




How to Solve Metric Measure Questions Step by Step
The most common method for determining height, distance, and weight is the metric system of measurement. By definition, the metric system of measurement in mathematics is the set of standard units defined to measure length, weight, area, and capacity. It is based on the decimal system as it includes numbers in powers of 10. The base units of length (distance), capacity (volume), and weight (mass) in the metric system are the metre, litre, and gramme, respectively. Measurements for length, width, and height are made using millimetres (mm), decimeters (dm), centimetres (cm), metres (m), and kilometres (km).
Metric System of Weights and Measures Used in the Unit
For measuring length, mass, area, and capacity, metric units come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The metric units for measuring length include millimetres, centimetres, metres, and kilometres. The units used to measure weight are grammes and kilograms. To grasp all the metric system units used for various applications, look at the table below which shows the metric system of weights and measures used in the unit as:
Conversion of Metric Measures
Converting from one metric system to another is known as the conversion of metric measures. The metric conversion ratio is a ratio that is equivalent to 1 in unit measurements. Unit factors are another name for it. The following list includes some of the most popular metric system conversion formulas:
Multiply 1000 to change km to m.
Multiply 100 to convert from m to cm.
Multiply 10 to convert 10 cm to mm.
Multiply 1000 to convert kilogrammes to grammes.
Multiply 1000 to convert grammes to milligrammes.
Divide 1000 to convert from litres to kiloliters.
Divide 1000 to convert millilitres to litres.
Chart for Metric Measures
The conversion formulas for the various metric units are contained in the chart of metric units. By examining its multiplication factor, you can rapidly convert one unit to another. For instance, you can see from the metric measures chart that 1 metre equals 100 centimetres. Let's look at the diagram of the metric system below:
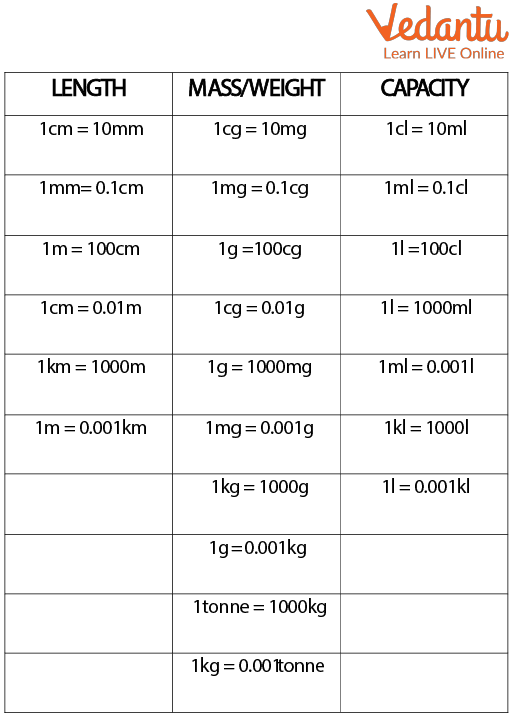
Conversions
Metric Measures Table
We have linear, area, volume, and cubic measures as follows:
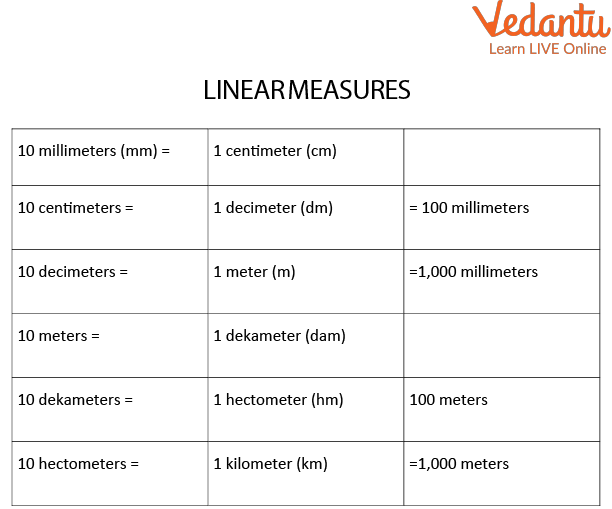
Linear measures
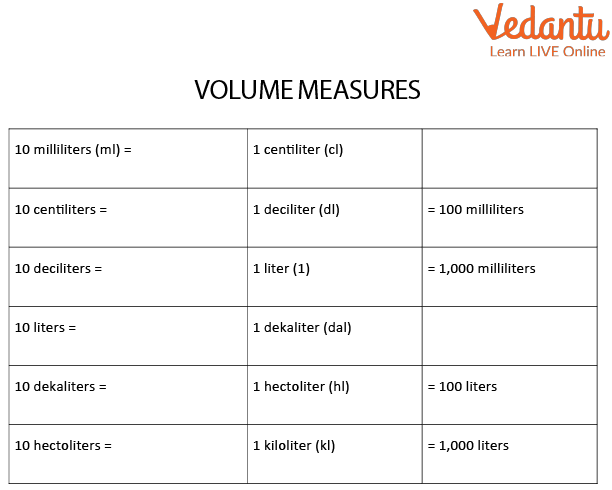
Volume measures
Table for Cubic Measures
What do the Metric Measures Indicate?
Metric measure indicates the base units of length (distance), capacity (volume), and weight (mass) in the metric system as metre, litre, and gram, respectively. We utilise units that are derived from metric units to measure smaller or greater quantities.
Solved Examples
Q 1. Conversion of 500 metres to kilometres.
