




Step-by-Step Guide to Making Horizontal Bar Graphs
Have you heard the term Bar graph horizontal or horizontal bar graph? A horizontal bar graph or bar graph horizontal is nothing but a way to represent data horizontally in a graph using bars. In horizontal bar graphs, we represent data categories on the x-axis whereas data values are on the y-axis. Horizontal bar graphs are generally used to compare different observations. Read the article below to have detailed information on Bar Graph Horizontal with interesting examples.
What is a Bar Graph?
Let us first know what a bar graph is, before knowing the horizontal bar graph in detail.
A bar graph, also known as a bar chart, is a graphical representation of data using bars of different heights.
Imagine you did a survey of 145 people to know which type of fruits are most liked by people.
On the bar graph, we can show this information as:
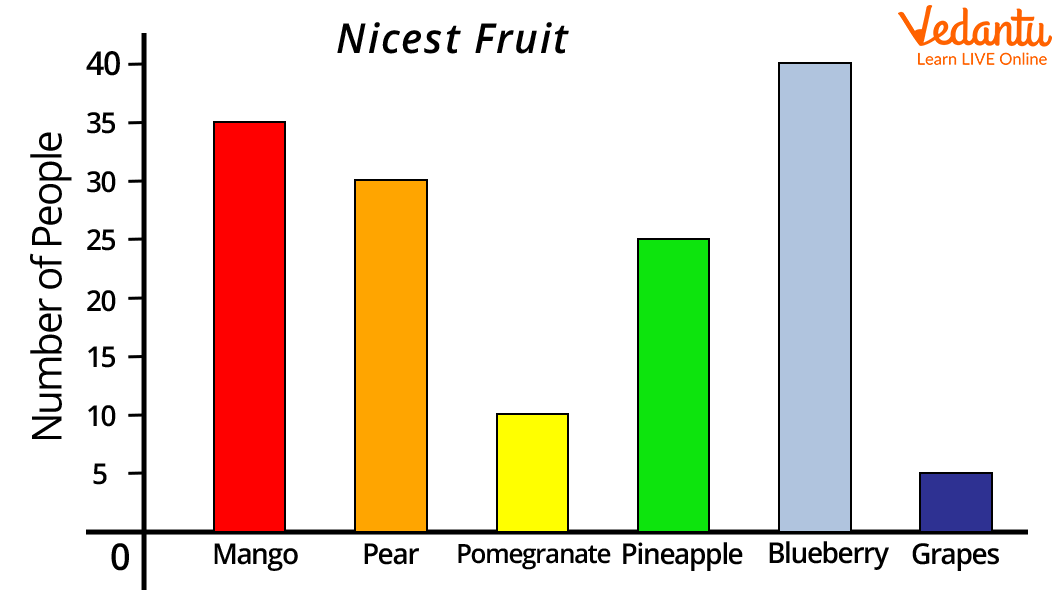
Image: Bar graph of fruits
A bar graph is an optimum way to show relative size. For example, in the above bar graph, we can say blueberries are most liked by the people whereas grapes are least liked by the people.
Types of Bar Graph
There are two different types of bar graphs namely:
Horizontal bar graph and
Vertical bar graph
In this article, we will discuss horizontal bar graphs in detail.
What Does Horizontal Bar Graph Mean?
A horizontal bar graph or bar graph horizontal is a way to represent data horizontally in a graph using bars. In horizontal bar graphs, data categories are represented on the x-axis whereas data values are represented on the y-axis. Horizontal bar graphs are widely used for easy and quick comparison among various observations based on certain parameters. In horizontal bar graphs, the length of the rectangular bars is proportional to their values. Also, all bars in the horizontal bar graph go from left to right.
How to Construct a Horizontal Bar Graph?
Following are the steps to construct a horizontal bar graph:
Step 1: On a graph paper, draw two perpendicular lines intersecting at O.
Step 2: The horizontal line on the bar graph is the x-axis whereas the vertical line on the bar graph is the y-axis.
Step 3: Along a horizontal axis, choose a suitable scale in order to determine the height of the bar for the given values (frequency is represented along the y-axis).
Step 4: Along a vertical axis, choose the uniform width of the bar, and uniform gap between the bars. Also, write the name of the data items whose values are to be marked.
Step 5: Calculate the height of the bar according to the value chosen for each graph and draw the horizontal bars accordingly.
Step 6: Give a suitable title to the graph.
The horizontal bar graph given below gives the information about temperature in celsius on different days of the week.
