




How is Torque Calculated for an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Field?
In JEE Physics, understanding the torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is critical for concept clarity and application in exams. This topic combines electrostatics and rotational dynamics, offering insights into the behavior of dipoles under the influence of external electric fields. Here we explore the fundamentals, vector derivation, examples, and real-world connections.
What is an Electric Dipole?
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a small fixed distance. The electric dipole moment is a vector quantity, given by the product of one charge's magnitude and the distance separating the charges, and it points from the negative to the positive charge.
- Consists of +q and –q charges
- Separation distance = d
- Dipole moment, p = q × d
- Direction: negative to positive
Electric dipoles are fundamental in explaining the interaction of matter with electric fields, especially in atomic and molecular physics.
Electric Dipole Moment and Properties
The dipole moment (p) is pivotal in characterising the electric dipole's strength and direction. It's expressed as p = q × d, where q is the magnitude of each charge and d is the separation vector. The SI unit is coulomb-metre (C·m).
- Vector quantity
- SI unit: coulomb-metre
- Direction: from –q to +q
- Magnitude: proportional to charge and distance
The arrangement and magnitude of the electric dipole moment affect how the system responds within external electric fields.
Concept of Uniform Electric Field
A uniform electric field has the same magnitude and direction at every point within the region. When a dipole is placed in such a field, it experiences specific electrostatic forces, leading to effects like force and torque. For more on how these fields are represented, see Electric Field Lines Properties on Vedantu.
These forces act differently on the +q and –q charges, causing rotational effects.
How Torque Acts on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field
Despite zero net force, a dipole in a uniform electric field experiences a couple that tends to align its dipole moment with the electric field. This results in torque but not linear acceleration, a crucial distinction in JEE problems.
- The forces on +q and –q are equal and opposite
- No net translation; only rotation (torque)
- Tendency to align dipole with field
This phenomenon forms the foundation for devices and experiments that utilize the orienting effect of electric fields on dipoles.
Mathematical Derivation of Torque on an Electric Dipole
To calculate the torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field, consider a dipole of charges +q and –q separated by distance d, placed in an electric field E making an angle θ with the dipole axis.
The force on +q is qE (in field direction), and on –q is –qE (opposite to field). These two equal and opposite forces act at different points, creating a torque acting on the electric dipole moment placed in the uniform electric field.
Torque, τ, is given by:
| Step | Expression |
|---|---|
| Force on charges | F = qE |
| Perpendicular distance | d sin θ |
| Torque on dipole | τ = qE × d sin θ |
| Using p=qd | τ = pE sin θ |
| Vector form | τ = p × E |
Thus, the torque acting on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is maximized when the dipole moment and field are perpendicular and zero when parallel.
The concept of electric potential due to an electric dipole also links to how the dipole’s orientation affects its potential energy in the field. For further visualization, examine Electric Potential due to an Electric Dipole in the diagram below.
Interpretation of the Torque Expression
The cross-product form τ = p × E shows that torque direction follows the right-hand rule. Its magnitude depends on the dipole moment’s magnitude, field strength, and sine of the angle between them.
- Torque maximum at θ = 90°
- Torque zero at θ = 0° or 180°
- Always tries to align p with E
- Direction given by right-hand rule
This principle is key in answering questions like “the torque acting on an electric dipole moment placed in a uniform electric field is…” since the mathematical form explains the physical rotation observed.
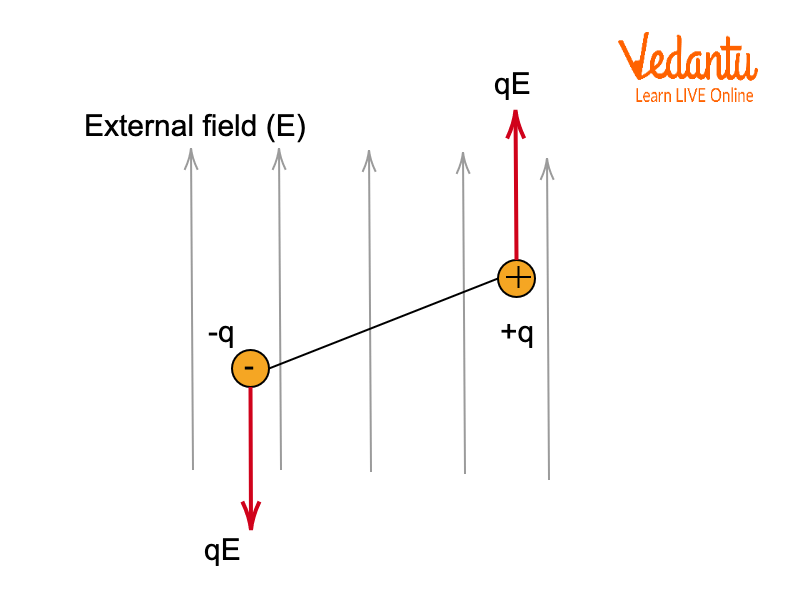
Visualization: Torque on an Electric Dipole
A clear understanding can be gained from schematic diagrams. The image below illustrates how the forces on the charges create a torque, tending to rotate the dipole to align with the electric field direction.
