How to Identify Basic Shapes in Everyday Life
Understanding all shapes names and characteristics is fundamental in both mathematics and everyday life. From the simple circle to the complex hexagon, each shape has distinct properties that define its structure and uses. This page will guide you through the most common geometric shapes, offering clear definitions and practical examples to help you recognise and understand them better. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious about geometry, this comprehensive guide will enhance your knowledge of shapes and their applications. Explore our detailed explanations and learn how these fundamental shapes form the building blocks of more complex geometric concepts.
Shapes and Their Names
Everywhere we see objects of different shapes and each shape holds significance and certain properties. So, if you look at a chocolate box, it looks like a rectangle and each piece of chocolate seems square in shape. So, what properties does each shape have and how do identify each shape and distinguish between these shapes, this is a major concern.
Now, let us go through various shapes and understand tips to distinguish between them with the help of properties.
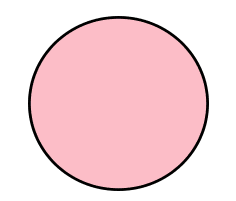
Circle
Definition: A round plane figure whose boundary (the circumference) is equidistant from the centre.
Properties:
No corners or edges.
All points on the circumference are the same distance from the centre.
The boundary is smooth and curved.
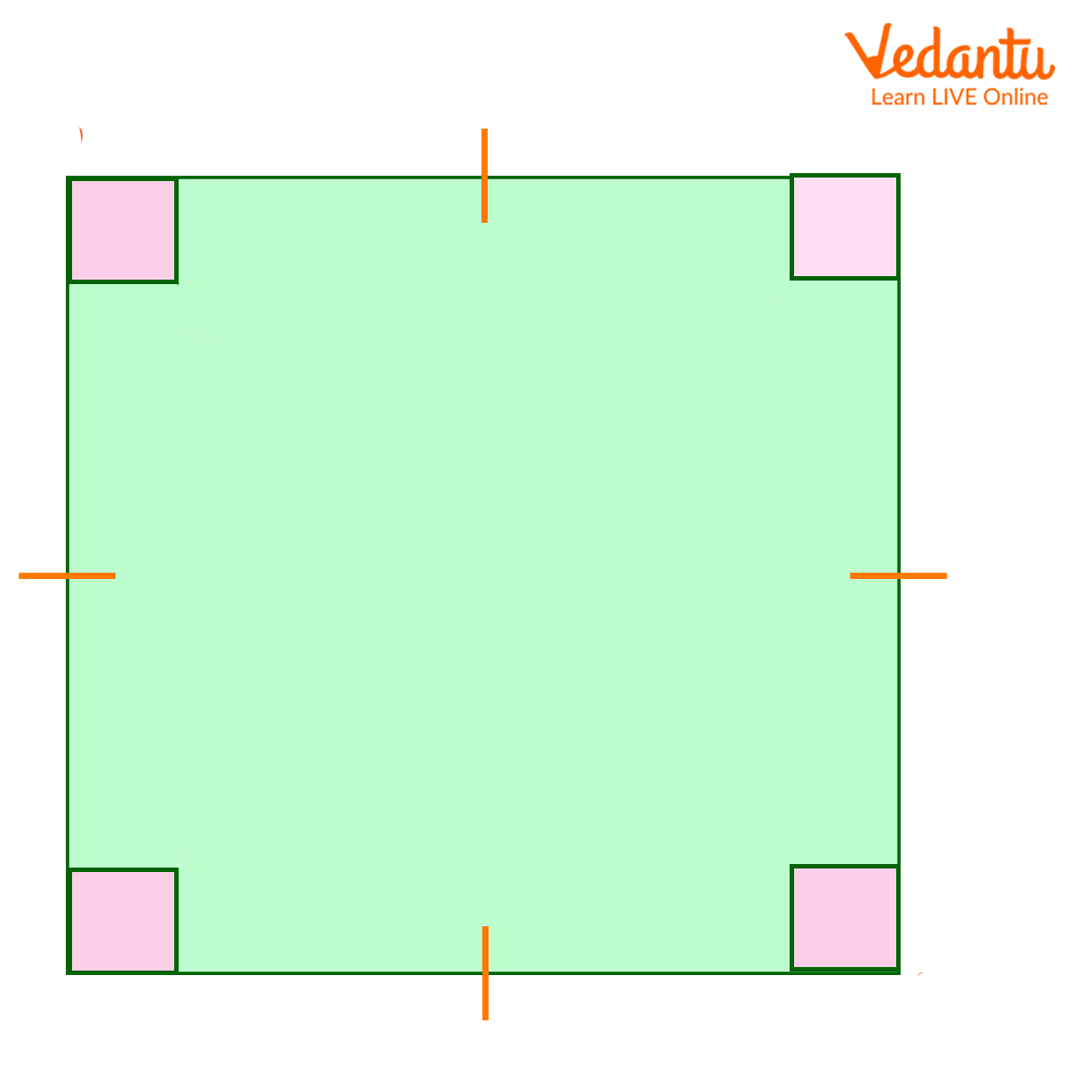
Square
Definition: A four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with equal-length sides and four right angles.
