




How to Use Metric Conversion Charts for Fast & Accurate Calculations
The most common method for determining height, distance, and other daily items is the metric system of measurement. Let's use a jar of milk as an example. To determine the amount of milk, we use litres, and to determine the height of the jar, we use metres (or centimetres). This is because these metric units, also known as SI units, are widely used throughout the world (International System of Units). Come on, let's start learning about the metric system. The man who is credited with creating the metric system of measurement is Gabriel Mouton. English clergyman John Wilkins proposed a system for measuring length, mass, area, and volume in 1668.
Metric Unit
For measuring length, mass, area, and capacity, different metric units are used. For instance, the metric units used to measure length are millimetres, centimetres, metres, and kilometres. The weight is measured in grams and kilograms. View the metric table to learn about all the metric system units used for various applications.
For measurement of Length
For measurement of Capacity or litre chart
For measurement of Mass or volume conversion
For measurement of Area
Metric System Chart
The formulas for converting between different metric units are contained in the metric system chart. By exploring its multiplying factor, you can quickly convert one unit to another. For example: you can see from the metric system chart that 1 metre equals 100 centimetres. By multiplying 5 metres by 100, you can convert 5 metres to centimetres using this formula.
For length:
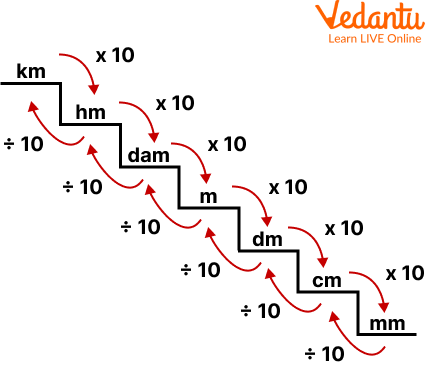
Conversion chart for length
1 cm = 10 mm
1 mm = 0.1 cm
1 m = 100 cm
1 cm = 0.01 m
1 km = 1000 m
1 m = 0.001 km
For Mass:
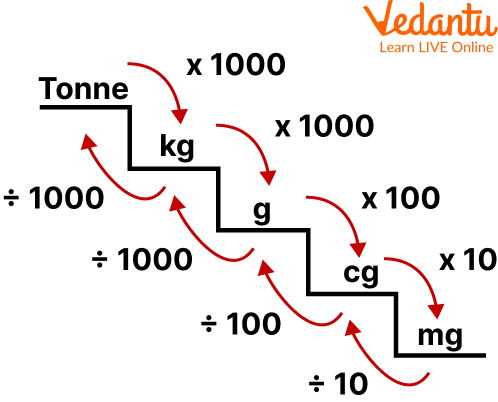
Conversion chart for mass
1 cg = 10 mg
1 mg = 0.1 cg
1 g = 100 cg
1 cg = 0.01 g
1 g = 1000 mg
1 mg = 0.001 g
1 kg = 1000 g
1 g = 0.001 kg
1 tonne = 1000 kg
1 kg = 0.001 tonne
For Capacity:
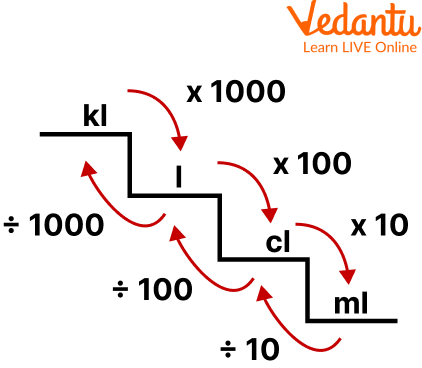
Conversion chart for capacity
1 cl = 10 ml
1 ml = 0.1 cl
1 l = 100 cl
1 cl = 0.01 l
1 l = 1000 ml
1 ml = 0.001 l
1 kl = 1000 l
1 l = 0.001 kl
Solved Examples
Q 1. Convert 2000 l into kl?
Ans: We are given a measurement in the form of litre i.e. $2000l$. As we know that
$1000 l=1 kl$. So we will divide the expression by 1000. So that we will convert them into expressions.
Step2: By simply following the unitary method, we will find the value:
If $1000 l=1 kl$
Then $1 l=\dfrac{1}{1000} kl$
Hence, the value of $2000 l=\dfrac{1 \times 2000}{1000}$
$=2 kl$
Hence the value is $2 kl$
Q 2. Convert 500 metres to kilometres.
