
The voltage across the \[10\Omega \] resistor in the given circuit is x volt. Then find the value of x to the nearest integer.
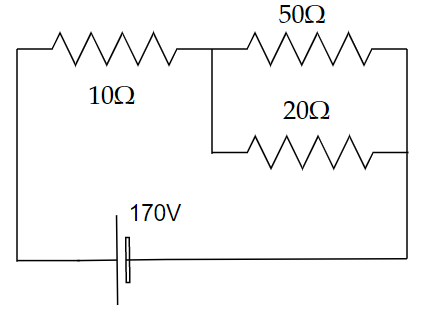
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to proceed with the problem first we need to know about ohm’s law. It states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
Formula Used:
To find the equation for voltage we have,
\[V = IR\]
Where, I is current and R is resistance.
Complete step by step solution:
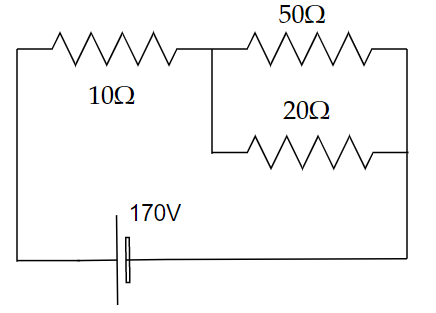
Image: A circuit consists of three resistors and a battery.
In the above circuit, the voltage across the \[10\Omega \] resistor in the given circuit is x volt. We need to find the value of x to the nearest integer. From ohm’s law, we have,
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow V = IR\]…………. (1)
In order to find the current in the circuit, we need to simplify the given circuit by finding the equivalent resistance of the two resistors given in a parallel combination.
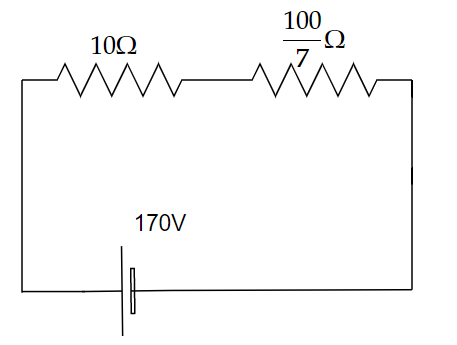
Image: An equivalent resistor.
The equivalent resistance is given by,
\[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_2} + {R_3}}}\]
Here, \[{R_2} = 50\Omega \] and \[{R_3} = 20\Omega \]
Substitute the value in the above equation we get,
\[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{50 \times 20}}{{50 + 20}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{1000}}{{70}}\Omega \]
\[\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{100}}{7}\Omega \]
Then,
\[R = {R_{eq}} + {R_1}\]
Here, \[{R_1} = 10\Omega \]
Then the above equation will become,
\[R = \dfrac{{100}}{7} + 10\]
\[\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{100 + 70}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{170}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = 7\Omega \]
Using Ohm’s law,
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
Now substitute the value of V and R in the above equation we get,
\[I = \dfrac{{170}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow I = 7A\]
Now, in order to find the voltage across \[10\Omega \] resistor, consider equation (1)
\[V = IR\]
\[\Rightarrow V = 7 \times 10\]
\[\therefore V = 70V\]
Therefore, the value of x is 70.
Note:Here it is important to remember that, in a circuit when two are more resistors are connected in parallel, we need to apply equivalent resistance formula as \[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_2} + {R_3}}}\] and if the resistors are connected in series, then we need to add all the resistors to get equivalent value of resistors.
Formula Used:
To find the equation for voltage we have,
\[V = IR\]
Where, I is current and R is resistance.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: A circuit consists of three resistors and a battery.
In the above circuit, the voltage across the \[10\Omega \] resistor in the given circuit is x volt. We need to find the value of x to the nearest integer. From ohm’s law, we have,
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow V = IR\]…………. (1)
In order to find the current in the circuit, we need to simplify the given circuit by finding the equivalent resistance of the two resistors given in a parallel combination.

Image: An equivalent resistor.
The equivalent resistance is given by,
\[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_2} + {R_3}}}\]
Here, \[{R_2} = 50\Omega \] and \[{R_3} = 20\Omega \]
Substitute the value in the above equation we get,
\[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{50 \times 20}}{{50 + 20}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{1000}}{{70}}\Omega \]
\[\Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{100}}{7}\Omega \]
Then,
\[R = {R_{eq}} + {R_1}\]
Here, \[{R_1} = 10\Omega \]
Then the above equation will become,
\[R = \dfrac{{100}}{7} + 10\]
\[\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{100 + 70}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{170}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = 7\Omega \]
Using Ohm’s law,
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
Now substitute the value of V and R in the above equation we get,
\[I = \dfrac{{170}}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow I = 7A\]
Now, in order to find the voltage across \[10\Omega \] resistor, consider equation (1)
\[V = IR\]
\[\Rightarrow V = 7 \times 10\]
\[\therefore V = 70V\]
Therefore, the value of x is 70.
Note:Here it is important to remember that, in a circuit when two are more resistors are connected in parallel, we need to apply equivalent resistance formula as \[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_2} + {R_3}}}\] and if the resistors are connected in series, then we need to add all the resistors to get equivalent value of resistors.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