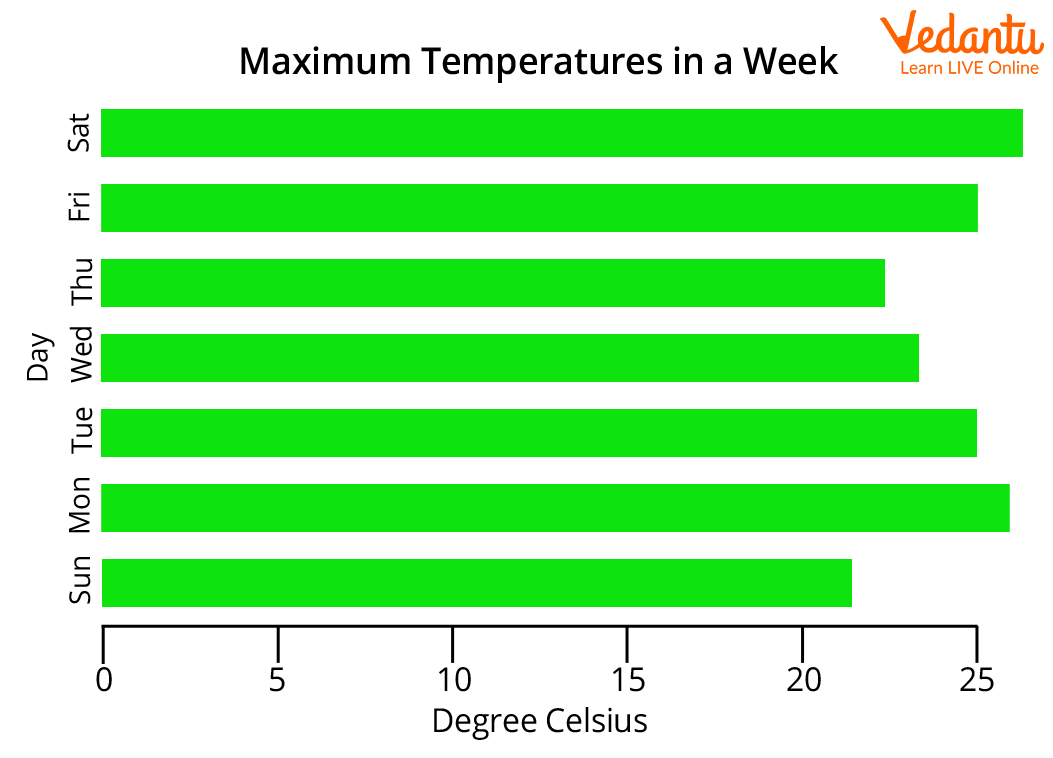
Image: Horizontal bar graph showing maximum temperature in a week
How to Read a Horizontal Bar Graph?
The horizontal bar graph is ead in the following manner:
The title of the bar graph tells about the data being represented by the graph.
The vertical axis of the horizontal bar graph represents the data categories. The data categories in the horizontal bar graph given below are “colours”.
The horizontal axis of the horizontal bar graph represents the values corresponding to each data value. The data values in the below horizontal bar graph represent the number of students who like a particular colour represented on the vertical axis.
The scale is showing the value of 1 unit on the horizontal axis.
