
The solar constant for the earth is S. The surface temperature of the sun is \[{T_{}}K\]. The sun subtends an angle \[\theta \] at the earth
(A) \[S \propto {T^4}\]
(B) \[S \propto {T^2}\]
(C) \[S \propto {\theta ^2}\]
(D) \[S \propto \theta \]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Let R be the distance between the center of earth and the surface of the sun and let \[{R_e}\]be the radius of the earth. Now, use the energy received per unit area on earth’s surface formula to find the relation.
Complete Step By Step Solution
Let us draw the given scenario in a simple diagram. The sun rays hit the earth across its center and tangent points. Let R be the distance between the surface of the sun and the centre of the earth. Now, \[{R_e}\] is the radius of the earth. The sun rays subtend an angle \[\theta \], with respect to R. The image is shown below:
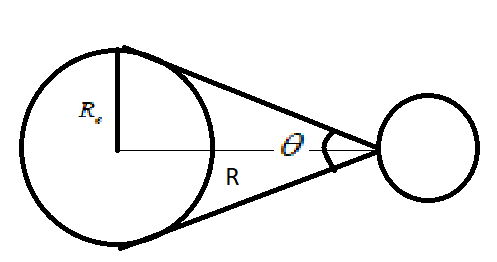
Now, Solar energy received per unit area is defined as the amount of solar energy received over the earth’s surface from the sun. Solar constant is defined as the ratio between the power received from the sun and the square of the distance between sun and center of the earth. Mathematically, given as
\[S = \dfrac{P}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\]
Power radiated by the sun is mathematically given as
\[P = {A_s} \times \sigma {T^4}\], where A is area of the sun, T is temperature on the surface of the sun and \[\sigma \] is Stefan-Boltzmann constant
Substituting P on the above formula we get,
\[ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{4\pi {R_s}^2 \times \sigma {T^4}}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\]
Cancelling out the common terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{R_s}^2 \times \sigma {T^4}}}{{{R^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow S \propto {T^4}\]
Thus, Option (A) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note The power radiated by the sun is defined as the product of power density of the sun’s rays and the total surface area of the sun. Since the sun is a star, the Stefan-Boltzmann law applies, which describes the power radiated by a black body with respect to its temperature.
Complete Step By Step Solution
Let us draw the given scenario in a simple diagram. The sun rays hit the earth across its center and tangent points. Let R be the distance between the surface of the sun and the centre of the earth. Now, \[{R_e}\] is the radius of the earth. The sun rays subtend an angle \[\theta \], with respect to R. The image is shown below:

Now, Solar energy received per unit area is defined as the amount of solar energy received over the earth’s surface from the sun. Solar constant is defined as the ratio between the power received from the sun and the square of the distance between sun and center of the earth. Mathematically, given as
\[S = \dfrac{P}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\]
Power radiated by the sun is mathematically given as
\[P = {A_s} \times \sigma {T^4}\], where A is area of the sun, T is temperature on the surface of the sun and \[\sigma \] is Stefan-Boltzmann constant
Substituting P on the above formula we get,
\[ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{4\pi {R_s}^2 \times \sigma {T^4}}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\]
Cancelling out the common terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{R_s}^2 \times \sigma {T^4}}}{{{R^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow S \propto {T^4}\]
Thus, Option (A) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note The power radiated by the sun is defined as the product of power density of the sun’s rays and the total surface area of the sun. Since the sun is a star, the Stefan-Boltzmann law applies, which describes the power radiated by a black body with respect to its temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