Ans: We know that
$1 m=\dfrac{1}{1000} \mathrm{~km}$
For 500 metres we have
$500 m=\dfrac{500}{1000} k m$
$500 m=\dfrac{1}{2} k m=0.5 \mathrm{~km}$
Thus, 500 metres is half a kilometre.
Q 2. In an aquarium, Paul spotted a 600 cm long enormous fish. Calculate its length in millimetres.
Ans. The abbreviations for two of the length measurement units of the metric system are centimetres and millimetres or $\mathrm{cm}, \mathrm{mm}$ respectively.
Since there are $10 \mathrm{~mm}$ in 1 $\mathrm{cm}$, multiply the provided amount by 10 to convert from centimetres to millimetres.
$1 \mathrm{~cm}=10 \mathrm{~mm}$
$600 \mathrm{~cm}=600 \times 10 \mathrm{~mm}$
$600 \mathrm{~cm}=6000 \mathrm{~mm}$
Q 3. Convert 3 km to m.
Ans: To convert from kilo to hecto, hecto to deca and deca to metre, we need to multiply it by 10.
So, we multiply by $10^{3}=1000$
$3 \mathrm{~km}=3 \times 1,000=3,000 \mathrm{~m}$.
Q 4. Convert 20 mm to cm.
Ans: To convert from milli to centi, we need to divide it by 10.
So, we divide by $10 .$
$20 \mathrm{~mm}=20 \div 10=2 \mathrm{~cm}$
Q 5. A wireless router supports a range of up to 4,572 cm indoors. Calculate that length in metres.
Ans: Since, 100 cm equals to 1 m. Therefore, to find for 4,572cm; we need to divide it by 100 to convert from cm to m.
Therefore, $\dfrac{4,572}{100}$
= 45.72 m
So, a wireless router supports a range of up to 45.72 metres.
Practice Questions
Q 1. Conversion of 356 centimetres to metres.
Ans: 3.56 metres
Q 2. Rahul finds a garden having a length as 500 cm. Calculate its length in millimetres.
Ans: 5000 mm
Q 3. Calculate a woman’s body mass of 53 kg in grams.
Ans: 53000 Grams
Q 4. How many metres are in 5.0 cm?
Ans: 0.050 cm
Summary
The metric system of measurement in mathematics is the set of standard units defined to measure length, weight, and capacity. The length/distance conversion chart gives the basic unit conversions related to length in a simple and easy form. The area Conversion chart gives the basic unit conversions related to the area. The area is the space occupied by a two-dimensional shape or figure. The area is measured in square units. The volume conversion chart gives the basic unit conversions related to volume. The term capacity or volume is used for measuring the space occupied by the object. Volume is the space enclosed or occupied by any three-dimensional object or solid shape. It has length, width, and height. It is measured in cubic units. In the end we have added some solved examples, on conversion of units. This will help in understanding and practising the questions.
FAQs on Metric Measures Explained: Key Concepts & Practical Uses
1. What exactly are metric measures?
Metric measures are a standard system used worldwide to measure three basic things: length (how long something is), weight (how heavy something is), and capacity (how much a container can hold). The main benefit of this system is that it's based on the number 10, which makes calculations and conversions very simple. The basic units are the metre for length, the gram for weight, and the litre for capacity.
2. What are the common metric units we use every day?
The common metric units are grouped by what they measure. Here are the most important ones:
- For Length: Millimetre (mm), Centimetre (cm), Metre (m), and Kilometre (km).
- For Weight (Mass): Milligram (mg), Gram (g), and Kilogram (kg).
- For Capacity (Volume): Millilitre (ml) and Litre (l).
3. How are the metric units for length arranged from smallest to largest?
The standard metric units for length, in order from the smallest to the largest, are: Millimetre (mm), which is used for very small lengths like the thickness of a coin; Centimetre (cm), used for measuring objects like a pencil; Metre (m), used for measuring a room or a piece of cloth; and Kilometre (km), used for measuring long distances between cities.
4. Why is the metric system considered easier to use than older measurement systems?
The primary advantage of the metric system is its simplicity. It is a decimal-based system, meaning all units are related by powers of 10. To convert between units, you simply multiply or divide by 10, 100, or 1000. This is much easier than older systems, like the imperial system, which use inconsistent numbers for conversion (for example, 12 inches in a foot, and 5280 feet in a mile).
5. How do you convert a bigger metric unit to a smaller one?
To convert from a larger metric unit to a smaller one, you multiply. The key is to know the relationship between the units. For example, since there are 100 centimetres in 1 metre, to convert metres to centimetres, you multiply the number of metres by 100. So, 5 metres becomes 5 x 100 = 500 centimetres.
6. Can you provide some real-world examples of where metric measures are used?
Yes, we use metric measures all the time. For example:
- When you buy milk or juice, it's usually sold in litres (l) or millilitres (ml).
- The distance to your school or the next town is measured in kilometres (km).
- When you buy vegetables or fruits, they are weighed in grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
- A doctor might prescribe medicine dosage in milligrams (mg).
7. When should I use kilometres instead of metres, or grams instead of kilograms?
Choosing the right unit depends on the size of what you are measuring. You should use the unit that gives you a simple, practical number. For instance:
- Use kilometres (km) for very long distances, like a road trip, because saying '5 km' is easier than saying '5000 metres'.
- Use metres (m) for shorter lengths, like the height of a door.
- Use kilograms (kg) for heavier objects, like your own body weight or a bag of rice.
- Use grams (g) for very light objects, like a feather or the ingredients for a cake.