Properties:
All sides are of equal length.
All internal angles are 90 degrees.
The opposite sides are parallel.
Triangle
Definition: A three-sided polygon with three corners or vertices.
Properties:
The sum of the internal angles is always 180 degrees.
Can be classified as equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), or scalene (all sides different).
Has three edges.

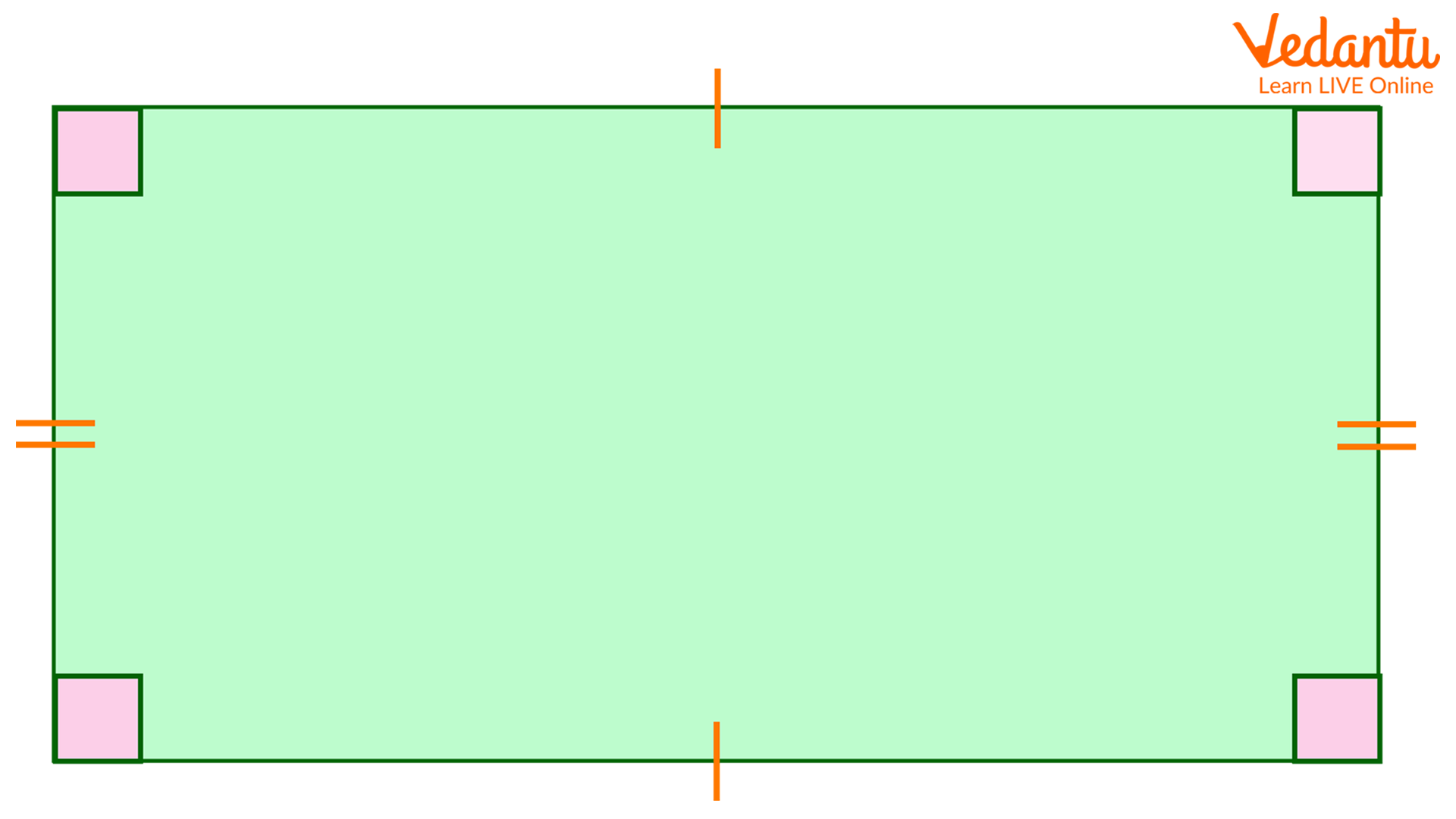
Rectangle
Definition: A four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with opposite sides equal in length and four right angles.