Applications and Importance for JEE
The concept of torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field underpins topics in both physics and engineering. It explains molecular orientation, dielectric behavior in capacitors, and features in problems with both rotational motion and electrostatics, such as those tied to Understanding Moment Of Inertia.
- Molecular alignment in external fields
- Working of liquid crystal displays (LCDs)
- Polarisation in dielectrics
- Design of electrometers and sensors
Questions like how to calculate the torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field test both formula application and physical interpretation in the JEE exam.
Key Takeaways and Conceptual Connections
Mastering the torque acting on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field also aids in understanding optical, magnetic, and mechanical analogies, expanding your problem-solving toolkit. For instance, rotational effects on electric dipoles parallel the torque experienced by bar magnets placed in magnetic fields. To broaden your concepts, check the Magnetic Effects Of Current section on Vedantu.
Through such cross-topic connections, you can build a robust foundation in physics, improving your readiness for both standard and advanced JEE questions. Remember that the core idea is how fields interact with dipoles, producing alignment tendencies, rotational motion, and physical phenomena that are observable in practical setups and devices.
FAQs on Understanding the Torque on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field
1. What is the torque experienced by an electric dipole in a uniform electric field?
The torque (τ) on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is given by the vector product of the dipole moment and the electric field. The magnitude is τ = pE sinθ where:
- p = dipole moment
- E = uniform electric field strength
- θ = angle between p and E
2. What is an electric dipole and its dipole moment?
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a fixed distance.
- Electric dipole moment (p) is defined as p = q × 2a, where q is the magnitude of each charge and 2a is the distance between charges.
- The direction of p is from negative to positive charge.
3. Derive the expression for torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
The torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field derives from the forces acting on each charge.
- The force on the positive charge is qE (along the field), and on the negative, -qE (opposite).
- The forces create a couple, producing torque.
- Magnitude of torque: τ = pE sinθ, where p = q × 2a is the dipole moment.
4. What will happen if the electric dipole is aligned parallel to the uniform electric field?
If an electric dipole aligns parallel to a uniform electric field, the torque on it will be zero.
- Torque is maximum when the dipole is perpendicular and zero when parallel (sin0° = 0).
- The stable equilibrium position of a dipole is when it is aligned with the field.
5. What is the physical significance of torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field?
The torque acts to rotate the dipole so that its moment aligns with the electric field.
- This explains why molecules and materials with dipoles orient themselves with external fields.
- It underlies various physical and chemical phenomena involving dipoles.
6. Can an electric dipole have a net force in a uniform electric field?
No, an electric dipole in a uniform electric field experiences no net force, but does experience a torque.
- The equal and opposite forces on the charges cancel out in a uniform field.
- Only rotational effect (torque) is produced, with no translational motion.
7. What is the work done in rotating an electric dipole in a uniform electric field?
The work done in rotating a dipole from angle θ1 to θ2 in a uniform electric field is given by the change in its potential energy.
W = pE (cosθ1 - cosθ2)
This formula summarizes the work required for any angular displacement within the field.
8. State the expression for potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
The potential energy (U) of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is:
- U = -pE cosθ, where θ is the angle between dipole moment (p) and electric field (E).
- Potential energy is minimum when the dipole is aligned with the field (θ = 0).
9. How does the direction of torque relate to the orientation of the electric dipole and the field?
The direction of torque on an electric dipole is given by the vector product τ = p × E, perpendicular to the plane containing the dipole moment and the field.
- The torque tries to turn the dipole to align with the electric field.
- Right-hand rule is used to determine the torque's direction.
10. What are some everyday examples of torque acting on electric dipoles?
Everyday examples of torque on electric dipoles include alignment of polar molecules in an electric field.
- Water molecules in a microwave oven align due to torque from the alternating electric field.
- Dielectric materials in capacitors exhibit dipole alignment under applied voltage.
