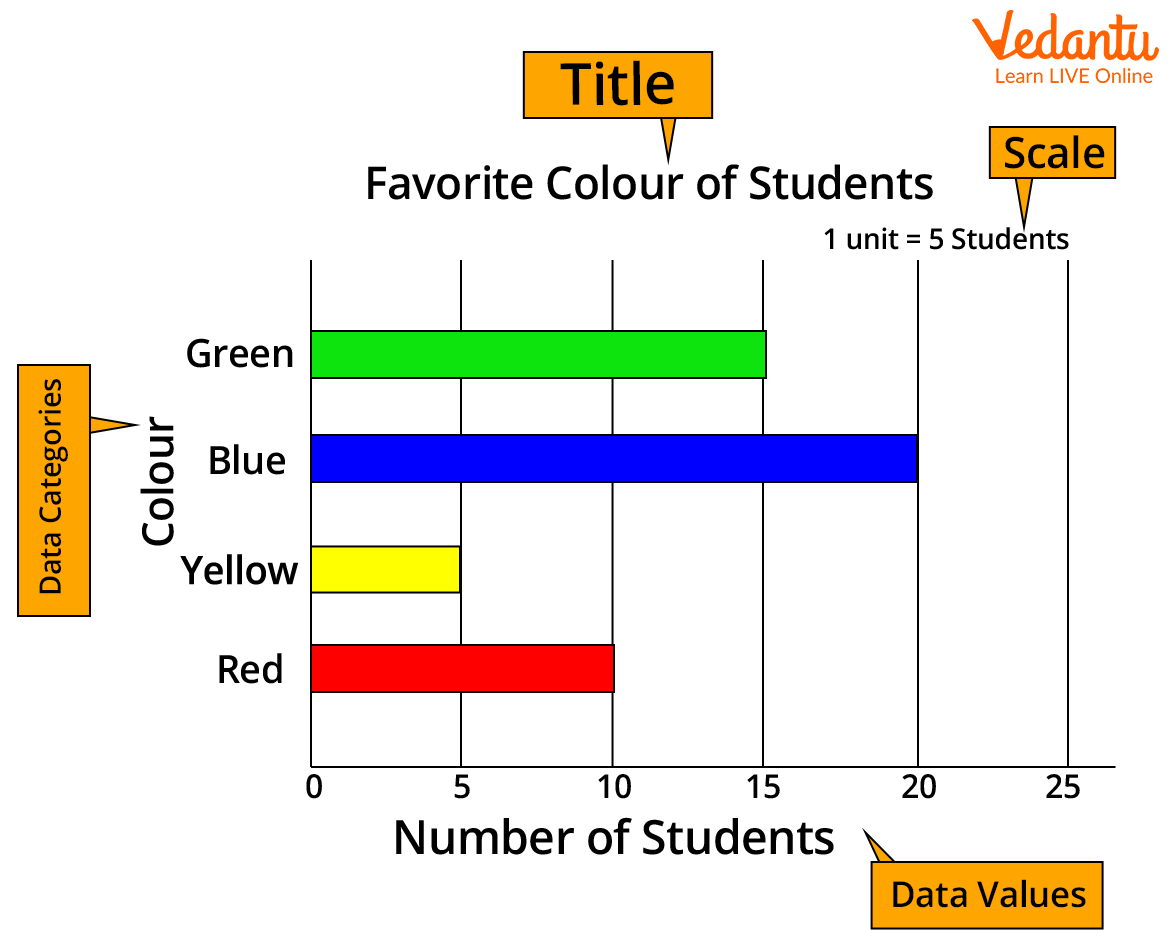
Image: Reading horizontal bar graph
From the above horizontal bar graph, we can infer that 1 unit represents 5 students. Accordingly, 10 students like the red colour, 5 students like the yellow colour, 20 students like blue colour, and 15 students like the green colour.
Horizontal Bar Graph Example
Let us understand the horizontal bar graph with an example:
Draw a horizontal bar graph on the basis of the following data.
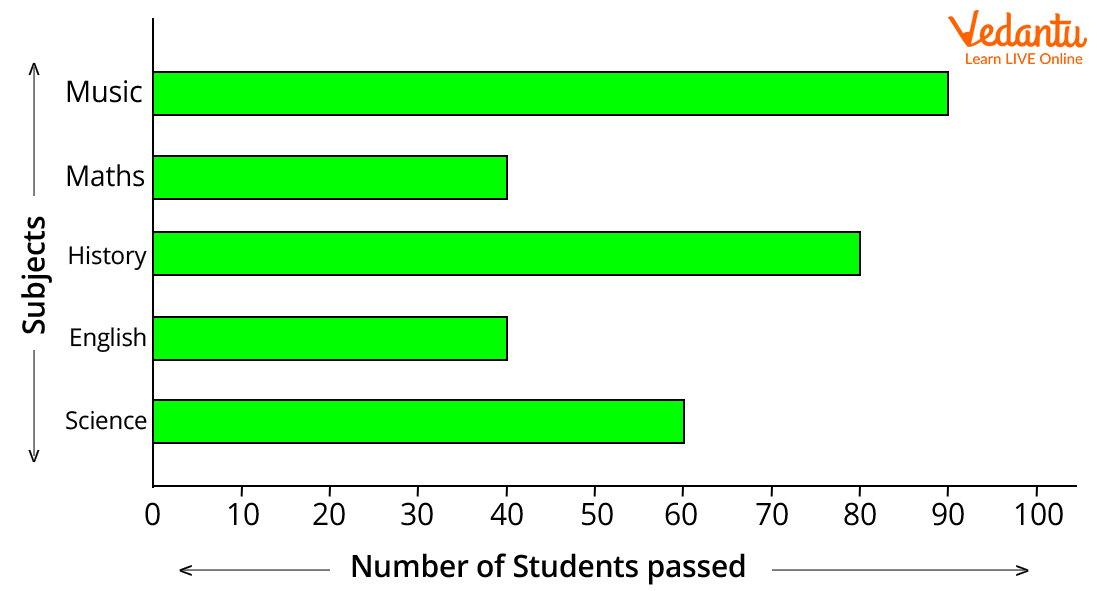
Image: A bar graph showing subjects and the number of students who passed
The horizontal bar graph gives the following information:
The total number of students passed in different subjects.