Properties:
Opposite sides are parallel and equal in length.
All internal angles are 90 degrees.
The sum of the internal angles is 360 degrees.
Oval
Definition: An elongated circle or an elliptical shape, with a smooth, curved boundary.
Properties:
No corners or edges.
The shape is symmetric along its long axis.
It has two focal points.

Pentagon
Definition: A five-sided polygon with five corners or vertices.
Properties:
The sum of the internal angles is 540 degrees.
Can be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular.
Has five edges.

Hexagon
Definition: A six-sided polygon with six corners or vertices.
Properties:
The sum of the internal angles is 720 degrees.
Can be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular.
Often seen in nature, such as in honeycombs.

Octagon
Definition: An eight-sided polygon with eight corners or vertices.
Properties:
The sum of the internal angles is 1080 degrees.
Can be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular.
Has eight edges.
Different Shapes for Kids
Various Geometric Shapes
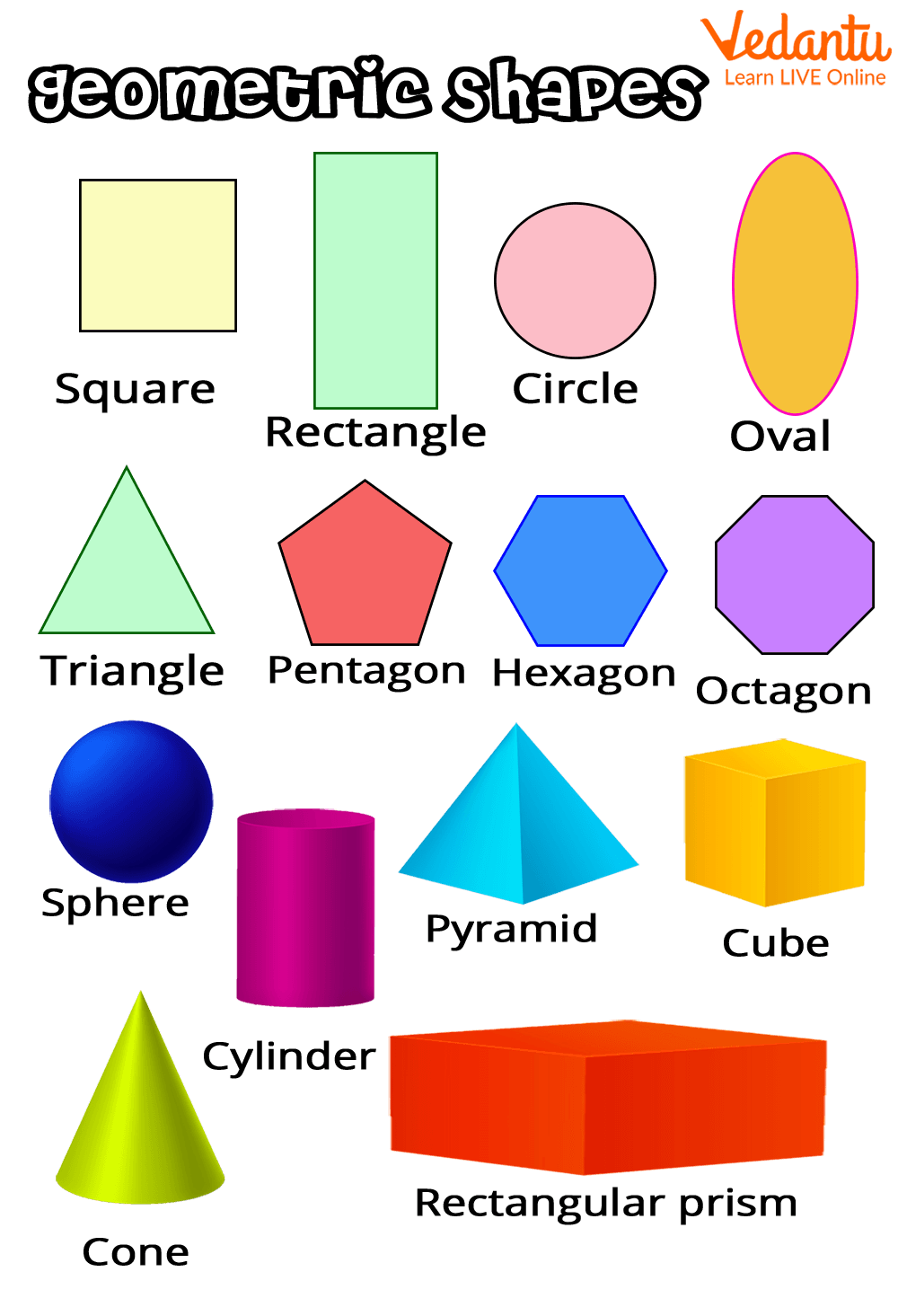
Image: Different shapes for Kids
List of all Shapes
Examples of Objects and Their Corresponding Shapes
Check your Knowledge of Shape Name in English
What shape is a standard soccer ball?
