines of symmetry types of angles inside shapes.
Encourage children to use terms like diagonal, vertical, horizontal, parallel, acute, obtuse, and right angle in their Maths. The use of terms can help kids to better understand the meaning of the phrases.
Use Protractor Mat with Kids
One of the most effective ways of teaching kids shapes in Year 5 is the use of protractors. As the instrument is used to measure the angles this activity can be both fun and beneficial. Make a 'protractor mat' for your children to practise using a protractor accurately. Create a 90-degree mat in the pattern of a quarter circle using the corner of a sheet of paper. For each 10°, draw a line. Alternatively, make a half-circle mat with an angle of 180 degrees. For each 10°, draw a line. This will assist them to become accustomed to the appearance of various degrees of increments.
Playing Games That Require the Use of Coordinates
One of the games that require the use of coordinates is the game named battleships. Coordinates are integers that show where a point on a map, grid, or graph is located. Brackets are used to record coordinates, with the two numbers separated by a comma, as in: (1, 2). The first integer in a coordinate indicates the location of the point on the x-axis also called the horizontal axis) The second number indicates the location of the point on the vertical axis, often known as the y-axis.
Reading and plotting coordinates can help your youngster learn. The coordinates for the plotted point in the example below are (5, 6), where 5 is the x-axis value and 6 is the y-axis value:
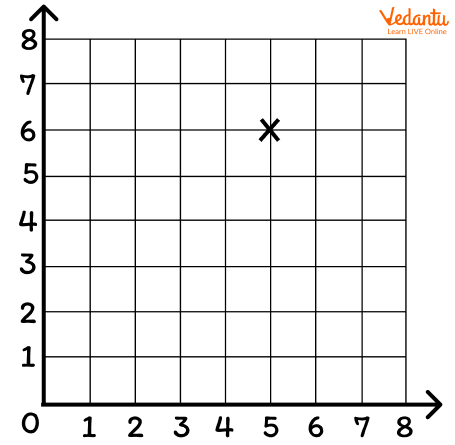
Graph representing the coordinates
In conclusion of the article, we have learnt about the topics that are usually taught in the introduction to shapes in Year 5. We have also learnt about some of the methods and activities that can be used in teaching shapes in Year 5.
FAQs on Year 5 Shapes Made Easy: Definitions, Facts & Examples
1. What are the main 2D and 3D shapes covered in the Class 5 Maths syllabus?
In Class 5, students learn about both two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) shapes. Key shapes include:
- 2D Shapes: These are flat shapes with only length and width. Examples are circles, squares, rectangles, and triangles. Students learn to identify them by their sides and corners (vertices).
- 3D Shapes: These shapes have length, width, and height. Common examples are the cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone, and sphere. Students explore their properties like faces, edges, and vertices.
2. How do you describe the properties of a 3D shape like a cube?
The properties of a 3D shape are described by its faces, edges, and vertices. For a cube, the properties are:
- Faces: These are the flat surfaces of the shape. A cube has 6 square faces.
- Edges: These are the lines where two faces meet. A cube has 12 edges of equal length.
- Vertices: These are the corners where the edges meet. A cube has 8 vertices.
3. What is the real-world difference between a 2D and a 3D shape?
The main difference is that a 2D shape is flat, while a 3D shape has depth and can be held. For example, a photograph of a ball is a 2D representation (a circle), but the actual ball is a 3D object (a sphere) because it occupies space. 2D shapes have only area, whereas 3D shapes have both area and volume.
4. What are the different types of angles a Class 5 student needs to know?
In Class 5, students are introduced to four basic types of angles based on their measurement in degrees:
- Acute Angle: An angle that measures less than 90°.
- Right Angle: An angle that measures exactly 90°.
- Obtuse Angle: An angle that measures more than 90° but less than 180°.
- Straight Angle: An angle that measures exactly 180°, forming a straight line.
5. How are angles related to the corners of a shape like a square or rectangle?
Angles are fundamental to defining a shape's corners (vertices). In a square or a rectangle, all four corners are perfect right angles, meaning they each measure 90 degrees. This property is what gives these shapes their distinct, boxy appearance. In contrast, the angles in a triangle can be acute, right, or obtuse, which determines the triangle's specific type.
6. What is the importance of learning about the nets of 3D shapes?
A net is a 2D pattern that can be folded to create a 3D shape. Understanding nets is important because it helps you visualise how a complex 3D object is constructed from a simple flat surface. For example, knowing the net of a cube helps in understanding that it is made of six square faces. This concept is crucial in real-world applications like packaging design and manufacturing, where flat materials like cardboard are folded to make boxes.
7. What is symmetry and how can you find the line of symmetry in a shape?
Symmetry in a shape means that it can be divided into two halves that are exact mirror images of each other. The dividing line is called the line of symmetry. To find it, you can imagine folding the shape along a line. If the two halves match up perfectly without any overlap, that fold line is a line of symmetry. For instance, a rectangle has two lines of symmetry, while a square has four.
8. What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
The key difference lies in their sides and angles. A regular shape has all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure. A square is a regular shape because all its sides and angles are equal. An irregular shape does not have all equal sides or all equal angles. A rectangle, for example, is an irregular shape because even though its angles are equal (all 90°), its adjacent sides are not of equal length.