The maximum number of students passed in Music.
The minimum number of students passed in English and Maths.
Students scored highest marks in Music but scored worst in English and Maths.
Hope you have understood what a horizontal bar graph is, and how to read and represent a horizontal bar graph. Now, you can visit Vedantu’s official website and try different questions based on this to understand the concept better.
FAQs on Horizontal Bar Graph: Definition, Types & How to Draw
1. How do you construct a horizontal bar graph step-by-step?
Constructing a horizontal bar graph involves a few key steps to ensure it accurately represents your data. Follow this method:
- Draw the Axes: Draw a vertical line (y-axis) and a horizontal line (x-axis) that meet at a point (the origin).
- Label the Vertical Axis: Along the y-axis, list the categorical data you are comparing (e.g., names of fruits, favourite subjects, countries). Ensure they are spaced out evenly.
- Choose a Scale: Determine a suitable scale for the x-axis based on the range of your data values. Label the x-axis with this numerical scale (e.g., 0, 5, 10, 15...). The x-axis represents the frequency or value of each category.
- Draw the Bars: For each category on the y-axis, draw a horizontal bar from the axis outwards. The length of each bar should correspond to its value on the x-axis scale.
- Add a Title and Labels: Give the graph a clear title that explains what it shows. Label both the x-axis (e.g., 'Number of Students') and y-axis (e.g., 'Favourite Colours') to provide context.
2. What do the horizontal and vertical axes represent in a horizontal bar graph?
In a horizontal bar graph, the roles of the axes are swapped compared to a vertical bar graph. The vertical axis (y-axis) is used to display the different categories or items being compared, such as names, places, or types of objects. The horizontal axis (x-axis) represents the numerical values or frequencies corresponding to each of those categories. The length of the bars extending horizontally shows the magnitude of each category's value.
3. What is the main difference between a horizontal and a vertical bar graph?
The main difference lies in the orientation of the bars and the placement of the axes. In a vertical bar graph, the categories are listed on the horizontal x-axis, and the bars extend upwards along the vertical y-axis which represents the values. In a horizontal bar graph, the categories are listed on the vertical y-axis, and the bars extend sideways along the horizontal x-axis which represents the values. Horizontal graphs are often preferred when the category labels are long, as they are easier to read on the vertical axis.
4. What kind of data is best shown using a horizontal bar graph?
A horizontal bar graph is ideal for displaying and comparing categorical data. This refers to data that can be sorted into distinct groups or categories. Examples include the number of cars of different colours sold, population figures for different cities, or students' favourite sports. It is especially effective when you have many categories or categories with long names that would be difficult to fit on the x-axis of a vertical chart.
5. Why is it important for the bars in a bar graph to have equal width?
It is crucial to draw all bars with an equal width and maintain uniform spacing between them to avoid misleading the viewer. In a bar graph, the length of the bar is the only dimension that should represent the data's value. If the widths were different, a wider bar might be perceived as representing a larger value or greater importance, even if its length is the same as a narrower bar. This ensures the graph provides a fair and accurate visual comparison.
6. When should you use a horizontal bar graph instead of a vertical one?
You should choose a horizontal bar graph primarily in two situations. First, when the labels for your categories are long or numerous, placing them on the vertical axis provides more space and improves readability. Second, horizontal bar graphs are excellent for ranking items, as the human eye can easily scan down the list to see which bar is the longest, clearly indicating the highest value without tilting one's head.
7. What is the most important consideration when choosing a scale for a horizontal bar graph?
The most important consideration when choosing a scale for the horizontal axis is to ensure it accurately and clearly represents the data without distortion. The scale should start at zero to avoid exaggerating differences between the bars. It must also have consistent, evenly spaced intervals (e.g., 0, 10, 20, 30...) that are appropriate for the range of your data. An improper scale can make small differences look large or large differences look insignificant, leading to incorrect interpretation of the graph.