What shape is typically used for a standard sheet of paper?
What shape is a traditional wedding ring?
What shape is a standard dice?
What shape is a piece of pizza commonly cut into?
What shape is a traffic sign with eight sides?
What shape is a typical window pane?
What shape is a standard baseball?
What shape is the base of a pyramid in ancient Egypt?
What shape is a classic dinner plate?
What shape is commonly seen in a honeycomb?
What shape is often used for a standard playing card?
What shape is a standard traffic cone?
What shape is a typical football?
What shape is a book cover usually?
Find Out if you Got them All Right from the Answers Below.
Rectangle
Circle
Cube
Triangle
Octagon
Rectangle or Square
Sphere
Square
Circle
Hexagon
Rectangle
Cone
Ellipsoid
Rectangle or Square
Takeaway from the Page:
Shapes Overview: Different shapes are fundamental in both geometry and daily life, with examples ranging from basic polygons to complex 3D figures.
Common Objects and Shapes: Understanding the shapes of common objects helps in recognising and classifying them easily.
Knowledge Check: Testing your knowledge of all shapes names can reinforce understanding and application of geometric concepts.
FAQs on Different Types of Shapes for Kids: Names, Definitions & Pictures
1. What are the 5 shapes for kids?
The 5 fundamental shapes for kids are commonly:
- Circle
- Square
- Rectangle
- Triangle
- Oval
2. What are the 7 basic geometric forms?
The 7 basic geometric forms often taught to kids include:
- Circle
- Triangle
- Square
- Rectangle
- Oval
- Diamond (Rhombus)
- Star
3. What are shapes for kids with examples?
Shapes for kids include simple, recognizable figures seen in everyday life. For example:
- Circle – A clock face
- Square – A chessboard
- Rectangle – A door
- Triangle – A traffic sign
- Oval – An egg
4. How to classify shapes for kids?
Classifying shapes for kids is made simple using features like:
- Number of sides (e.g., triangle has 3, square has 4)
- Length of sides (equal in a square, unequal in a rectangle)
- Presence of curves (circles and ovals are curved, rectangles and squares have straight edges)
5. What are the differences between 2D and 3D shapes for kids?
The key difference between 2D and 3D shapes for kids is:
- 2D shapes (two-dimensional) have only length and width, such as a rectangle or circle ($$A=lw$$ for a rectangle, $$A=\pi r^2$$ for a circle).
- 3D shapes (three-dimensional) have length, width, and height/depth, such as cubes, spheres, and cylinders.
6. How can parents help children learn shapes at home?
Parents can support shape learning by:
- Encouraging kids to identify shapes in common household objects (e.g., clock for circle, TV screen for rectangle)
- Using drawing and coloring activities focused on basic shapes
- Playing shape-sorting games and puzzles
- Joining Vedantu’s online workshops and classes for interactive shape activities
7. Why is it important for kids to learn about different shapes?
Learning about different shapes helps children develop critical thinking, spatial awareness, and problem-solving abilities. Recognizing shapes serves as the building block for understanding numbers, patterns, geometry, and even art. Through Vedantu’s curriculum, students gain foundational math skills essential for future success.
8. What are some fun activities to teach shapes to kids?
Engaging activities to teach shapes include:
- Shape scavenger hunts around the house or classroom
- Crafting objects using cut-out paper shapes
- Building 3D models with blocks or clay
- Interactive shape quizzes on Vedantu’s digital learning platform
9. How do shapes help children in math and everyday life?
Understanding shapes is crucial for recognizing patterns, measuring objects, and solving spatial problems. Shapes form the core of geometry, and help kids in reading maps, organizing spaces, and even in art and design. Vedantu classes incorporate real-world examples to highlight the practical uses of shapes in daily life.
10. At what age should children start learning about shapes?
Children can start recognizing basic shapes as early as ages 2–3. Simple concepts like circles and squares are taught first, followed by more complex ones. Vedantu offers age-appropriate math lessons, ensuring kids are introduced to different types of shapes through interactive and engaging methods right from the foundational years.