Ans: Both metres and kilometres are metric system units of measuring distance. In $1 \mathrm{~m}$, there is $\dfrac{1}{1000} \mathrm{~km}$.
$\Rightarrow 1 \mathrm{~m}=\dfrac{1}{1000} \mathrm{~km}$
$\Rightarrow 500 \mathrm{~m}=\dfrac{500}{1000} \mathrm{~km}$
$\Rightarrow 500 \mathrm{~m}=\dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{~km}=0.5 \mathrm{~km}$
Therefore, 500 metres equals half a kilometre or $0.5 \mathrm{~km}$.
Q 3: How many centigrams are there in 12 grams?
Ans: Centigrams and grams are the units of the metric system. In 1 gram, there are 100 centigrams.
$\Rightarrow 1 \mathrm{~g}=100 \mathrm{cg}$
$\Rightarrow 12 \mathrm{~g}=12 \times 100 \mathrm{cg}$
$\Rightarrow 12 \mathrm{~g}=1200 \mathrm{cg}$
Therefore, there are 1200 centigrams in 12 grams.
Practice Problems
Q 1. Convert 55 ml into l. (Ans: 0.055 l)
Q 2. Convert 21 kg 46 g into kilograms. (Ans: 21.046 kg)
Summary
As discussed above, The metric system of measurement is the most popular way to determine the height, distance, and other everyday items. The common measurement system that uses decimal values is the metric system. It uses powers of ten for unit conversions. The metric system of units can be used to measure length, weight, area, capacity, speed, distance, time, etc. In the metric system, length is measured in metres, centimetres, and kilometres; weight is measured in kilogrammes, milligrammes, and grammes; capacity is measured in litres, kiloliters, centilitres, and millilitres; and time is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds.
FAQs on Metric Conversion Chart: Definitions, Examples & Solved Problems
1. What is a metric conversion chart and why is it useful?
A metric conversion chart is a visual tool that shows how different units within the metric system are related. It helps you quickly convert a measurement from one unit to another, like from kilometres to metres or grams to milligrams. It is very useful because it organises all the units in a logical order, making calculations much simpler.
2. What are the three most common base units in the metric system?
The three most common base units used in daily life and school are:
- Metre (m), which measures length or distance.
- Gram (g), which measures mass or weight.
- Litre (L), which measures capacity or volume.
All other metric units are derived from these base units using prefixes like kilo-, centi-, and milli-.
3. How do you convert from a bigger metric unit to a smaller one?
To convert from a bigger unit to a smaller one (for example, from metres to centimetres), you multiply by a power of 10. This is the same as moving the decimal point to the right. The number of places you move the decimal depends on how many steps apart the two units are on the conversion chart.
4. What is a simple trick to remember the order of metric prefixes?
A popular mnemonic to remember the prefixes in order from largest to smallest is: "King Henry Doesn't Usually Drink Chocolate Milk". Each word's first letter stands for a prefix:
- King → Kilo- (1000)
- Henry → Hecto- (100)
- Doesn't → Deca- (10)
- Usually → Unit (metre, gram, litre)
- Drink → Deci- (0.1)
- Chocolate → Centi- (0.01)
- Milk → Milli- (0.001)
5. Why is the metric system considered easier to use than other systems like the imperial system?
The metric system is considered much simpler because it is a decimal-based system. This means all conversions are done by multiplying or dividing by powers of 10. The imperial system (using inches, feet, and pounds) has inconsistent conversion factors (e.g., 12 inches in a foot, 3 feet in a yard), which makes calculations more difficult.
6. Where might I use metric conversions in my daily life?
You use metric conversions more often than you might think. For example:
- When you buy groceries, vegetables are weighed in grams (g) and kilograms (kg).
- The volume of a water bottle or milk carton is shown in litres (L) or millilitres (mL).
- Distances on road signs are often in kilometres (km).
- In science class, you will measure length in centimetres (cm) and millimetres (mm).
7. Can you convert a unit of length to a unit of mass, for example, metres to grams?
No, you cannot directly convert units that measure different types of quantities. A metre measures length, while a gram measures mass. They are fundamentally different properties. Metric conversion only works between units that measure the same property, such as metres and kilometres (both length) or grams and kilograms (both mass).























